Traits of Life PPT
... reproduction, offspring will differ from their parents in some ways because they will be inheriting DNA from both the sperm and egg. ...
... reproduction, offspring will differ from their parents in some ways because they will be inheriting DNA from both the sperm and egg. ...
What You Absolutely Must Know to Pass the NYS Living
... food chain. As a result, organisms high on the food chain have less energy available to them and must have smaller populations. D. Environmental factors (air, water, light, temperature, pH, food, predators etc) determine which organisms can live in an ecosystem and how large the population can get. ...
... food chain. As a result, organisms high on the food chain have less energy available to them and must have smaller populations. D. Environmental factors (air, water, light, temperature, pH, food, predators etc) determine which organisms can live in an ecosystem and how large the population can get. ...
B2 Knowledge Powerpoint
... water and other organism in the area. • Biodiversity = the different plants and animals in an area. • Ecosystem = an area in which all the living organisms and all the non living organism form a relationship in order to survive. • Habitat = where the plants and animals are found/living. • Population ...
... water and other organism in the area. • Biodiversity = the different plants and animals in an area. • Ecosystem = an area in which all the living organisms and all the non living organism form a relationship in order to survive. • Habitat = where the plants and animals are found/living. • Population ...
B2 Knowledge Powerpoint
... water and other organism in the area. • Biodiversity = the different plants and animals in an area. • Ecosystem = an area in which all the living organisms and all the non living organism form a relationship in order to survive. • Habitat = where the plants and animals are found/living. • Population ...
... water and other organism in the area. • Biodiversity = the different plants and animals in an area. • Ecosystem = an area in which all the living organisms and all the non living organism form a relationship in order to survive. • Habitat = where the plants and animals are found/living. • Population ...
Amoeba Sisters Video Refreshers April 2015
... can this transport system support other plant systems, such as the plant’s reproductive system? Stomata (singular: stoma) must open or close based on environmental conditions. Stomata need to be opened to allow gases in, but the plant can lose water by doing so. How might this relate to the transpor ...
... can this transport system support other plant systems, such as the plant’s reproductive system? Stomata (singular: stoma) must open or close based on environmental conditions. Stomata need to be opened to allow gases in, but the plant can lose water by doing so. How might this relate to the transpor ...
POLYGENIC INHERITANCE The term “polygenic inheritance” is
... containing genes which are exact copies of the original. So each cell of the embryo, and the adult organism into which it develops, contains cells which are genetically identical. This is fortunate because the body's immune system will target any "foreign" cells (normally invading microbes) which di ...
... containing genes which are exact copies of the original. So each cell of the embryo, and the adult organism into which it develops, contains cells which are genetically identical. This is fortunate because the body's immune system will target any "foreign" cells (normally invading microbes) which di ...
Microorganism Vocabulary Words 1. Amoeba Single-celled life
... A form of reproduction in which a new organism is created by combining the genetic material of two organisms of the same or similar genetic species. ...
... A form of reproduction in which a new organism is created by combining the genetic material of two organisms of the same or similar genetic species. ...
Science 9-Asexual Reproduction Name: Station #1: Microviewer
... caught in and on nets and tossed back. Often, though, when the starfish are tossed back, an arm is sometimes detached from the body in the process. Explain how this affects the starfish population. 6. Name what type of asexual reproduction is occurring and explain your reasoning: a. Jenny cut a piec ...
... caught in and on nets and tossed back. Often, though, when the starfish are tossed back, an arm is sometimes detached from the body in the process. Explain how this affects the starfish population. 6. Name what type of asexual reproduction is occurring and explain your reasoning: a. Jenny cut a piec ...
Sexual reproduction
... • During mitosis and cell division, a body cell and its nucleus divide once and produce 2 identical cells. • The two daughter cells produced by mitosis and cell division have the same genetic ...
... • During mitosis and cell division, a body cell and its nucleus divide once and produce 2 identical cells. • The two daughter cells produced by mitosis and cell division have the same genetic ...
