PHY215: Study Guide for Introductory Quantum Mechanics Explain 1. Cathode Ray tubes, Cathode rays, and the generation of X‐rays.
... hand to alert the course staff members present at the exam. You have 25 minutes to work out the quiz problems. The relevant formulae are provided in on the last sheet, which you can detach when you solve the problems. Do not separate the remaining sheets. Calculator Policy: all memories and register ...
... hand to alert the course staff members present at the exam. You have 25 minutes to work out the quiz problems. The relevant formulae are provided in on the last sheet, which you can detach when you solve the problems. Do not separate the remaining sheets. Calculator Policy: all memories and register ...
Chap 3.
... There is no restriction on the value of k. Thus a free particle, even in quantum mechanics, can have any non-negative value of the energy h̄2 k 2 E= ...
... There is no restriction on the value of k. Thus a free particle, even in quantum mechanics, can have any non-negative value of the energy h̄2 k 2 E= ...
Homework 3
... 1. Explain the terms wavelength and amplitude. If a photon has a frequency of 9 1010 Hz what is its wavelength? Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum does this correspond to? ...
... 1. Explain the terms wavelength and amplitude. If a photon has a frequency of 9 1010 Hz what is its wavelength? Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum does this correspond to? ...
Slide 1
... oWhen an e- occupies an orbit greater than the lowest possible energy level it is said to be in an “excited state” oΔE=-Rhc(1/nf2 - 1/ni2) Rhc=1312 kJ/mol Wave/particle duality oTaken from idea that light, usually considered to exhibit wave properties, actually consists of particles (photons) oSim ...
... oWhen an e- occupies an orbit greater than the lowest possible energy level it is said to be in an “excited state” oΔE=-Rhc(1/nf2 - 1/ni2) Rhc=1312 kJ/mol Wave/particle duality oTaken from idea that light, usually considered to exhibit wave properties, actually consists of particles (photons) oSim ...
Document
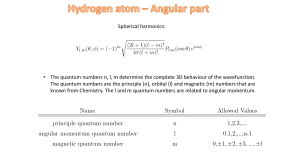
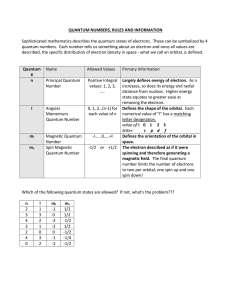
... 1.4 Postulates of QM (i) What Ψ represents (ii) Hermitian operators for dynamical variables (iii) Operators for position, momentum, ang. Mom. (iv) Result of measurement ...
... 1.4 Postulates of QM (i) What Ψ represents (ii) Hermitian operators for dynamical variables (iii) Operators for position, momentum, ang. Mom. (iv) Result of measurement ...
January 1999
... J99T.1—Weirdons Problem Suppose a new kind of particle is discovered. This particle is known as the weirdon since it obeys weird statistics in which a given state may contain 0, 1, or 2 particles. Furthermore, weirdons are one dimensional and we will be considering a gas of non-interacting weirdons ...
... J99T.1—Weirdons Problem Suppose a new kind of particle is discovered. This particle is known as the weirdon since it obeys weird statistics in which a given state may contain 0, 1, or 2 particles. Furthermore, weirdons are one dimensional and we will be considering a gas of non-interacting weirdons ...
Arrangement of Electrons In Atoms
... an atom’s main energy levels, the number of orbitals per energy sublevel, and the number of orbitals per main energy level ...
... an atom’s main energy levels, the number of orbitals per energy sublevel, and the number of orbitals per main energy level ...
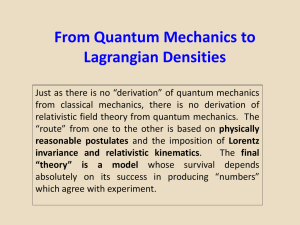
Lecture6.QM.to.Lagrangian.Densities
... Quantization arises from placing boundary conditions on the wave function. It is a mathematical result! ...
... Quantization arises from placing boundary conditions on the wave function. It is a mathematical result! ...
Relativity Problem Set 9
... state energy E0 , find the constant B. (b) Find the constant A by imposing the normalization of the wave function. ...
... state energy E0 , find the constant B. (b) Find the constant A by imposing the normalization of the wave function. ...
ppt
... Remember? Probability of an event is given by |f|2 where f is a complex number (probability amplitude) Born equated the y r with an amplitude, and thus the equivalent intensity is ...
... Remember? Probability of an event is given by |f|2 where f is a complex number (probability amplitude) Born equated the y r with an amplitude, and thus the equivalent intensity is ...
Particle in a box

In quantum mechanics, the particle in a box model (also known as the infinite potential well or the infinite square well) describes a particle free to move in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example a ball trapped inside a large box, the particle can move at any speed within the box and it is no more likely to be found at one position than another. However, when the well becomes very narrow (on the scale of a few nanometers), quantum effects become important. The particle may only occupy certain positive energy levels. Likewise, it can never have zero energy, meaning that the particle can never ""sit still"". Additionally, it is more likely to be found at certain positions than at others, depending on its energy level. The particle may never be detected at certain positions, known as spatial nodes.The particle in a box model provides one of the very few problems in quantum mechanics which can be solved analytically, without approximations. This means that the observable properties of the particle (such as its energy and position) are related to the mass of the particle and the width of the well by simple mathematical expressions. Due to its simplicity, the model allows insight into quantum effects without the need for complicated mathematics. It is one of the first quantum mechanics problems taught in undergraduate physics courses, and it is commonly used as an approximation for more complicated quantum systems.