Genetic Engineering
... Genetic Engineering the manipulation of living organisms for human use Chapter 13 ...
... Genetic Engineering the manipulation of living organisms for human use Chapter 13 ...
Unit 4 Review Sheet Genetics and Biotechnology Vocabulary
... - What are its building blocks? - What bases are found in DNA/RNA? - What’s the Base-Pair rule? - Where is DNA/RNA found in the cell? - What is a chromosome? How many do we have? What’s special about sex chromosomes? - How is RNA similar and different to DNA? DNA Replication - Why is DNA replication ...
... - What are its building blocks? - What bases are found in DNA/RNA? - What’s the Base-Pair rule? - Where is DNA/RNA found in the cell? - What is a chromosome? How many do we have? What’s special about sex chromosomes? - How is RNA similar and different to DNA? DNA Replication - Why is DNA replication ...
Study Guide – Unit 6 Test: Genetics and DNA Name: Per: 1 2 3 4 5 6
... How many chromosomes are shown in a normal human karyotype? ...
... How many chromosomes are shown in a normal human karyotype? ...
Name - EdWeb
... 18. The passing of traits from parents to a child is the basis of _______________________________ 19. Every child receives __________ of its chromosomes from his mother, and _______from his father. 20. When a sperm and egg join, they create a single cell called a _______________________________ 21. ...
... 18. The passing of traits from parents to a child is the basis of _______________________________ 19. Every child receives __________ of its chromosomes from his mother, and _______from his father. 20. When a sperm and egg join, they create a single cell called a _______________________________ 21. ...
DNA intro review worksheet
... iii. Which is the most commonly used today? Why? c. If 2 individuals had 2 different RFLPs, how would their DNA look on a gel? i. How would you prepare the DNA? d. If 2 individuals had 2 different STRs, how would their DNA look on a gel? i. How would you prepare the DNA? e. If 2 individuals had 2 di ...
... iii. Which is the most commonly used today? Why? c. If 2 individuals had 2 different RFLPs, how would their DNA look on a gel? i. How would you prepare the DNA? d. If 2 individuals had 2 different STRs, how would their DNA look on a gel? i. How would you prepare the DNA? e. If 2 individuals had 2 di ...
DNA Fingerprinting Notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... protein synthesis genetic recombination ...
... protein synthesis genetic recombination ...
Ch 11 homework
... B) fact that individuals of the same species have different phenotypes. C) process by which genetic information flows from genes to proteins. D) fact that certain genes are visible as dark stripes on a chromosome. E) flow of information from parent to offspring. 2. Outline the function of the lac op ...
... B) fact that individuals of the same species have different phenotypes. C) process by which genetic information flows from genes to proteins. D) fact that certain genes are visible as dark stripes on a chromosome. E) flow of information from parent to offspring. 2. Outline the function of the lac op ...
DNA Structure and Lab
... 2. Pour your salt water solution into a test tube. The test tubes are filled with water and dishwashing liquid. Record observations in table. 3. Place your thumb over the top of the test tube and GENTLY rock the tube back and forth for a couple (2) minutes. Record observations in table. 4. Ask your ...
... 2. Pour your salt water solution into a test tube. The test tubes are filled with water and dishwashing liquid. Record observations in table. 3. Place your thumb over the top of the test tube and GENTLY rock the tube back and forth for a couple (2) minutes. Record observations in table. 4. Ask your ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 1. What is a plant that has two dominant genes or two recessive genes called? 2. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are made up of __________. 3. What is heredity? 4. How are sex cells different from other human cells? 5. What is the name of the process for the way cells divide in asexual reproduction? 6 ...
... 1. What is a plant that has two dominant genes or two recessive genes called? 2. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are made up of __________. 3. What is heredity? 4. How are sex cells different from other human cells? 5. What is the name of the process for the way cells divide in asexual reproduction? 6 ...
7.1 - DNA Structure
... DNA has a uniform diameter along its entire length due to complementary base pairing. The two polynucleotide chains are antiparallel, with the polynucleotides formed around the outside of the helix and the bases extending into the centre. The chains held together by hydrogen bonding between the base ...
... DNA has a uniform diameter along its entire length due to complementary base pairing. The two polynucleotide chains are antiparallel, with the polynucleotides formed around the outside of the helix and the bases extending into the centre. The chains held together by hydrogen bonding between the base ...
Chapter Fourteen ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS All the
... 8. VNTR sequences are larger and a wider range of alleles results. 9. A heterozygote has 2 peaks for a particular locus whereas a homozygote has one. 10. Population databases are necessary to interpret DNA fingerprints because alleles are present in different frequencies in different populations. 11 ...
... 8. VNTR sequences are larger and a wider range of alleles results. 9. A heterozygote has 2 peaks for a particular locus whereas a homozygote has one. 10. Population databases are necessary to interpret DNA fingerprints because alleles are present in different frequencies in different populations. 11 ...
2D Barcode Quiz
... All proteins begin with the amino acid Methionine A codon is a series of four sequential nucleotides which codes for an amino acid Polymerase is an enzyme which breaks down DNA molecules Transcription is the process of making an amino acid sequence from messenger RNA VNTR (Variable Number Tandem Rep ...
... All proteins begin with the amino acid Methionine A codon is a series of four sequential nucleotides which codes for an amino acid Polymerase is an enzyme which breaks down DNA molecules Transcription is the process of making an amino acid sequence from messenger RNA VNTR (Variable Number Tandem Rep ...
6.3 Advances in Genetics
... technology include studying the human genome in detail and identifying people.” • Genome- all the DNA in one cell of an organism • DNA finger printing is used to show if people are related using • Except for identical twins every person has different DNA fingerprints • Scientists use mitochondrial D ...
... technology include studying the human genome in detail and identifying people.” • Genome- all the DNA in one cell of an organism • DNA finger printing is used to show if people are related using • Except for identical twins every person has different DNA fingerprints • Scientists use mitochondrial D ...
Study Guide: The Cell
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
DNA Testing Submission Process
... Please allow at least 4 weeks for the DNA testing process. To make sure your DNA results are not delayed, complete and email the electronic order form to: [email protected] and to [email protected]. Step 1: Download electronic forms. Step 2: Determine what DNA tests you want compl ...
... Please allow at least 4 weeks for the DNA testing process. To make sure your DNA results are not delayed, complete and email the electronic order form to: [email protected] and to [email protected]. Step 1: Download electronic forms. Step 2: Determine what DNA tests you want compl ...
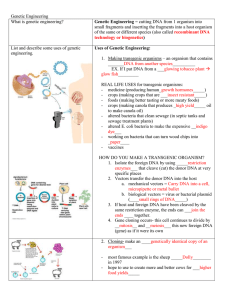
Genetic Engineering
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
Genealogical DNA test

A genealogical DNA test looks at a person's genome at specific locations. Results give information about genealogy or personal ancestry. In general, these tests compare the results of an individual to others from the same lineage or to current and historic ethnic groups. The test results are not meant for medical use, where different types of genetic testing are needed. They do not determine specific genetic diseases or disorders (see possible exceptions in Medical information below). They are intended only to give genealogical information.