Modern Physics
... The Schrödinger wave equation is one of the most powerful techniques for solving problems in quantum physics In general the equation is applied in three dimensions of space as well as time For simplicity we will consider only the one dimensional, time independent case The wave equation for a wave of ...
... The Schrödinger wave equation is one of the most powerful techniques for solving problems in quantum physics In general the equation is applied in three dimensions of space as well as time For simplicity we will consider only the one dimensional, time independent case The wave equation for a wave of ...
practice exam available as a MS Word file
... like a macroscopic wave in that an attempt to detect the electron finds it at one particular position, and not with intensity spread out over a spatial region. ...
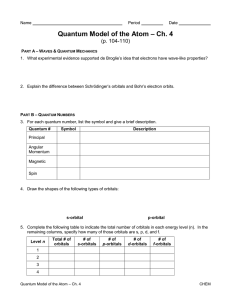
... like a macroscopic wave in that an attempt to detect the electron finds it at one particular position, and not with intensity spread out over a spatial region. ...
Relativity Problem Set 7 - Solutions Prof. J. Gerton October 24, 2011
... so-called virial theorem, valid also in classical mechanics). So, U α~c α2 me c2 E(= En ) = ...
... so-called virial theorem, valid also in classical mechanics). So, U α~c α2 me c2 E(= En ) = ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 11. Derive the Schroedinger time-independent wave equation from the time-dependent one. 12. What is a hermitian operator and its significance? Show that eigen functions corresponding to two different eigen values of a hermitian operator are orthogonal. 13. Show that in spherical polar coordinates th ...
... 11. Derive the Schroedinger time-independent wave equation from the time-dependent one. 12. What is a hermitian operator and its significance? Show that eigen functions corresponding to two different eigen values of a hermitian operator are orthogonal. 13. Show that in spherical polar coordinates th ...
Example solution to the exercise 1
... Find a way to express the total energy as a function of the radius r. After this you can use the Larmor equation and the chain rule df (x) df (x) dx ...
... Find a way to express the total energy as a function of the radius r. After this you can use the Larmor equation and the chain rule df (x) df (x) dx ...
File - SPHS Devil Physics
... a. The order of magnitude estimates from the uncertainty principle may include (but is not limited to) estimates of the energy of the ground state of an atom, the impossibility of an electron existing within a nucleus, and the lifetime of an electron in an excited energy state ...
... a. The order of magnitude estimates from the uncertainty principle may include (but is not limited to) estimates of the energy of the ground state of an atom, the impossibility of an electron existing within a nucleus, and the lifetime of an electron in an excited energy state ...
Particle in a box

In quantum mechanics, the particle in a box model (also known as the infinite potential well or the infinite square well) describes a particle free to move in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example a ball trapped inside a large box, the particle can move at any speed within the box and it is no more likely to be found at one position than another. However, when the well becomes very narrow (on the scale of a few nanometers), quantum effects become important. The particle may only occupy certain positive energy levels. Likewise, it can never have zero energy, meaning that the particle can never ""sit still"". Additionally, it is more likely to be found at certain positions than at others, depending on its energy level. The particle may never be detected at certain positions, known as spatial nodes.The particle in a box model provides one of the very few problems in quantum mechanics which can be solved analytically, without approximations. This means that the observable properties of the particle (such as its energy and position) are related to the mass of the particle and the width of the well by simple mathematical expressions. Due to its simplicity, the model allows insight into quantum effects without the need for complicated mathematics. It is one of the first quantum mechanics problems taught in undergraduate physics courses, and it is commonly used as an approximation for more complicated quantum systems.