three possibile models for replication
... Prokaryotic organisms (ex: bacteria) have a single origin of replication on their circular chromosome, whereas eukaryotic organisms have multiple starting places on their linear chromosomes (because they have so much DNA and it needs to be copied efficiently). 16. At the origin of replication, the D ...
... Prokaryotic organisms (ex: bacteria) have a single origin of replication on their circular chromosome, whereas eukaryotic organisms have multiple starting places on their linear chromosomes (because they have so much DNA and it needs to be copied efficiently). 16. At the origin of replication, the D ...
Chapter 12
... A book can store information, you can copy information from this book and the book after being copied can be transmitted or given to others. ...
... A book can store information, you can copy information from this book and the book after being copied can be transmitted or given to others. ...
Microbial Genetics
... the enzyme "reverse transcriptase" to transcribe DNA from a RNA template. The viral DNA then integrates into the nucleus of the host cell. Then it is transcribed, and further translated into proteins. This biological process effectively adds another pathway to the central dogma of molecular biology. ...
... the enzyme "reverse transcriptase" to transcribe DNA from a RNA template. The viral DNA then integrates into the nucleus of the host cell. Then it is transcribed, and further translated into proteins. This biological process effectively adds another pathway to the central dogma of molecular biology. ...
DNA Flipbook Objective: You will create an informational Flipbook
... Objective: You will create an informational Flipbook explaining in words and pictures the parts of DNA, DNA replication, Transcription, and Translation. As you complete each task, place a check to keep track of your progress. Label each flip as outlined below. Directions: Each page should be titled ...
... Objective: You will create an informational Flipbook explaining in words and pictures the parts of DNA, DNA replication, Transcription, and Translation. As you complete each task, place a check to keep track of your progress. Label each flip as outlined below. Directions: Each page should be titled ...
Biology and you - properties of life and the scientific method
... There are ___46__ chromosomes (strands of DNA) in the body cells of humans. ____23___ come from mom and ____23_____ come from dad. A cells shape and function is controlled by particular ____________ of DNA being ...
... There are ___46__ chromosomes (strands of DNA) in the body cells of humans. ____23___ come from mom and ____23_____ come from dad. A cells shape and function is controlled by particular ____________ of DNA being ...
DNA- HL sample test
... A biochemist isolated and purified molecules needed for DNA replication. When some DNA was added replication occurred, but the DNA molecules formed were defective. Each consisted of a normal DNA strand paired with segments of DNA a few hundred nucleotides long. Which of the following had been left o ...
... A biochemist isolated and purified molecules needed for DNA replication. When some DNA was added replication occurred, but the DNA molecules formed were defective. Each consisted of a normal DNA strand paired with segments of DNA a few hundred nucleotides long. Which of the following had been left o ...
Nucleotides and DNA Structure
... C) leucine and alanine D) leucine and arginine Which does not apply to most bacterial DNA? A) Circular. B) Relaxed. C) Not packed into nucleosomes. D) Supercoiled. Which best describes the structure of a nucleosome core particle? A) A histone octamer with DNA threaded through its center. B) About 50 ...
... C) leucine and alanine D) leucine and arginine Which does not apply to most bacterial DNA? A) Circular. B) Relaxed. C) Not packed into nucleosomes. D) Supercoiled. Which best describes the structure of a nucleosome core particle? A) A histone octamer with DNA threaded through its center. B) About 50 ...
Microbial genetics
... The component of nucleic acid bases will be produce in the mRNA pairing the bases in DNA template, for example, a G with C, via versa However in RNA, there are no T so they replace it with U that will be paired with A the DNA strand have 3’ and 5’ ends, so mRNA strand will start copy the bases ...
... The component of nucleic acid bases will be produce in the mRNA pairing the bases in DNA template, for example, a G with C, via versa However in RNA, there are no T so they replace it with U that will be paired with A the DNA strand have 3’ and 5’ ends, so mRNA strand will start copy the bases ...
Review Answers
... Well, this is a tri-hybrid cross – lots of potential offspring in the punnet square. .. . Possible gametes are: ABC, ABc, AbC, Abc, aBC, abC, aBc, abc 8 gametes on top and 8 gametes on the side of a Punnett create 64 squares in between. Then count up how many squares out of 64 have a dominant A, dom ...