Cell Cycle/Mitosis/Meiosis
... 3. Diploid cell (2N) – any cell with 2 complete sets of chromosomes. All of your body cells are diploid. How many chromosomes are in your skin cell? 46 Body cells are called somatic cells. 4. Haploid Cell (1N)- a cell with only 1 complete set of chromosomes. What cells are haploid? Sex cells ( sperm ...
... 3. Diploid cell (2N) – any cell with 2 complete sets of chromosomes. All of your body cells are diploid. How many chromosomes are in your skin cell? 46 Body cells are called somatic cells. 4. Haploid Cell (1N)- a cell with only 1 complete set of chromosomes. What cells are haploid? Sex cells ( sperm ...
Review Guide for Body Systems and Cells Test
... Key Concept 3: Cells make up all living organisms, unicellular or multicellular, and have similarities in structure cells and all cells need genetic and environmental information in order to and function. The cell theory states that new cells come from old survive. Key Concept 4: Cells use a series ...
... Key Concept 3: Cells make up all living organisms, unicellular or multicellular, and have similarities in structure cells and all cells need genetic and environmental information in order to and function. The cell theory states that new cells come from old survive. Key Concept 4: Cells use a series ...
BCPS Biology Reteaching Guide Cells Vocab Chart
... A temporary cytoplasmic protrusion in amoebas and other protozoans, used for locomotion and to take up food ...
... A temporary cytoplasmic protrusion in amoebas and other protozoans, used for locomotion and to take up food ...
Practice Quiz
... 4. The kidney tubules are composed of ____________________________ epithelium for absorption and secretion. 5. ____________________ cells produce cartilage. 6. The salivary glands are a good example of a (an) ____________________ gland. 7. ______________________________ cells support and nourish neu ...
... 4. The kidney tubules are composed of ____________________________ epithelium for absorption and secretion. 5. ____________________ cells produce cartilage. 6. The salivary glands are a good example of a (an) ____________________ gland. 7. ______________________________ cells support and nourish neu ...
The Cell - ESC-2
... solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the following is the correct term used to describe a group of body parts working together to perform a specific function? A an organism ...
... solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the following is the correct term used to describe a group of body parts working together to perform a specific function? A an organism ...
2015-16 Fall Semester Exam REVIEW KEY
... 27. What is homeostasis? Give an example of how humans maintain homeostasis. The body’s ability to maintain balance. Humans sweat when it is hot to maintain homeostasis. Humans shiver when it is cold to maintain homeostasis. Humans also vomit to maintain homeostasis. 28. What role does the heart pla ...
... 27. What is homeostasis? Give an example of how humans maintain homeostasis. The body’s ability to maintain balance. Humans sweat when it is hot to maintain homeostasis. Humans shiver when it is cold to maintain homeostasis. Humans also vomit to maintain homeostasis. 28. What role does the heart pla ...
Afterschool Biology EOC Program
... Biology Teachers Katie Sparks **Tiffaney Clark Lauren Edmonds and Susan Waldron Reagan Davis and Erica Flint Callie Kresta Kathleen Farmer ...
... Biology Teachers Katie Sparks **Tiffaney Clark Lauren Edmonds and Susan Waldron Reagan Davis and Erica Flint Callie Kresta Kathleen Farmer ...
EOC Review 2015 answer key A
... 45) How did the invention of the microscope allow the cell theory to be developed? The invention of the microscope enabled scientists to discover the cell and learn more about it. 46) Why do plant cells have both a chloroplast and a mitochondria but animal cells have only a mitochondria? The chlorop ...
... 45) How did the invention of the microscope allow the cell theory to be developed? The invention of the microscope enabled scientists to discover the cell and learn more about it. 46) Why do plant cells have both a chloroplast and a mitochondria but animal cells have only a mitochondria? The chlorop ...
Unit 1 Cellular Biology Test Review
... How can the cell be compared to a working factory? Why are mitochondria called the power plants of cells? Where would you find a high concentration of mitochondria? Low concentration? Chemistry of Biology o What are the 4 types of macromolecules in the body? o Carbohydrates – simple vs. comple ...
