* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture28 - Purdue Physics
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
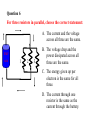
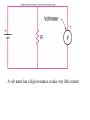
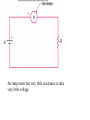
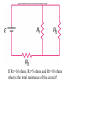
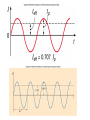
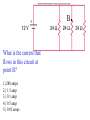
Reading Quiz • Which will draw more current, connecting a 9 volt battery in a circuit with a 1 Ohm resistance or with a 100 Ohm resistance? • 1 Ohm • 100 Ohms • Same current for both Physics Help Center Room 237 Physics Building: 8am to 5:30pm Ask for help from graduate students on homework and exams Can enter solutions on the computers in the room to check your solution. NEXT EXAM Wednesday April 7th @7pm to 9pm Chapters 10,11,12,13,14,15 Summary of electric circuits: 1. The amount of current is the same at every place in a series circuit; I=q/t. 2. The power provided by the battery (P=IDV) is exactly equal to the power dissipated in the resistors (P=I2R). 3. Ohm’s Law applies to resistors: DV=IR 4. Series circuit: effective R = R1 + R2 + R3 5. Parallel circuit: effective R is 1 1 1 1 Reff R1 R2 R3 6. Charge is conserved 7. Current is conserved 8. The voltage drops around a circuit is zero Question 1 How much current I runs through this circuit? A. 0.333 Amps 1W 1.5 V 2W B. 0.500 A C. 1.000 A D. 2.250 A E. 3.000 A Choose the answer closest to your result. Question 2 How much current I is generated by the battery? A. 0.333 Amps B. 0.500 A 1.5 V 1W 2W C. 1.000 A D. 2.250 A E. 3.000 A Choose the answer closest to your result. Question 3 What is the voltage drop across the 2 Ohm resistor? A. Zero 1.5 V 1W 2W B. The same as the drop across the other resistor. C. More than across the other resistor. D. Less than across the other resistor. switch Question 4: This circuit has 2 identical light bulbs. After the switch is closed, + VV A A. A is brighter than B. B. A is dimmer than B. C. A & B are equally bright, but dimmer than A was before. D. A & B are equally bright, but brighter than A was before. E. A & B are equally bright, and the same as A was before. B Question 5: Light bulbs A, B, & C are identical. After the switch is closed, switch + A VV C A. A & C both get brighter. B. A & C both get dimmer. C. A is brighter, and C is dimmer. D. A is dimmer, and C is brighter. E. A & C stay the same. B Question 6 For three resistors in parallel, choose the correct statement: A. The current and the voltage across all three are the same. EMF volts 1 2 3 B. The voltage drop and the power dissipated across all three are the same. C. The energy given up per electron is the same for all three. D. The current through one resistor is the same as the current through the battery. By placing all electric items in parallel they receive the same voltage By placing electrical items in series they receive the same current A volt meter has a high resistance so take very little current Fig. 13.13 An Amp meter has very little resistance so take very little voltage Question 14 If R1=10 ohms, R2=5 ohms and R3=10 ohms what is the total resistance of the circuit? Energy source => Potential Energy => Kinetic Energy => Heat Power = Energy/unit time P=V * I P= (I*R) *I= I2 R Units of Power WATTS = Joules/second Note: Energy = power * time We purchase electrical energy by the Kilowatt-hr If the resistance of the light is 20 ohms what is the power given off by the light? If the light were to be on for 24 hours how much energy would be used up? Summary 5 Fig. 13.18 B What is the current that flows in this circuit at point B? 1.)288 amps 2.) 1.5 amp 3.) 0.1 amp 4.) 0.5 amp 5.) 0.03 amps . By placing all electric items in parallel they receive the same voltage By placing electrical items in series they receive the same current