Eoct_review
... • Early prokaryotes engulfed other prokaryotes and developed symbiotic relationships • Evidence includes mitochondria and chloroplast have prokaryotic type DNA ...
... • Early prokaryotes engulfed other prokaryotes and developed symbiotic relationships • Evidence includes mitochondria and chloroplast have prokaryotic type DNA ...
EOC Review PPT
... • Early prokaryotes engulfed other prokaryotes and developed symbiotic relationships • Evidence includes mitochondria and chloroplast have prokaryotic type DNA ...
... • Early prokaryotes engulfed other prokaryotes and developed symbiotic relationships • Evidence includes mitochondria and chloroplast have prokaryotic type DNA ...
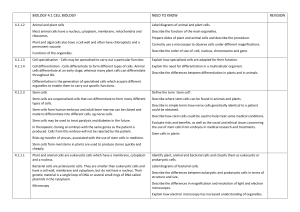
BIOLOGY 4.1 CELL BIOLOGY NEED TO KNOW REVISION
... Prepare slides of plant and animal cells and describe the procedure. Correctly use a microscope to observe cells under different magnifications. Describe the order of size of: cell, nucleus, chromosome and gene. ...
... Prepare slides of plant and animal cells and describe the procedure. Correctly use a microscope to observe cells under different magnifications. Describe the order of size of: cell, nucleus, chromosome and gene. ...
AG1 INVESTIGATOR Name Miyuki Yamamoto Address
... Dedkov, E.I., Borisov, A.B., Wernig, A., and Carlson, B.M. (2003). Aging of skeletal muscle does not affect the response of satellite cells to denervation. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 51(7), 853-863. Keller, C., Hansen, M.S., Coffin, C.M., and Capecchi, M.R. (2004). Pax3:Fkhr interferes with embryonic P ...
... Dedkov, E.I., Borisov, A.B., Wernig, A., and Carlson, B.M. (2003). Aging of skeletal muscle does not affect the response of satellite cells to denervation. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 51(7), 853-863. Keller, C., Hansen, M.S., Coffin, C.M., and Capecchi, M.R. (2004). Pax3:Fkhr interferes with embryonic P ...
Biology I Outline
... carbon dioxide f. Explain how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment g. Identify the basic unit of the nervous system, the neuron, and explain generally how it works h. Explain how the muscular/skeletal system wo ...
... carbon dioxide f. Explain how the nervous system mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment g. Identify the basic unit of the nervous system, the neuron, and explain generally how it works h. Explain how the muscular/skeletal system wo ...
Unit 2 - Glow Blogs
... A condition where the sufferer cannot control glucose levels in their body Glands A group of cells that produce and secrete chemicals into the body Pancreas The organ responsible for the production of digestive enzymes and the hormones insulin and glucagon Glycogen Animal storage carbohydrate locate ...
... A condition where the sufferer cannot control glucose levels in their body Glands A group of cells that produce and secrete chemicals into the body Pancreas The organ responsible for the production of digestive enzymes and the hormones insulin and glucagon Glycogen Animal storage carbohydrate locate ...
Asexual Reproduction Spore Production – Vegetative Reproduction –
... Inherited and Non-inherited Characteristics Inherited (heritable) characteristics are those traits which are passed on to offspring directly from their parents. These traits are passed on by way of the genetic material that is combined from the parents during the process of sexual reproduction. Heri ...
... Inherited and Non-inherited Characteristics Inherited (heritable) characteristics are those traits which are passed on to offspring directly from their parents. These traits are passed on by way of the genetic material that is combined from the parents during the process of sexual reproduction. Heri ...
Notes Unit 4 Part 1
... 1. Interphase = the _________ part of the cell cycle in which all organelles are doubled except the ___________ a. G1 phase = Gap I phase in which the cell grows in _______ and protein production is ________ nerve cells cannot replicate because they get _________ in this phase b. S phase = Synthes ...
... 1. Interphase = the _________ part of the cell cycle in which all organelles are doubled except the ___________ a. G1 phase = Gap I phase in which the cell grows in _______ and protein production is ________ nerve cells cannot replicate because they get _________ in this phase b. S phase = Synthes ...
Levels of Organization Notes (pg 418-427)
... All matter is made of atoms. Atoms combine and form molecules. Molecules make up cells. A large animal, such as a Komodo dragon, is not made of one cell. Instead, it is made of trillions of cells working together. The skin of the Komodo dragon, shown in Figure 1 in your text, is made of many cells t ...
... All matter is made of atoms. Atoms combine and form molecules. Molecules make up cells. A large animal, such as a Komodo dragon, is not made of one cell. Instead, it is made of trillions of cells working together. The skin of the Komodo dragon, shown in Figure 1 in your text, is made of many cells t ...
File
... 1. Investigate living things; and identify and apply scientific ideas used to interpret their general structure, function and organization • investigate and describe example scientific studies of the characteristics of living things (e.g., investigate and describe an ongoing scientific study of a lo ...
... 1. Investigate living things; and identify and apply scientific ideas used to interpret their general structure, function and organization • investigate and describe example scientific studies of the characteristics of living things (e.g., investigate and describe an ongoing scientific study of a lo ...
