PCR denaturation temperature 94C The hydrogen bonds are broken
... The hydrogen bonds are broken in the double stranded DNA, creating single strands of DNA that are susceptible to copying. ...
... The hydrogen bonds are broken in the double stranded DNA, creating single strands of DNA that are susceptible to copying. ...
DNA REVIEW SHEET
... 14. What are the three kinds of RNA? 15. Where is an anticodon located? 16. A codon that has no anticodon match would be called a ___________________. 17. What does DNA polymerase do? 18. Anything ending in –ase would be classified as an ____________________> 19. What 3 things make up DNA? 20. DNA i ...
... 14. What are the three kinds of RNA? 15. Where is an anticodon located? 16. A codon that has no anticodon match would be called a ___________________. 17. What does DNA polymerase do? 18. Anything ending in –ase would be classified as an ____________________> 19. What 3 things make up DNA? 20. DNA i ...
I am found in the nucleus and I hold genes
... I am the name given to the triplet of bases I am the structure that controls the on an mRNA strand synthesis of RNA and other components needed to build ribosomes ...
... I am the name given to the triplet of bases I am the structure that controls the on an mRNA strand synthesis of RNA and other components needed to build ribosomes ...
Unraveling DNA
... 10. Look at Figure 1, part b. How is the chromatin bundled in the nucleus? ____________________ 11. Look at Figure 1, part c. What is the DNA in the chromatin coiled around? ____________________ 12. Look at Figure 1, part d. How many strands of DNA are connected in the middle? _______ 13. Look at Fi ...
... 10. Look at Figure 1, part b. How is the chromatin bundled in the nucleus? ____________________ 11. Look at Figure 1, part c. What is the DNA in the chromatin coiled around? ____________________ 12. Look at Figure 1, part d. How many strands of DNA are connected in the middle? _______ 13. Look at Fi ...
nucleic acids definitions
... GENES: A segment of DNA and it controls the making of specific proteins in the body, making that body unique and different. ...
... GENES: A segment of DNA and it controls the making of specific proteins in the body, making that body unique and different. ...
BIOL 222 - philipdarrenjones.com
... C) prokaryotes cannot remove eukaryotic introns D) prokaryotes use different nucleotides than eukaryotes E) bacterial DNA is not found in a membrane-bound nucleus and is therefore incompatible with mammalian DNA ...
... C) prokaryotes cannot remove eukaryotic introns D) prokaryotes use different nucleotides than eukaryotes E) bacterial DNA is not found in a membrane-bound nucleus and is therefore incompatible with mammalian DNA ...
The Genetic Code
... DNA replication is a biological process that occurs in all living organisms and copies their DNA; it is the basis for biological inheritance. ...
... DNA replication is a biological process that occurs in all living organisms and copies their DNA; it is the basis for biological inheritance. ...
assignment DNA - UniMAP Portal
... _____________ A mutagen that is incorporated into DNA in place of a normal base _____________ A mutagen that causes the formation of highly reactive ions _____________ A mutagen that alters adenine so that it base-pairs with cytosine _____________ A mutagen that causes insertions _____________ A mut ...
... _____________ A mutagen that is incorporated into DNA in place of a normal base _____________ A mutagen that causes the formation of highly reactive ions _____________ A mutagen that alters adenine so that it base-pairs with cytosine _____________ A mutagen that causes insertions _____________ A mut ...
Slide
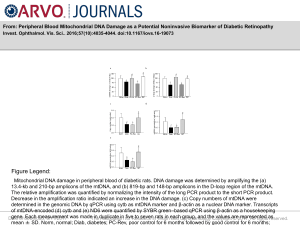
... Mitochondrial DNA damage in peripheral blood of diabetic rats. DNA damage was determined by amplifying the (a) 13.4-kb and 210-bp amplicons of the mtDNA, and (b) 819-bp and 148-bp amplicons in the D-loop region of the mtDNA. The relative amplification was quantified by normalizing the intensity of t ...
