* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review 1 Electron negative Proton positive Neutron
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
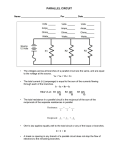
Review 1 1. List the three basic elements of an atom and state the charge of each (positive, negative, or neutral). Element Charge Electron negative Proton positive Neutron neutral 2. An electron forced out of orbit by an external force is called a Free electron . 3. Conductors allow many free electrons to flow when an external electric force is applied. 4. Which of the following materials are good conductors? a. copper b. plastic c. silver d. rubber 5. e. f. g. h. aluminum glass iron mica Semiconductor devices can be manufactured to allow many electrons to flow in one direction and few electrons to flow in the opposite direction 177 Review 2 1. Elements are identified by the number of electrons in orbit around the nucleus. 2. A material that has an excess of electrons is said to have a negative charge. 3. A material that has a deficiency of electrons is said to have a positive charge. 4. Like charges repel and unlike charges attract . 5. The force that is applied to a conductor to cause current flow is voltage . 6. Electrons move from a or b . a. positive to negative b. negative to positive 7. With an increase of length or a decrease of crosssection of a conductor, resistance will increase . a. increase b. decrease Review 3 V=I*R . 1. The basic Ohm’s Law formula is 2. When solving circuit problems; current must always be expressed in ampere , voltage must always be expressed in volt , and resistance must always be expressed in ohm (Ω) . 3. The total current of a simple circuit with a voltage supply of 12 volts and a resistance of 24 Ω is 0.5 amps. From Ohm's law ↓ I = V / R = 12 / 24 = 0.5 A 4. What is the total resistance of a series circuit with following values: R1=10 Ω , R2=15 Ω , and R3=20 Ω ? = 45 Ω . Rt = R1+R2+R3 = 10+15+20 = 45 Ω 5. What is total current of a series circuit that has a 120 volt supply and 60 Ω resistance? 2 amps From Ohm's law ↓ I = V / R = 120 / 60 = 2 A 6. In the following circuit, the voltage dropped across R1 is 6 volts and R2 is 6 volts. 1.5 Ω 1.5 Ω R1 R2 12 V R1 & R2 are connected In series ↓ Rt = R1+R2 = 1.5+1.5= 3 Ω It = I1=I2=Vt / Rt = 12 / 3 = 4 A V1= I1*R1 = 4 * 1.5 = 6 V V2= I2*R2 = 4 * 1.5 = 6V 7. In the following circuit, voltage dropped across R1 is 71.4 volts and across R2 is 28.6 volts. 100 V R1 & R2 are connected In series ↓ Rt = R1+R2 = 5+2= 7 Ω It = I1=I2=Vt / Rt = 100 / 7 = 14.3 A V1= I1*R1 = 14.3 * 5 = 71.4 V V2= I2*R2 = 14.3 * 2 = 28.6 V 5Ω 2Ω R1 R2 Review 4 1. The total resistance of a parallel circuit that has four 20 Ω resistors is 5Ω. Rt = the value of one resister ÷ the number of resisters Rt = 20/4 = 5 Ω 2. Rt for the following circuit is 5.45 Ω. R2 R2 R3 10 Ω 20 Ω 30 Ω 1/Rt = 1/R1+ 1/R2 + 1/R3 1/Rt = 1/10 + 1/20 + 1/30 1/Rt = 3/30 + 1.5/30 + 1/30 1/Rt = 5.5/30 Rt= 30/5.5 = 5.45 Ω 3. Rt for the following circuit is 3.33Ω. R1 R2 5Ω 10 Ω Rt = ( R1 * R2 ) ÷ ( R1+ R2 ) Rt = ( 5 * 10 ) / ( 5 + 10 ) = 50 / 15 = 3.33 Ω 4. Voltage available at R2 in the following circuit is 12 volts. 12 V Vt = 12 v In parallel circuits the voltage is constant Vt = V1 = V2 V2 = 12v R1 R2 5Ω 10 Ω 5. In a parallel circuit with two resistors of equal value and a total current flow of 12 amps, the value of current through each resistor is 6 amps. R1= R2 In parallel circuits the voltage is constant Vt = V1 = V2 It = I1 + I2 ---------------V1/R1 = V2/R2 I1 = V1 / R1 I2 = V2 / R2 → I1 = I2 → It = I1 + I2 → 12 = I1+ I2 → I1 = 6 → I2 = 6 6. In the following circuit, current flow through R1 is _____ 2.4 amps, and through R2 is 1.6 amps. 24 Volts In parallel circuits the voltage is constant Vt = V1 = V2 = 12v -------------From Ohm's law ↓ I1 = V1/R1 = 24/10 = 2.4 amps I2 = V2/R2 = 24/15 = 1.6 amps R1 R2 10 Ω 15 Ω Review 5 1. Calculate equivalent resistance for R1 and R2 and totalresistance for the entire circuit. R1 20 Ω R3 10 Ω + R2 30 Ω _ R1 & R2 are connected In parallel ↓ R1&2 = ( R1 * R2 ) ÷ ( R1+ R2 ) R1&2 = ( 20 * 30 ) / ( 20 + 30 ) = 600 / 50 = 12Ω R3 & R1&2 are connected In series ↓ R1&2&3 = R3 + R1&2 = 10 + 12 = 22 Ω 2. Calculate equivalent resistance for R1 and R2 and total resistance for the entire circuit. R1 30 Ω + _ R3 20 Ω R2 10 Ω R1 & R2 are connected In series ↓ R1&2 = R1 + R2 = 30 + 10 = 40 Ω R3 & R1&2 are connected In parallel ↓ R1&2&3 = (R1&2 × R3 ) ÷ (R1&2 + R3 ) R1&2&3 = ( 40 × 20 ) ÷ ( 40 + 20 ) = 800 / 60 = 13.33Ω Review 6 1. The rate at which work is done is called power . 2. The basic formulas for power in a DC circuit are: P=IxV P = I2 x R P = V2/R 3. In a circuit with a 12 volt supply and 4 Ω resistance, the power consumed is 36 watts. --------------P = V2/R P = 122 / 4 = 144/4 = 36w