Fruit Salad—Hold the DNA, Please
... bond together in a double-helix form. It is a very long molecule made of millions of nucleotides. Between two individuals only small portions of their DNA will differ. Scientists have investigated specific pieces of DNA that tend to differ more between individuals. These pieces are called markers, a ...
... bond together in a double-helix form. It is a very long molecule made of millions of nucleotides. Between two individuals only small portions of their DNA will differ. Scientists have investigated specific pieces of DNA that tend to differ more between individuals. These pieces are called markers, a ...
DNA Notes
... Purines vs. Pyrimadines • Adenine and Guanine are PURINES • Thymine and Cytosine are PYRIMIDINES ...
... Purines vs. Pyrimadines • Adenine and Guanine are PURINES • Thymine and Cytosine are PYRIMIDINES ...
Unit 4 Genetics and Heredity Study Guide Below are some key
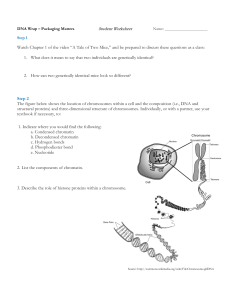
... 1. What is a Karyotype? What are the first 22 pairs of chromosomes called and what is their purpose? What is the 23rd pair and what is its purpose? 2. What are the four major types of b ...
... 1. What is a Karyotype? What are the first 22 pairs of chromosomes called and what is their purpose? What is the 23rd pair and what is its purpose? 2. What are the four major types of b ...
Chapter 12 Assessment
... A genetic disorder is an abnormal condition that an organism inherits from its parents. Genetic disorders are not contagious, and a parent with a genetic disorder does not always pass it to offspring. Some genetic disorders appear at birth, and others do not show up until later in life. For this pro ...
... A genetic disorder is an abnormal condition that an organism inherits from its parents. Genetic disorders are not contagious, and a parent with a genetic disorder does not always pass it to offspring. Some genetic disorders appear at birth, and others do not show up until later in life. For this pro ...
BY2208 SF Genetics Central Dogma McConnell_1.1
... Genes must contain information! Genes must replicate! ...
... Genes must contain information! Genes must replicate! ...
Learning Targets
... kinds of nitrogen bases that exist? Explain how they pair up. 6. What are the differences between DNA and RNA (hint: 4 for each)? ...
... kinds of nitrogen bases that exist? Explain how they pair up. 6. What are the differences between DNA and RNA (hint: 4 for each)? ...
BIO 220 Chapter 8 lecture outline Vocabulary Central dogma of
... Mutations Types Silent Base substitution (point mutation) Missense Nonsense Frameshift Mugatens Nitrous acid Nucleoside analogs Aflatoxin Radiation Identification of mutants Positive and negative selection Ames test Horizonal gene transfer Transformation ...
... Mutations Types Silent Base substitution (point mutation) Missense Nonsense Frameshift Mugatens Nitrous acid Nucleoside analogs Aflatoxin Radiation Identification of mutants Positive and negative selection Ames test Horizonal gene transfer Transformation ...
Microarrays = Gene Chips
... 8. If the PCR product has stuck on it will glow 9. The computer can then say which of the bacterial species the PCR products have stuck to and this indicates which species are present in the sample ...
... 8. If the PCR product has stuck on it will glow 9. The computer can then say which of the bacterial species the PCR products have stuck to and this indicates which species are present in the sample ...
Document
... 27. Give the phenotype for the parents. 28. What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring? 29. What is the genotypic ratio of the offspring? 30. What is the phenotypic ratio of the offspring? 31. What environmental factors might affect the expression of these genes for height? Explain. 32. ...
... 27. Give the phenotype for the parents. 28. What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring? 29. What is the genotypic ratio of the offspring? 30. What is the phenotypic ratio of the offspring? 31. What environmental factors might affect the expression of these genes for height? Explain. 32. ...
Name _________KEY___________________________
... 32. What is electrophoresis used for? Separating fragments of DNA according to size (in base pairs) 33. What is a DNA fingerprint? The pattern of bands that results when an individual’s DNA fragments are separated 34. What is Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)? A process used to make many copies of sel ...
... 32. What is electrophoresis used for? Separating fragments of DNA according to size (in base pairs) 33. What is a DNA fingerprint? The pattern of bands that results when an individual’s DNA fragments are separated 34. What is Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)? A process used to make many copies of sel ...