... Well, this is a tri-hybrid cross – lots of potential offspring in the punnet square. .. . Possible gametes are: ABC, ABc, AbC, Abc, aBC, abC, aBc, abc 8 gametes on top and 8 gametes on the side of a Punnett create 64 squares in between. Then count up how many squares out of 64 have a dominant A, dom ...
Chapter 9 Notes Guide – Mendel and Heredity
... Section 10.15 22) Now you have learned about transcription and translation. We are going to draw a large, comprehensive picture of the entire process. Please make sure you are taking notes on any part that you are confused about. Your drawing needs to be neat and done in pencil. ...
... Section 10.15 22) Now you have learned about transcription and translation. We are going to draw a large, comprehensive picture of the entire process. Please make sure you are taking notes on any part that you are confused about. Your drawing needs to be neat and done in pencil. ...
Class Presentation Questions for CH 12 Part 1(Sections 1-2-3).
... 2. Where is DNA found in a eukaryotic cell? 3. Before a cell divides, the DNA must be duplicated/copied in a process called ______________________. 4. What happens during DNA replication? 5. Define enzyme. 6. Define catalyst. 7. The enzymes that carry out DNA replication have two main functions. Lis ...
... 2. Where is DNA found in a eukaryotic cell? 3. Before a cell divides, the DNA must be duplicated/copied in a process called ______________________. 4. What happens during DNA replication? 5. Define enzyme. 6. Define catalyst. 7. The enzymes that carry out DNA replication have two main functions. Lis ...
Study Guide A - WordPress.com
... MAIN IDEA: Proteins carry out the process of replication. 7. Circle all of the roles that proteins play during DNA replication. a. They help unzip the DNA strand. b. They hold the DNA strands apart. c. They attach nucleotides to the nucleus. d. They remove nucleotides from the DNA strands. e. They b ...
... MAIN IDEA: Proteins carry out the process of replication. 7. Circle all of the roles that proteins play during DNA replication. a. They help unzip the DNA strand. b. They hold the DNA strands apart. c. They attach nucleotides to the nucleus. d. They remove nucleotides from the DNA strands. e. They b ...
code sequence practice
... Transcription – making mRNA from DNA 2. If this is your original DNA strand, what is the mRNA sequence that is synthesized? DNA Strand: C A G T G C A T T mRNA strand: 3. Now go backwards, if you are given the following mRNA strand, write the DNA strand that goes with it. mRNA strand: U C G A C C G A ...
... Transcription – making mRNA from DNA 2. If this is your original DNA strand, what is the mRNA sequence that is synthesized? DNA Strand: C A G T G C A T T mRNA strand: 3. Now go backwards, if you are given the following mRNA strand, write the DNA strand that goes with it. mRNA strand: U C G A C C G A ...
PCR questions
... 3. What is the purpose of heating the DNA sample to 94-96 C? 4. What is the process of adding primers called? What kind of bond forms between the primers and the DNA? ...
... 3. What is the purpose of heating the DNA sample to 94-96 C? 4. What is the process of adding primers called? What kind of bond forms between the primers and the DNA? ...
Section 6.2 Questions, page 279 1. If Hershey and Chase had found
... 2. The sample of DNA will contain 32 % thymine, 18 % guanine, and 18 % cytosine. 3. DNA is a polymer composed of a nucleotide monomer unit. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The phosphate group bonds to the neighbouring nucleotide’s ribose sugar ...
... 2. The sample of DNA will contain 32 % thymine, 18 % guanine, and 18 % cytosine. 3. DNA is a polymer composed of a nucleotide monomer unit. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The phosphate group bonds to the neighbouring nucleotide’s ribose sugar ...
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... a. provided evidence for the semiconservative model of DNA replication. (pg. 299-300) 7. Watson and Crick concluded that each base could not pair with itself because b. the uniform width of 2 nm would not permit two purines or two pyrimidines to pair together. (pg. 298) 8. The joining of nucleotides ...
... a. provided evidence for the semiconservative model of DNA replication. (pg. 299-300) 7. Watson and Crick concluded that each base could not pair with itself because b. the uniform width of 2 nm would not permit two purines or two pyrimidines to pair together. (pg. 298) 8. The joining of nucleotides ...
Slide
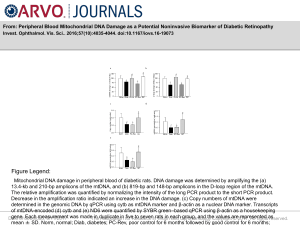
... 13.4-kb and 210-bp amplicons of the mtDNA, and (b) 819-bp and 148-bp amplicons in the D-loop region of the mtDNA. The relative amplification was quantified by normalizing the intensity of the long PCR product to the short PCR product. Decrease in the amplification ratio indicated an increase in the ...
