DNA and Genes - Mecca Hosting Client Sites on rhode
... 7. Each set of three nitrogen basesthat .E ...
... 7. Each set of three nitrogen basesthat .E ...
RT-PCR lab
... DNA unwind to allow synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from one strand (the coding strand) • The mRNA moves out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm • mRNA binds to Ribosomes to code for a protein- protein made (translation) • Protein carries out intent of gene (red hair protein = hair gene) ...
... DNA unwind to allow synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from one strand (the coding strand) • The mRNA moves out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm • mRNA binds to Ribosomes to code for a protein- protein made (translation) • Protein carries out intent of gene (red hair protein = hair gene) ...
DNA Composition and Structure
... 1:1:1:1 for A, G, C, and T, but the ratios of adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine remained constant at approximately 1:1 between each two; and 2) The base composition was not the same in all organisms. ...
... 1:1:1:1 for A, G, C, and T, but the ratios of adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine remained constant at approximately 1:1 between each two; and 2) The base composition was not the same in all organisms. ...
Slide 1
... determine the entire sequence of human DNA identify all the genes in human DNA store this information in databases improve tools for data analysis transfer related technologies to the private sector address the ethical, legal, and social issues (ELSI) that may arise from the project. ...
... determine the entire sequence of human DNA identify all the genes in human DNA store this information in databases improve tools for data analysis transfer related technologies to the private sector address the ethical, legal, and social issues (ELSI) that may arise from the project. ...
Assay for Methylation of genes
... These are microsatellite stable (MSS). Microsatellite instability (MSI) is observed in about 1015% of sporadic colon carcinomas. The vast majority of colon cancers occur sporadically in older individuals, but a few have family histories. Microsatellite Instability (MSI) Microsatellites are short re ...
... These are microsatellite stable (MSS). Microsatellite instability (MSI) is observed in about 1015% of sporadic colon carcinomas. The vast majority of colon cancers occur sporadically in older individuals, but a few have family histories. Microsatellite Instability (MSI) Microsatellites are short re ...
Teaching Biotechnology, Brief History & Introduction to Recombinant
... •Air and water purification •Food production?? ...
... •Air and water purification •Food production?? ...
DNA typing and forensic anthropology
... c. Some sections of DNA vary from individual to individual d. Scientists can link a strand of DNA to a given individual e. 2 different people could possibly have the same blood type, not ______ *** 3. Criminal investigations a. Specimens: ______________________________________________ ...
... c. Some sections of DNA vary from individual to individual d. Scientists can link a strand of DNA to a given individual e. 2 different people could possibly have the same blood type, not ______ *** 3. Criminal investigations a. Specimens: ______________________________________________ ...
Honours Genetics Research Tutorial
... Brown et al (1998) • Studied the mtDNA of modern Native Americans 4 main types (A-D) • Minor 5th type (X) in Native Americans found also in Europeans but not Asians • So how did it get there? By crossing the Atlantic? • Used a network based on maximum parsimony to illustrate relationships of haplot ...
... Brown et al (1998) • Studied the mtDNA of modern Native Americans 4 main types (A-D) • Minor 5th type (X) in Native Americans found also in Europeans but not Asians • So how did it get there? By crossing the Atlantic? • Used a network based on maximum parsimony to illustrate relationships of haplot ...
Introduction to Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources
... follows: • Cytosine (C) combines with Guanine (G) • Adenine (A) combines with Thymine (T) ...
... follows: • Cytosine (C) combines with Guanine (G) • Adenine (A) combines with Thymine (T) ...
Chapter 16 and 17 Test Review
... 9. What supplies the reaction energy for DNA replication and what significance this has on the direction of replication? 10. Describe the formation of leading and lagging strands of a replicating DNA molecule. What allows for the speed at which eukaryotes can replicate their DNA? 11. What are telome ...
... 9. What supplies the reaction energy for DNA replication and what significance this has on the direction of replication? 10. Describe the formation of leading and lagging strands of a replicating DNA molecule. What allows for the speed at which eukaryotes can replicate their DNA? 11. What are telome ...
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
... DNA he or she is interested in studying. Then, the scientist will create or have someone else create primers. Primers are small strands of DNA which match the DNA of interest. These specific sequences are called primers because the enzyme DNA polymerase will only work correctly if there are some nuc ...
... DNA he or she is interested in studying. Then, the scientist will create or have someone else create primers. Primers are small strands of DNA which match the DNA of interest. These specific sequences are called primers because the enzyme DNA polymerase will only work correctly if there are some nuc ...
Slide 1
... The result is more than just eery situations (the mother mentioned above vacations with the other families and remarked on how the children look alike). For some parents, the prevalence of babies from a single donor has raised the possibility that their children may inadvertently cross paths with ha ...
... The result is more than just eery situations (the mother mentioned above vacations with the other families and remarked on how the children look alike). For some parents, the prevalence of babies from a single donor has raised the possibility that their children may inadvertently cross paths with ha ...
