Created with Sketch. Student activity
... 1. Decide in your group which lollies will be the bases (remember there are four sorts of these), the phosphate groups and the sugar. 2. Use the toothpicks and florist wire as bonds to hold parts together, just like in the real DNA molecule. A DNA molecule has two strands – how will you join the str ...
... 1. Decide in your group which lollies will be the bases (remember there are four sorts of these), the phosphate groups and the sugar. 2. Use the toothpicks and florist wire as bonds to hold parts together, just like in the real DNA molecule. A DNA molecule has two strands – how will you join the str ...
DNA Structure Worksheet
... 5. These bases are of two different types of molecules: purines and pyrimidines. Purines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure, and pyrimidines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure. 6. The two bases that are purines are _____________________ and _________________ ...
... 5. These bases are of two different types of molecules: purines and pyrimidines. Purines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure, and pyrimidines have _______________________ ring(s) in their structure. 6. The two bases that are purines are _____________________ and _________________ ...
You should be familiar with the following vocabulary terms for the
... Biology UNIT 2 TEST ch 11, 10, 12, 13 You should be familiar with the following vocabulary terms for the next Unit Test 4. After each chapter list are some basic concepts on which to focus. Ch 12 vocab Amino acids anticodon Base pairs Chromosome Codon DNA KNOW: ...
... Biology UNIT 2 TEST ch 11, 10, 12, 13 You should be familiar with the following vocabulary terms for the next Unit Test 4. After each chapter list are some basic concepts on which to focus. Ch 12 vocab Amino acids anticodon Base pairs Chromosome Codon DNA KNOW: ...
Vocabulary Assignment Unit 06
... i. Term used for the process of DNA being copied into an mRNA strand j. An accidental change in the genetic information of an organism, resulting from a mutagen or a mistake in replication k. DNA that combines the genetic material of more than one species, as a result of laboratory experimentation l ...
... i. Term used for the process of DNA being copied into an mRNA strand j. An accidental change in the genetic information of an organism, resulting from a mutagen or a mistake in replication k. DNA that combines the genetic material of more than one species, as a result of laboratory experimentation l ...
Is an inducible operon normally off or on?
... What is meant by the term coupled transcription/translation? ...
... What is meant by the term coupled transcription/translation? ...
Name Date ______ Period
... Write out your name in the space provided on the next page. Use the additional page provided to convert your regular name to its DNA alias. Find each letter of your name on the chart. Look at the “Simplified Codon” column to find the DNA code for each letter. Replace each letter of your name with it ...
... Write out your name in the space provided on the next page. Use the additional page provided to convert your regular name to its DNA alias. Find each letter of your name on the chart. Look at the “Simplified Codon” column to find the DNA code for each letter. Replace each letter of your name with it ...
Quiz 4 - chem.uwec.edu
... Chem 452 - Fall 2012 - Quiz 4 1. Identify the term that best completes each of the following statements about carbohydrates: ...
... Chem 452 - Fall 2012 - Quiz 4 1. Identify the term that best completes each of the following statements about carbohydrates: ...
DNA Structure - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The bases bond to each other in pairs and make up the internal structure of the molecule. This is like the rungs or steps of the spiral staircase. ...
... The bases bond to each other in pairs and make up the internal structure of the molecule. This is like the rungs or steps of the spiral staircase. ...
Lab Restriction Enzyme Analysis
... • 2. Become familiar with -Restriction enzymes -Electrophoresis -Analysis of DNA bands ...
... • 2. Become familiar with -Restriction enzymes -Electrophoresis -Analysis of DNA bands ...
1. A double helix looks like: A. A solid sphere B. A hollow tube C. A
... D. That splitting DNA molecules results in nuclear reactions ...
... D. That splitting DNA molecules results in nuclear reactions ...
What is DNA? - Mr. C at Hamilton
... After a cell has “chosen” a gene from which it will build a protein, it makes a copy of the information in the form of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) to send to the protein-building machinery. The synthesis of a RNA molecule from a DNA template is referred to as transcription. The structure of RN ...