... How can the cell be compared to a working factory? Why are mitochondria called the power plants of cells? Where would you find a high concentration of mitochondria? Low concentration? Chemistry of Biology o What are the 4 types of macromolecules in the body? o Carbohydrates – simple vs. comple ...
No Slide Title
... the switching on of many PR genes •there are also hundreds of very small proteins (called defensins) which are induced and lead to pathogen cell wall and other damage. Defensins are produced by birds, insects and mammals as well. B4. Phytoalexins •low molecular weight antimicrobial compounds that ac ...
... the switching on of many PR genes •there are also hundreds of very small proteins (called defensins) which are induced and lead to pathogen cell wall and other damage. Defensins are produced by birds, insects and mammals as well. B4. Phytoalexins •low molecular weight antimicrobial compounds that ac ...
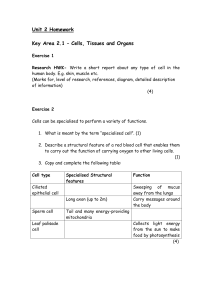
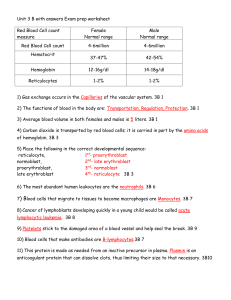
Red Blood Cell count measure Female Normal range Male Normal
... 2nd- late erythroblast proerythroblast, 3rd- normoblast late erythroblast 4th- reticulocyte 3B 3 6) The most abundant human leukocytes are the neutrophils. 3B 6 7) Blood cells that migrate to tissues to become macrophages are Monocytes. 3B 7 8) Cancer of lymphoblasts developing quickly in a young ch ...
... 2nd- late erythroblast proerythroblast, 3rd- normoblast late erythroblast 4th- reticulocyte 3B 3 6) The most abundant human leukocytes are the neutrophils. 3B 6 7) Blood cells that migrate to tissues to become macrophages are Monocytes. 3B 7 8) Cancer of lymphoblasts developing quickly in a young ch ...
Mitosis/Meiosis Notes
... join together (in the process of ____________________) to form a fertilization fertilized egg (______________). The sperm and egg each carry zygote 1/2 the genetic information for the new individual. _____ each ***The fertilized egg carries genetic information from _________ _______________. parent ...
... join together (in the process of ____________________) to form a fertilization fertilized egg (______________). The sperm and egg each carry zygote 1/2 the genetic information for the new individual. _____ each ***The fertilized egg carries genetic information from _________ _______________. parent ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell - GMCbiology
... nucleus or membrane-bound structures called organelles – small single-celled Eukaryotes include most other cells & have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (plants, fungi, & animals) – larger than prokaryotes and can be either unicellular or multicellular ...
... nucleus or membrane-bound structures called organelles – small single-celled Eukaryotes include most other cells & have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (plants, fungi, & animals) – larger than prokaryotes and can be either unicellular or multicellular ...
Study Guide : Life Science
... complete metamorphosis : egg-larva-adult; complete change in body form incomplete metamorphosis : egg-nymph-adult; not much change in body form simple eye : detects light and dark The First Vertebrates Fish – live entire life in water (gills, scales) ectotherm : (cold-blooded); “outside heat” – ...
... complete metamorphosis : egg-larva-adult; complete change in body form incomplete metamorphosis : egg-nymph-adult; not much change in body form simple eye : detects light and dark The First Vertebrates Fish – live entire life in water (gills, scales) ectotherm : (cold-blooded); “outside heat” – ...
Important Concepts - Alaska K-12 Science Curricular Initiative (AKSCI)
... many of them microscopic, cannot be neatly classified as either plants or animals. · Similarities among organisms are found in internal anatomical features, which can be used to infer the degree of relatedness among organisms. · Traditionally, a species has been defined as all organisms that can mat ...
... many of them microscopic, cannot be neatly classified as either plants or animals. · Similarities among organisms are found in internal anatomical features, which can be used to infer the degree of relatedness among organisms. · Traditionally, a species has been defined as all organisms that can mat ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are