Biological Classification / Biomes
... are called nonvascular plants (they also don’t have true roots or stems). *Leaves are the place where most photosynthesis takes place because they have the most chloroplasts (organelle that changes light energy to food). *Stomata are pores in a leaf that allow CO2 in to plant & H2O vapor out. *Roots ...
... are called nonvascular plants (they also don’t have true roots or stems). *Leaves are the place where most photosynthesis takes place because they have the most chloroplasts (organelle that changes light energy to food). *Stomata are pores in a leaf that allow CO2 in to plant & H2O vapor out. *Roots ...
ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION
... rates: – Minimal rates support basic life functions, such as breathing, – Maximal rates occurs during peak activities, such as all-out running. ...
... rates: – Minimal rates support basic life functions, such as breathing, – Maximal rates occurs during peak activities, such as all-out running. ...
Biology 1st Semester Exam
... Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: 16. Nucleotides are to __________ as _____________ are to proteins a. nucleic acids; amino acids b. polymers; lipids 17. _____Which of the following organel ...
... Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: 16. Nucleotides are to __________ as _____________ are to proteins a. nucleic acids; amino acids b. polymers; lipids 17. _____Which of the following organel ...
FOA 9-19-2011
... that is found between the cell membrane and the nucleus, which primarily consists of water and holds organelles? A. mitochondria C. chloroplast B. cytoplasm D. cell membrane ...
... that is found between the cell membrane and the nucleus, which primarily consists of water and holds organelles? A. mitochondria C. chloroplast B. cytoplasm D. cell membrane ...
7th Grade Science Standards—Life Science (one semester)
... performed by cells to sustain a living organism (e.g., division to produce more cells, taking in nutrients, releasing waste, using energy to do work, and producing materials the organism needs). ...
... performed by cells to sustain a living organism (e.g., division to produce more cells, taking in nutrients, releasing waste, using energy to do work, and producing materials the organism needs). ...
Study Guide Answers
... 5. What does photosynthesis turn light energy into? Chemical energy 6. How do small molecules cross the cell membrane? diffusion 7. Which organelle produces proteins? ribosomes ...
... 5. What does photosynthesis turn light energy into? Chemical energy 6. How do small molecules cross the cell membrane? diffusion 7. Which organelle produces proteins? ribosomes ...
Animal and Plant Classification
... Conifers are plants that make seeds but do not have flowers. In conifers, the seeds are in the cones. Some plants have no seeds at all. They use spores to reproduce. A spore is a single cell surrounded by a cell wall. It can grow into a new plant if it falls on a place where it can get the water and ...
... Conifers are plants that make seeds but do not have flowers. In conifers, the seeds are in the cones. Some plants have no seeds at all. They use spores to reproduce. A spore is a single cell surrounded by a cell wall. It can grow into a new plant if it falls on a place where it can get the water and ...
Chapter 5 Questions
... 15. For each of the following groups or organisms, give examples of animals for each and list their derived (unique) characteristics. a. Porifera They have support in the form of sessile, which are connected needlelike spicules. At their larval stage, porifera are planktonic and float freely. They a ...
... 15. For each of the following groups or organisms, give examples of animals for each and list their derived (unique) characteristics. a. Porifera They have support in the form of sessile, which are connected needlelike spicules. At their larval stage, porifera are planktonic and float freely. They a ...
Animal Form and Function (Ch. 40)
... connected to muscles with tendons used for movement and support B. four levels of organization 1. cell – basic unit; many types; dozens to hundreds of types in most adult vertebrates 2. tissue – a group of cells similar in structure and function most differentiate early in development from thr ...
... connected to muscles with tendons used for movement and support B. four levels of organization 1. cell – basic unit; many types; dozens to hundreds of types in most adult vertebrates 2. tissue – a group of cells similar in structure and function most differentiate early in development from thr ...
gastrulation - Instructure
... Gastrulation requires coordinated cell movements, signaling, differentiation and proliferation to create cell layers. – Inducers are key signaling cells that influence surrounding tissues to initiate tissue formation. – Different organisms have different patterns of gastrulation typified by partic ...
... Gastrulation requires coordinated cell movements, signaling, differentiation and proliferation to create cell layers. – Inducers are key signaling cells that influence surrounding tissues to initiate tissue formation. – Different organisms have different patterns of gastrulation typified by partic ...
File
... on separate plants (unisexual) monoicious—male and female parts on one plant produce seeds that are covered by fruit seed is formed when the pollen and the ovule unite during pollination ...
... on separate plants (unisexual) monoicious—male and female parts on one plant produce seeds that are covered by fruit seed is formed when the pollen and the ovule unite during pollination ...
Asexual Reproduction Content Practice B LESSON 2
... Directions: On the line before each statement, write T if the statement is true or F if the statement is false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word(s) to make it true. Write your changes on the lines provided. ...
... Directions: On the line before each statement, write T if the statement is true or F if the statement is false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word(s) to make it true. Write your changes on the lines provided. ...
Cells - College of Science | Oregon State University
... __________________________ cells (choose from the list above). When you view the model from the side, the muscle cells look long and tubular in shape. When you view the model from above, what shape does each muscle cell seem to have? ____________________ This difference in appearance from different ...
... __________________________ cells (choose from the list above). When you view the model from the side, the muscle cells look long and tubular in shape. When you view the model from above, what shape does each muscle cell seem to have? ____________________ This difference in appearance from different ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are