... After a cell has “chosen” a gene from which it will build a protein, it makes a copy of the information in the form of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) to send to the protein-building machinery. The synthesis of a RNA molecule from a DNA template is referred to as transcription. The structure of RN ...
Coding Exercises Worksheet
... tRNA Mutations occur when there is a spelling error in the DNA code. Show what would happen step by step if the 8th letter in the DNA strand from above was changed to a “G”. Use the chart at the top of the page to determine the amino acid coded for by mRNA DNA: T A C C C A A G T C G T A A C T G C G ...
... tRNA Mutations occur when there is a spelling error in the DNA code. Show what would happen step by step if the 8th letter in the DNA strand from above was changed to a “G”. Use the chart at the top of the page to determine the amino acid coded for by mRNA DNA: T A C C C A A G T C G T A A C T G C G ...
Chapter 11 A - Iowa State University
... iv. Variation- Differences in genetic materials must account for variations within a species. II. _________ are the building blocks of DNA and RNA. (if you don’t know this I dis-own you as my SI students : ) nucleotides III. What are the 3 components of the answer above? Phosphate, pentose sugar, ni ...
... iv. Variation- Differences in genetic materials must account for variations within a species. II. _________ are the building blocks of DNA and RNA. (if you don’t know this I dis-own you as my SI students : ) nucleotides III. What are the 3 components of the answer above? Phosphate, pentose sugar, ni ...
DNA and RNA
... (DNA)--contains all the information for growth and function. Chromosomes are made of DNA. Double Helix- Large DNA molecule that looks like a twisted ladder. Each step of the ladder is made of nitrogen bases connected by phosphates and sugars. ...
... (DNA)--contains all the information for growth and function. Chromosomes are made of DNA. Double Helix- Large DNA molecule that looks like a twisted ladder. Each step of the ladder is made of nitrogen bases connected by phosphates and sugars. ...
Ch. 16
... 8. Why does adenine always pair with thymine and guanine with cytosine in DNA? 9. What is meant by the term that DNA replication is semiconservative? 10. Detail the Meselson and Stahl experiment concerning DNA replication. 11. How is bacterial DNA replication accomplished? 12. What are DNA polymeras ...
... 8. Why does adenine always pair with thymine and guanine with cytosine in DNA? 9. What is meant by the term that DNA replication is semiconservative? 10. Detail the Meselson and Stahl experiment concerning DNA replication. 11. How is bacterial DNA replication accomplished? 12. What are DNA polymeras ...
Chapter 16 and 17 Test Review
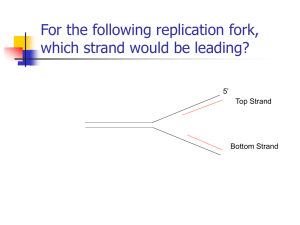
... 10. Describe the formation of leading and lagging strands of a replicating DNA molecule. What allows for the speed at which eukaryotes can replicate their DNA? 11. What are telomeres? Telomerase? What affect do they have on the DNA strands? 12. Compare the major differences in Eukaryotic and Prokary ...
... 10. Describe the formation of leading and lagging strands of a replicating DNA molecule. What allows for the speed at which eukaryotes can replicate their DNA? 11. What are telomeres? Telomerase? What affect do they have on the DNA strands? 12. Compare the major differences in Eukaryotic and Prokary ...
Substance Patent of Nucleic Acid Delivery Technology was allowed
... Biotechnology-based drugs such as a nucleic acid are widely recognized as the next generation drugs. However, the stability of such nucleic acids in body is very low and accordingly the utilization of a carrier is inevitable to deliver appropriately to the target cells, the development of a great po ...
... Biotechnology-based drugs such as a nucleic acid are widely recognized as the next generation drugs. However, the stability of such nucleic acids in body is very low and accordingly the utilization of a carrier is inevitable to deliver appropriately to the target cells, the development of a great po ...
