Gas Exchange in Plants
... stem. The arrangement of cells in the stem is shown in Figure 8.33. Inside the plant, oxygen dissolves in the water of the moist cell membrane and then diffuses across the cell membrane into the cell. Carbon dioxide follows the opposite path, diffusing across the cell membrane into the intracellular ...
... stem. The arrangement of cells in the stem is shown in Figure 8.33. Inside the plant, oxygen dissolves in the water of the moist cell membrane and then diffuses across the cell membrane into the cell. Carbon dioxide follows the opposite path, diffusing across the cell membrane into the intracellular ...
Scott Foresman Science
... in food to grow and heal wounds. Few cells move around. But all cells have moving parts inside them. Cells sense and respond to changes around them. Cells often communicate and work with other cells. All cells need energy to survive. They must grow, move, and divide into new cells. Most cells get en ...
... in food to grow and heal wounds. Few cells move around. But all cells have moving parts inside them. Cells sense and respond to changes around them. Cells often communicate and work with other cells. All cells need energy to survive. They must grow, move, and divide into new cells. Most cells get en ...
Biology Final Review
... 71. What do some mammals have to release heat from their bodies? 72. The mammalian circulatory system consists of how many chambers and how many loops? ...
... 71. What do some mammals have to release heat from their bodies? 72. The mammalian circulatory system consists of how many chambers and how many loops? ...
biology a2
... from the pulmonary artery the blood enters the capillary system on the lung alveoli at the arterial bed; At this point carbonic acid and carbonmonohaemoglobin dissociates; to release carbon (iv) oxide; which diffuses across the capillary wall and wall of alveoli into the alveolar cavity; (12mks) Tot ...
... from the pulmonary artery the blood enters the capillary system on the lung alveoli at the arterial bed; At this point carbonic acid and carbonmonohaemoglobin dissociates; to release carbon (iv) oxide; which diffuses across the capillary wall and wall of alveoli into the alveolar cavity; (12mks) Tot ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... 01. Define prokaryotic cell. 02. Give the principle of dark field microscope. 03. What are polysomes? 04. Pinocytosis – Explain. 05. What are SAT chromosomes? 06. Define karyotype. 07. Briefly explain amitosis. 08. What happens during G1 phase of Cell Cycle? 09. What is mutation theory? 10. What is ...
... 01. Define prokaryotic cell. 02. Give the principle of dark field microscope. 03. What are polysomes? 04. Pinocytosis – Explain. 05. What are SAT chromosomes? 06. Define karyotype. 07. Briefly explain amitosis. 08. What happens during G1 phase of Cell Cycle? 09. What is mutation theory? 10. What is ...
Specialized Cells - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... This is because the original cell became specialized as it divided and multiplied through mitosis, which results in daughter cells with identical genetic information. As the human body grows, cells that start out being the same undergo cell differentiation, which results in cells becoming specialize ...
... This is because the original cell became specialized as it divided and multiplied through mitosis, which results in daughter cells with identical genetic information. As the human body grows, cells that start out being the same undergo cell differentiation, which results in cells becoming specialize ...
0011657857 - University of Oxford
... The University of Oxford is a complex and stimulating organisation, which enjoys an international reputation as a world-class centre of excellence in research and teaching. It employs over 10,000 staff and has a student population of over 22,000. Most staff are directly appointed and managed by one ...
... The University of Oxford is a complex and stimulating organisation, which enjoys an international reputation as a world-class centre of excellence in research and teaching. It employs over 10,000 staff and has a student population of over 22,000. Most staff are directly appointed and managed by one ...
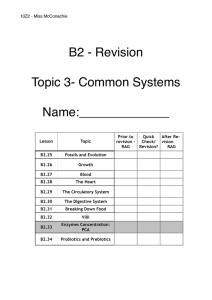
b2- revision booklet topic 3
... The fossil record is incomplete and has many gaps. These gaps mean that scientists must interpret how organisms change over time from incomplete data. How might this lead some people to believe in divine intelligence and not evolution?! ...
... The fossil record is incomplete and has many gaps. These gaps mean that scientists must interpret how organisms change over time from incomplete data. How might this lead some people to believe in divine intelligence and not evolution?! ...
Characteristics of Living Things
... offspring that share traits from both parents. • Asexual reproduction- reproduction that does not involve the union of sex cells and in which one parent produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent. ...
... offspring that share traits from both parents. • Asexual reproduction- reproduction that does not involve the union of sex cells and in which one parent produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent. ...
Chromosomes
... Chromosomes contain DNA. Almost all cells have 46 chromosomes, except gametes (sex cells: egg and sperm). If a cell has 46 chromosomes it is considered to be diploid (2n). If it has half the number of chromosomes it is haploid (n), these are found in the gametes. A human has 46 diploid (2n) ...
... Chromosomes contain DNA. Almost all cells have 46 chromosomes, except gametes (sex cells: egg and sperm). If a cell has 46 chromosomes it is considered to be diploid (2n). If it has half the number of chromosomes it is haploid (n), these are found in the gametes. A human has 46 diploid (2n) ...
The!cell!
... molecules!to!simpler!compounds.!E.g.!converting!the!chemical!energy!stored!in! glucose!molecules!into!ATP!for!use!in!cellular!processes!and!activities.! Other!pathways!consume!energy!to!build!complex!molecules!from!simpler!ones! (anabolism).!E.g.!synthesis!of!a!protein!from!amino!acids.! ...
... molecules!to!simpler!compounds.!E.g.!converting!the!chemical!energy!stored!in! glucose!molecules!into!ATP!for!use!in!cellular!processes!and!activities.! Other!pathways!consume!energy!to!build!complex!molecules!from!simpler!ones! (anabolism).!E.g.!synthesis!of!a!protein!from!amino!acids.! ...