Nucleic acid review sheet
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
Recombinant DNA technology.ppt [Compatibility Mode]
... Use of hybridization to identify a clone with a particular DNA segment ...
... Use of hybridization to identify a clone with a particular DNA segment ...
IntrotoBiotechRestrictionEnzymes2011
... • some restriction enzymes (like EcoRI) produce cuts in the DNA that result in the formation of sticky ends on the DNA fragments that are formed. • sticky ends indicates that unpaired bases are left hanging off the cut. other restriction enzymes produce blunt ends, that is, the DNA is cut directly ...
... • some restriction enzymes (like EcoRI) produce cuts in the DNA that result in the formation of sticky ends on the DNA fragments that are formed. • sticky ends indicates that unpaired bases are left hanging off the cut. other restriction enzymes produce blunt ends, that is, the DNA is cut directly ...
DNA Paper Model Activity Try to attach and mode the Gene Reading
... DNA ribbon that is not spooled around a histone or covered by a methyl. Can the machinery read any significant stretch of DNA? No, it cannot. 2. Refer to question 1, would this be an active or inactive gene? Explain. It’s inactive, because the methyl groups make the DNA inaccessible. 3. Try to attac ...
... DNA ribbon that is not spooled around a histone or covered by a methyl. Can the machinery read any significant stretch of DNA? No, it cannot. 2. Refer to question 1, would this be an active or inactive gene? Explain. It’s inactive, because the methyl groups make the DNA inaccessible. 3. Try to attac ...
DNA fingerprinting
... Applications of DNA fingerprinting • microbial diagnostics • genetic diagnostics • forensic identification • paternity analysis • phylogenetic identification ...
... Applications of DNA fingerprinting • microbial diagnostics • genetic diagnostics • forensic identification • paternity analysis • phylogenetic identification ...
Supplemental Data
... were spread onto Zeocin selective plate immediately (A). When colonies appeared, single colony was transferred to selective liquid medium for subculture, and passage cells were spread onto the selective plate again (B). DNA and RNA were extracted from transformed cells and subjected to PCR (C) and R ...
... were spread onto Zeocin selective plate immediately (A). When colonies appeared, single colony was transferred to selective liquid medium for subculture, and passage cells were spread onto the selective plate again (B). DNA and RNA were extracted from transformed cells and subjected to PCR (C) and R ...
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS
... cells are removed; but ! Mutations in germ cells and embryos can cause developmental defects; mutations in adult cells can cause cancer ! The genetic code has apparently evolved to minimize the effects of mutation ...
... cells are removed; but ! Mutations in germ cells and embryos can cause developmental defects; mutations in adult cells can cause cancer ! The genetic code has apparently evolved to minimize the effects of mutation ...
File - Ms. Breeze Biology
... 2. In DNA, ___________________ always forms ________________________ bonds with guanine (G). 3. The sequence of ________________________ carries the genetic information of an organism. 4. The process of ____________________________ produces a new copy of an organism’s genetic information, which is p ...
... 2. In DNA, ___________________ always forms ________________________ bonds with guanine (G). 3. The sequence of ________________________ carries the genetic information of an organism. 4. The process of ____________________________ produces a new copy of an organism’s genetic information, which is p ...
My Dinosaur
... • This uses the genes nucleotide sequence for the genetic structure needed • The DNA sequence allows scientist to have defined fragments of DNA, which is greatly needed in the cloning process ...
... • This uses the genes nucleotide sequence for the genetic structure needed • The DNA sequence allows scientist to have defined fragments of DNA, which is greatly needed in the cloning process ...
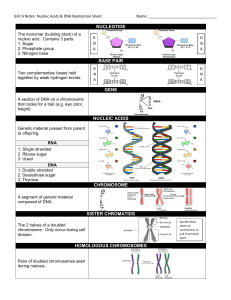
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... A section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a trait (e.g. eye color, ...
... A section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a trait (e.g. eye color, ...
DNA and DNA Replication Guided Notes
... The number of ___________________and mutations are reduced by “proofreading enzymes” ...
... The number of ___________________and mutations are reduced by “proofreading enzymes” ...
mutations
... Somatic mutations: mutations that take place in the body cells DNA , but do not affect their offspring. FYI- albinism can be the result of a somatic or germ-line mutation ...
... Somatic mutations: mutations that take place in the body cells DNA , but do not affect their offspring. FYI- albinism can be the result of a somatic or germ-line mutation ...
Microsatellite

A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from 2–5 base pairs) are repeated, typically 5-50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations in the human genome and they are notable for their high mutation rate and high diversity in the population. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name ""satellite"" refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying ""satellite"" layers of repetitive DNA. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.They are widely used for DNA profiling in kinship analysis and in forensic identification. They are also used in genetic linkage analysis/marker assisted selection to locate a gene or a mutation responsible for a given trait or disease.












![Recombinant DNA technology.ppt [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022508436_1-26bb714d45e9a2e7cd265480e0da1a03-300x300.png)