... Mitochondrial DNA damage in peripheral blood of diabetic rats. DNA damage was determined by amplifying the (a) 13.4-kb and 210-bp amplicons of the mtDNA, and (b) 819-bp and 148-bp amplicons in the D-loop region of the mtDNA. The relative amplification was quantified by normalizing the intensity of t ...
STRUCTURE:
... DNA is found in ____________________ mRNA is made in the ___________________ from DNA template mRNA carries the message to the _______________________ Protein is made using mRNA code like a “_________________” and amino acids as ...
... DNA is found in ____________________ mRNA is made in the ___________________ from DNA template mRNA carries the message to the _______________________ Protein is made using mRNA code like a “_________________” and amino acids as ...
Cell Theory Quiz Study Guide Name
... 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic _______. 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is a ...
... 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic _______. 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is a ...
What Makes Living Things Different from each other?
... What Makes Living Things Different from each other? ...
... What Makes Living Things Different from each other? ...
Ch. 12 Review- pg. 315 1-23 Answers The process by which one
... 6. The main enzyme involved in linking individual nucleotides into DNA molecules is d. DNA polymerase 7. The process by which the genetic code of DNA is copied into a strand of RNA is called b. transcription ...
... 6. The main enzyme involved in linking individual nucleotides into DNA molecules is d. DNA polymerase 7. The process by which the genetic code of DNA is copied into a strand of RNA is called b. transcription ...
Chromosomes and DNA Replication
... forming tightly packed chromosomes you can see with a microscope ...
... forming tightly packed chromosomes you can see with a microscope ...
DNA versus RNA Notes File
... • Finally, both DNA and RNA can contain four nitrogenous bases, BUT RNA does not have Thymine. • Thymine is replaced by a similar base called uracil (U). ...
... • Finally, both DNA and RNA can contain four nitrogenous bases, BUT RNA does not have Thymine. • Thymine is replaced by a similar base called uracil (U). ...
DNA, RNA, Genetic Engineering
... Semiconservative (one original and one new strand) Copying done by DNA polymerase Okazaki fragments 3’ to 5’ (leading v. lagging strand) Mitosis and Meiosis ...
... Semiconservative (one original and one new strand) Copying done by DNA polymerase Okazaki fragments 3’ to 5’ (leading v. lagging strand) Mitosis and Meiosis ...
DNA and RNA study guide Answer Key
... 1. What is the structure of DNA? DNA is a double helix model, much like a zipper on a jacket. 2. What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA? Adenine, Guanine , Cytosine, Thymine 3. What are the four nitrogenous bases in RNA? Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil 4. A single strand of DNA acts as a temp ...
... 1. What is the structure of DNA? DNA is a double helix model, much like a zipper on a jacket. 2. What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA? Adenine, Guanine , Cytosine, Thymine 3. What are the four nitrogenous bases in RNA? Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil 4. A single strand of DNA acts as a temp ...
Name - Canvas by Instructure
... RNA structure DNA replication Translation and transcription (Protein synthesis) Know how to translate and transcribe. I will provide the amino acid chart. Important scientists and their discoveries. Types of mutations and their overall effect on protein synthesis. ...
... RNA structure DNA replication Translation and transcription (Protein synthesis) Know how to translate and transcribe. I will provide the amino acid chart. Important scientists and their discoveries. Types of mutations and their overall effect on protein synthesis. ...
Chapter 11 review - Canvas by Instructure
... RNA structure DNA replication Translation and transcription (Protein synthesis) Know how to translate and transcribe. I will provide the amino acid chart. Important scientists and their discoveries. Types of mutations and their overall effect on protein synthesis. ...
... RNA structure DNA replication Translation and transcription (Protein synthesis) Know how to translate and transcribe. I will provide the amino acid chart. Important scientists and their discoveries. Types of mutations and their overall effect on protein synthesis. ...
DNA polymerase

The DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this process, DNA polymerase “reads” the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerase is required to help duplicate the cell’s DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each of the daughter cells. In this way, genetic information is transmitted from generation to generation.Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightly woven form. This opens up or “unzips” the double-stranded DNA to give two single strands of DNA that can be used as templates for replication.