... 13.4-kb and 210-bp amplicons of the mtDNA, and (b) 819-bp and 148-bp amplicons in the D-loop region of the mtDNA. The relative amplification was quantified by normalizing the intensity of the long PCR product to the short PCR product. Decrease in the amplification ratio indicated an increase in the ...
Nitrogenous base Number of strands Sugar DNA RNA Ribose Deoxy
... Phosphate group Sugar (deoxyribose) DNA nucleotide Polynucleotide ...
... Phosphate group Sugar (deoxyribose) DNA nucleotide Polynucleotide ...
DNA Study Guide - Liberty Union High School District
... 26. What parts of a chromosome are transcribed? 27. Describe the difference between and Exon and Intron. 28. How many different amino acids are there? ____________ 29. How can that many amino acids form 100,000’s of different proteins? 30. Is the DNA exactly the same in each cell in your body? Expla ...
... 26. What parts of a chromosome are transcribed? 27. Describe the difference between and Exon and Intron. 28. How many different amino acids are there? ____________ 29. How can that many amino acids form 100,000’s of different proteins? 30. Is the DNA exactly the same in each cell in your body? Expla ...
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 10-1 Discovery of DNA
... a. serve as a storage form for unused nucleotides. b. occupy space in the nucleus to keep the nucleus from collapsing. c. store information that tells the cells which proteins to make. d. serve as a template for making long, spiral carbohydrates. 2. ______The two strands of DNA molecules are held to ...
... a. serve as a storage form for unused nucleotides. b. occupy space in the nucleus to keep the nucleus from collapsing. c. store information that tells the cells which proteins to make. d. serve as a template for making long, spiral carbohydrates. 2. ______The two strands of DNA molecules are held to ...
Document
... 16. Number the steps of DNA replication in the correct order (1, 2, 3) _______ Daughter strands are formed using complementary base pairing. _______ DNA unwinds _______ The DNA of the daughter strands winds with together with its parent strand. 17. Why is DNA replication called "semi-conservative"? ...
... 16. Number the steps of DNA replication in the correct order (1, 2, 3) _______ Daughter strands are formed using complementary base pairing. _______ DNA unwinds _______ The DNA of the daughter strands winds with together with its parent strand. 17. Why is DNA replication called "semi-conservative"? ...
A new method for strand discrimination in
... either corrects a nonsense mutation in the drug resistance gene, or eliminates a unique restriction site, on the vector. They require two rounds of transformation to select the desired mutant. Here I describe a new simple method for the strand discrimination, ...
... either corrects a nonsense mutation in the drug resistance gene, or eliminates a unique restriction site, on the vector. They require two rounds of transformation to select the desired mutant. Here I describe a new simple method for the strand discrimination, ...
Chapter 9 DNA: THE Genetic Material
... Base-pairing rules – cytosine pairs with guanine and adenine with thymine. These base pairing rules are supported by Chargaff's observations. The strictness of basepairing results in 2 strands containing complementary base pairs. ...
... Base-pairing rules – cytosine pairs with guanine and adenine with thymine. These base pairing rules are supported by Chargaff's observations. The strictness of basepairing results in 2 strands containing complementary base pairs. ...
DNA replication
DNA replication is the process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule. This biological process occurs in all living organisms and is the basis for biological inheritance. DNA is made up of two strands and each strand of the original DNA molecule serves as a template for the production of the complementary strand, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. Cellular proofreading and error-checking mechanisms ensure near perfect fidelity for DNA replication.In a cell, DNA replication begins at specific locations, or origins of replication, in the genome. Unwinding of DNA at the origin and synthesis of new strands results in replication forks growing bidirectional from the origin. A number of proteins are associated with the replication fork which helps in terms of the initiation and continuation of DNA synthesis. Most prominently, DNA polymerase synthesizes the new DNA by adding complementary nucleotides to the template strand.DNA replication can also be performed in vitro (artificially, outside a cell). DNA polymerases isolated from cells and artificial DNA primers can be used to initiate DNA synthesis at known sequences in a template DNA molecule. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a common laboratory technique, cyclically applies such artificial synthesis to amplify a specific target DNA fragment from a pool of DNA.