Zoology Semester Exam Study Guide
... 1. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have __________ __________. 2. If a cell contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles, it is _______________________. 3. An animal is: unicellular or multicellular; autotrophic or heterotrophic; prokaryotic or eukaryotic; 4. Only 5% of all animals have ...
... 1. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have __________ __________. 2. If a cell contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles, it is _______________________. 3. An animal is: unicellular or multicellular; autotrophic or heterotrophic; prokaryotic or eukaryotic; 4. Only 5% of all animals have ...
Lec. No.10 Centrosome In cell biology, the centrosome is an
... nor are bounded by membranes. The most common inclusions are glycogen, lipid droplet, pigments, and crystals. 1-Glycogen: is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals and fungi. The olysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose ...
... nor are bounded by membranes. The most common inclusions are glycogen, lipid droplet, pigments, and crystals. 1-Glycogen: is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals and fungi. The olysaccharide structure represents the main storage form of glucose ...
Development Reading Guide File
... contributes to the development of membranes that will nourish and protect the embryo. The inner cell mass will eventually form the organism itself. 3. What is the name of the rapid cell division that produces the morula? 4. How does the morula differ from the blastula? 5. What does the blastula do u ...
... contributes to the development of membranes that will nourish and protect the embryo. The inner cell mass will eventually form the organism itself. 3. What is the name of the rapid cell division that produces the morula? 4. How does the morula differ from the blastula? 5. What does the blastula do u ...
Development
... (I) Embryonic Development In the early stages of development, the organism is called an embryo The process of embryonic ...
... (I) Embryonic Development In the early stages of development, the organism is called an embryo The process of embryonic ...
Study Guide for Exam 1 Dr. Osborne
... Stratified squamous epithelium has flat cells and is found in skin ii. Stratified cuboidal epithelium has all cubic cells and is found in the sweat ducts iii. Stratified columnar epithelium has tall cells and is found in mammary gland ducts ...
... Stratified squamous epithelium has flat cells and is found in skin ii. Stratified cuboidal epithelium has all cubic cells and is found in the sweat ducts iii. Stratified columnar epithelium has tall cells and is found in mammary gland ducts ...
National 5 Biology Unit 1 cell Biology – Homework 2
... What is the name given to the difference in concentration of a substance on either side of a cell membrane? ...
... What is the name given to the difference in concentration of a substance on either side of a cell membrane? ...
WHAT IS AN ANIMAL?
... The relationship between form and function has repeated itself throughout the year... At many levels of biological hierarchy...from molecules, to cellular structures, to tissues, to organs and systems, to body shapes... the forms taken by structures have been shaped by natural selection for their fu ...
... The relationship between form and function has repeated itself throughout the year... At many levels of biological hierarchy...from molecules, to cellular structures, to tissues, to organs and systems, to body shapes... the forms taken by structures have been shaped by natural selection for their fu ...
The Cell Cycle
... The changes that occur in the regulation of cell growth and division of cancer cells are due to mutations. Various environmental factors can affect the occurrence of cancer cells. ...
... The changes that occur in the regulation of cell growth and division of cancer cells are due to mutations. Various environmental factors can affect the occurrence of cancer cells. ...
Hoerner EDAY 2
... Lesson Overview/Procedures/Length of Time to Complete: We have learned quite a bit about the human body over the last 9 or 10 weeks. An important part of learning is reviewing to make sure that you still remem ...
... Lesson Overview/Procedures/Length of Time to Complete: We have learned quite a bit about the human body over the last 9 or 10 weeks. An important part of learning is reviewing to make sure that you still remem ...
Water Cycle
... 41. What are 4 ways that seeds are dispersed away from the mother plant? Wind, water, animals, fruit 42. How are the following fruits or seeds dispersed? ...
... 41. What are 4 ways that seeds are dispersed away from the mother plant? Wind, water, animals, fruit 42. How are the following fruits or seeds dispersed? ...
Biology Glossary
... a diagram representing a system of connections or interrelations among two or more things by a number of distinctive dots, lines, bars, etc. a transitional biome that is found between a desert and a forest destruction or fragmentation of an area that supports living organisms sex cells with 1/2 as m ...
... a diagram representing a system of connections or interrelations among two or more things by a number of distinctive dots, lines, bars, etc. a transitional biome that is found between a desert and a forest destruction or fragmentation of an area that supports living organisms sex cells with 1/2 as m ...
Unit IV- Nervous System
... Embryo - a fertilized egg from conception to the eighth embryonic week Fetus - A developing human from approximately eight weeks after conception until the time of its birth ...
... Embryo - a fertilized egg from conception to the eighth embryonic week Fetus - A developing human from approximately eight weeks after conception until the time of its birth ...
Prokaryotes
... divided into equal halves by drawing any number of lines through its center (1) Organism is usually round (2) Ex: sand dollar ii) Bilateral symmetry – organism can be divided into two matching halves only at one point (1) Most animals have bilateral symmetry (2) Ex: humans ...
... divided into equal halves by drawing any number of lines through its center (1) Organism is usually round (2) Ex: sand dollar ii) Bilateral symmetry – organism can be divided into two matching halves only at one point (1) Most animals have bilateral symmetry (2) Ex: humans ...
Unit 8-B Study Guide Questions
... 1) List and explain the six characteristics of life. 2) Give two examples of different organisms with different structures that have the same function. 3) Discuss Darwin’s species of finches and their variation in bill shape. 4) List the six of the eight main organ systems and identify the main stru ...
... 1) List and explain the six characteristics of life. 2) Give two examples of different organisms with different structures that have the same function. 3) Discuss Darwin’s species of finches and their variation in bill shape. 4) List the six of the eight main organ systems and identify the main stru ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are