Connectivity of Earth`s largest biomes: the deep Atlantic to the
... genome and for many individuals (pool samples) 4. Sequence the DNA on a next-generation sequencing platform (ex. Illumina) 5. Run an analysis that will allow you to compare all the same pieces of DNA. Identify DNA difference across the entire genome (1000s-10,000s basepairs) ...
... genome and for many individuals (pool samples) 4. Sequence the DNA on a next-generation sequencing platform (ex. Illumina) 5. Run an analysis that will allow you to compare all the same pieces of DNA. Identify DNA difference across the entire genome (1000s-10,000s basepairs) ...
Worksheet for videos below
... ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? __________ ...
... ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? __________ ...
rnalabreport_1
... Objectivity - Excessive expressions of emotion, opinions, and stereotyping are tip-offs that the information on a site may be biased. Ownership and contributors - Go to the Home or About page of the website and find out who sponsors and writes for the site. Look for contributors who have reliable cr ...
... Objectivity - Excessive expressions of emotion, opinions, and stereotyping are tip-offs that the information on a site may be biased. Ownership and contributors - Go to the Home or About page of the website and find out who sponsors and writes for the site. Look for contributors who have reliable cr ...
Lesson Plans Teacher: Robinson Dates: 3.27
... I can analyze and explain the molecular basis of heredity and the inheritance of traits to successive generations. I can describe various types of chromosomal and gene mutations. I can identify inheritance by recognizing similarities displayed by gel electrophoresis. 1. Get your “notes packet” out, ...
... I can analyze and explain the molecular basis of heredity and the inheritance of traits to successive generations. I can describe various types of chromosomal and gene mutations. I can identify inheritance by recognizing similarities displayed by gel electrophoresis. 1. Get your “notes packet” out, ...
SEG exam 2 1
... a. each daughter duplex will have one of the original parental strands and one new strand. b. one daughter duplex will be entirely new and the other will have both original parental strands. c. both daughter duplexes will be entirely new and the parental duplex will be degraded. d. each strand of ea ...
... a. each daughter duplex will have one of the original parental strands and one new strand. b. one daughter duplex will be entirely new and the other will have both original parental strands. c. both daughter duplexes will be entirely new and the parental duplex will be degraded. d. each strand of ea ...
Gel Electrophoresis
... Separation of DNA Note applied electrical charge- DNA is negatively charged and will migrate to the positive pole Gel matrix acts as a “seive” for DNA Large DNA molecules cannot pass through the small holes in the gel Small molecules move easily through the gel ...
... Separation of DNA Note applied electrical charge- DNA is negatively charged and will migrate to the positive pole Gel matrix acts as a “seive” for DNA Large DNA molecules cannot pass through the small holes in the gel Small molecules move easily through the gel ...
Biology Spring Semester Final Exam Review
... 22. What is the female sex chromosome designation? How many copies of every gene on the X chromosome does a female have? 23. What are sex-linked genes? 24. Why is colorblindness more common in males than in females? 25. In blood types, what blood types have two genotypes that result in the same phen ...
... 22. What is the female sex chromosome designation? How many copies of every gene on the X chromosome does a female have? 23. What are sex-linked genes? 24. Why is colorblindness more common in males than in females? 25. In blood types, what blood types have two genotypes that result in the same phen ...
Organelle genome evolution
... selection asymmetry could favour the movement of mitochondrial genes to the nucleus. We agree that their proposal can be added, together with other hypotheses, such as Muller’s ratchet and the high mutagenicity of free radicals1, to selective pressures that, in some but not all lineages, contribute ...
... selection asymmetry could favour the movement of mitochondrial genes to the nucleus. We agree that their proposal can be added, together with other hypotheses, such as Muller’s ratchet and the high mutagenicity of free radicals1, to selective pressures that, in some but not all lineages, contribute ...
tggccatcgtaaggtgcgacc ggtagca
... Identify: Write DNA, Genes, or Chromosomes to show which each statement is describing. The ...
... Identify: Write DNA, Genes, or Chromosomes to show which each statement is describing. The ...
Genealogical DNA test

A genealogical DNA test looks at a person's genome at specific locations. Results give information about genealogy or personal ancestry. In general, these tests compare the results of an individual to others from the same lineage or to current and historic ethnic groups. The test results are not meant for medical use, where different types of genetic testing are needed. They do not determine specific genetic diseases or disorders (see possible exceptions in Medical information below). They are intended only to give genealogical information.