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
... all the genetic diversity seen in living things. • They had a larger alphabet (20 “letters” vs. 4), which meant they must be capable of storing larger and more varied amounts of information. ...
... all the genetic diversity seen in living things. • They had a larger alphabet (20 “letters” vs. 4), which meant they must be capable of storing larger and more varied amounts of information. ...
How does DNA work
... DNA is a double helix with base pairs complimenting each other. Adenine and thymine/ Guanine and Cytosine are base pairs Each strand of DNA exposes the necessary information to build two identical strands of DNA ...
... DNA is a double helix with base pairs complimenting each other. Adenine and thymine/ Guanine and Cytosine are base pairs Each strand of DNA exposes the necessary information to build two identical strands of DNA ...
RNA
... Nucleic acid in nucleoprotein structure provides storage, realization and transfer of the hereditary information In 1868 the Swiss chemist F. Mischer for the first time extracted from human leucocite nuclei a new type of compound unknown before and named them nucleins (from lat. nucleus). Then nucl ...
... Nucleic acid in nucleoprotein structure provides storage, realization and transfer of the hereditary information In 1868 the Swiss chemist F. Mischer for the first time extracted from human leucocite nuclei a new type of compound unknown before and named them nucleins (from lat. nucleus). Then nucl ...
DNA Replication Amoeba Sisters Video
... As you watch the animation on DNA Replication, answer the following questions. ...
... As you watch the animation on DNA Replication, answer the following questions. ...
HRW BIO CRF Ch 09_p01-58
... a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar molecule, and a nitrogen base It stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. a ...
... a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar molecule, and a nitrogen base It stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. a ...
DNA-protein on steroidsud
... 2.Two strands DNA form (sense and anti-sense) 3.Enzymes help new nucleotides pair with free ends on single strand of DNA: A-T and C-G 4. A-T and C-G form hydrogen bonds between new nucleotide and the strand of DNA ...
... 2.Two strands DNA form (sense and anti-sense) 3.Enzymes help new nucleotides pair with free ends on single strand of DNA: A-T and C-G 4. A-T and C-G form hydrogen bonds between new nucleotide and the strand of DNA ...
DNA SCAVENGER HUNT
... How does the Nitrogen Base pairing make each species unique, if all species use the same 4 bases? The sequence and amounts of the nucleotides varies from species to species and individual to individual! (My DNA base sequence is different than yours!) What is DNA Replication? DNA making copies of its ...
... How does the Nitrogen Base pairing make each species unique, if all species use the same 4 bases? The sequence and amounts of the nucleotides varies from species to species and individual to individual! (My DNA base sequence is different than yours!) What is DNA Replication? DNA making copies of its ...
DNA nanotechnology

DNA nanotechnology is the design and manufacture of artificial nucleic acid structures for technological uses. In this field, nucleic acids are used as non-biological engineering materials for nanotechnology rather than as the carriers of genetic information in living cells. Researchers in the field have created static structures such as two- and three-dimensional crystal lattices, nanotubes, polyhedra, and arbitrary shapes, as well as functional devices such as molecular machines and DNA computers. The field is beginning to be used as a tool to solve basic science problems in structural biology and biophysics, including applications in crystallography and spectroscopy for protein structure determination. Potential applications in molecular scale electronics and nanomedicine are also being investigated.The conceptual foundation for DNA nanotechnology was first laid out by Nadrian Seeman in the early 1980s, and the field began to attract widespread interest in the mid-2000s. This use of nucleic acids is enabled by their strict base pairing rules, which cause only portions of strands with complementary base sequences to bind together to form strong, rigid double helix structures. This allows for the rational design of base sequences that will selectively assemble to form complex target structures with precisely controlled nanoscale features. A number of assembly methods are used to make these structures, including tile-based structures that assemble from smaller structures, folding structures using the DNA origami method, and dynamically reconfigurable structures using strand displacement techniques. While the field's name specifically references DNA, the same principles have been used with other types of nucleic acids as well, leading to the occasional use of the alternative name nucleic acid nanotechnology.