Gateway Biology Review- Answer Key Characteristics of Living
... Characteristics of Living Things ...
... Characteristics of Living Things ...
EOCT REVIEW
... – Descent w/modificationorganisms come from a common ancestor – Natural Selection • All organisms produce more offspring than can survive. • All offspring are genetically varied (may not always be obvious based on phenotype) • Variations in genes enable some offspring to outcompete others • Those wi ...
... – Descent w/modificationorganisms come from a common ancestor – Natural Selection • All organisms produce more offspring than can survive. • All offspring are genetically varied (may not always be obvious based on phenotype) • Variations in genes enable some offspring to outcompete others • Those wi ...
#1 Scientific Method
... • Chart that shows the relationship within a family. • Can be used to show how a gene is passed from one generation to the next. • Males• Females- ...
... • Chart that shows the relationship within a family. • Can be used to show how a gene is passed from one generation to the next. • Males• Females- ...
5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living
... D. A strainer separates water from noodles similar to the way kidneys remove waste from cells. ...
... D. A strainer separates water from noodles similar to the way kidneys remove waste from cells. ...
grade unit title: # of weeks
... organization of cells into tissues and the organization of tissues into organs. The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
... organization of cells into tissues and the organization of tissues into organs. The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
EOCT REVIEW
... – Descent w/modificationorganisms come from a common ancestor – Natural Selection • All organisms produce more offspring than can survive. • All offspring are genetically varied (may not always be obvious based on phenotype) • Variations in genes enable some offspring to outcompete others • Those wi ...
... – Descent w/modificationorganisms come from a common ancestor – Natural Selection • All organisms produce more offspring than can survive. • All offspring are genetically varied (may not always be obvious based on phenotype) • Variations in genes enable some offspring to outcompete others • Those wi ...
unit 6. living things/biosphere
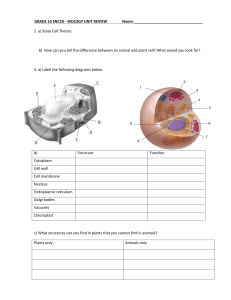
... CELL MEMBRANE: is a thin layer that surround and protect the whole cell. It regulates which substances enter and exit the cell CYTOPLASM: is the inside of the cell. It is a jelly-like substance. Many of the chemical reactions of the cell take place here. Organelles are small structures in the cytopl ...
... CELL MEMBRANE: is a thin layer that surround and protect the whole cell. It regulates which substances enter and exit the cell CYTOPLASM: is the inside of the cell. It is a jelly-like substance. Many of the chemical reactions of the cell take place here. Organelles are small structures in the cytopl ...
What is Life? - bms8thgradescience
... What characteristics must something have to be considered alive? 1. Cellular organization 2. Common chemical makeup 3. Use Energy 4. Grow and Develop (Repair, Maintain, ...
... What characteristics must something have to be considered alive? 1. Cellular organization 2. Common chemical makeup 3. Use Energy 4. Grow and Develop (Repair, Maintain, ...
Cells and Tissues
... • Basic units of structure and function • Humans are made of trillions of cells and there are hundreds of different types. ...
... • Basic units of structure and function • Humans are made of trillions of cells and there are hundreds of different types. ...
Classification
... They are then broken down into smaller groups, then smaller groups, then smaller and so on until there is just one… ____________ is the most specific group… ...
... They are then broken down into smaller groups, then smaller groups, then smaller and so on until there is just one… ____________ is the most specific group… ...
Biology Frameworks
... Central Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, and S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary f ...
... Central Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, and S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary f ...
PASS study guide 2 - Cells_ Genetics_ Human Body
... Used determine the possibilities of the combinations of alleles that the offspring may receive; tool used to predict the ratio or percentage of the possible genes that an offspring will have based on the genes of the parent; alleles for one parent are placed at the top and the alleles of the other p ...
... Used determine the possibilities of the combinations of alleles that the offspring may receive; tool used to predict the ratio or percentage of the possible genes that an offspring will have based on the genes of the parent; alleles for one parent are placed at the top and the alleles of the other p ...
eoct review
... – Descent w/modificationorganisms come from a common ancestor – Natural Selection • All organisms produce more offspring than can survive. • All offspring are genetically varied (may not always be obvious based on phenotype) • Variations in genes enable some offspring to outcompete others • Those wi ...
... – Descent w/modificationorganisms come from a common ancestor – Natural Selection • All organisms produce more offspring than can survive. • All offspring are genetically varied (may not always be obvious based on phenotype) • Variations in genes enable some offspring to outcompete others • Those wi ...
BIOLOGY EOCT REVIEW
... – Descent w/modificationorganisms come from a common ancestor – Natural Selection • All organisms produce more offspring than can survive. • All offspring are genetically varied (may not always be obvious based on phenotype) • Variations in genes enable some offspring to outcompete others • Those wi ...
... – Descent w/modificationorganisms come from a common ancestor – Natural Selection • All organisms produce more offspring than can survive. • All offspring are genetically varied (may not always be obvious based on phenotype) • Variations in genes enable some offspring to outcompete others • Those wi ...
E. coli - Marcotte Lab
... - artemisin (current best anti-malarial drug) - ethanol, other bio-fuels 2 make new model systems 3 intervene in biological systems to figure out how they work, for example rearrange the genes in a bacterial operon 4 understand the limitations of evolution and perhaps augment biology with additional ...
... - artemisin (current best anti-malarial drug) - ethanol, other bio-fuels 2 make new model systems 3 intervene in biological systems to figure out how they work, for example rearrange the genes in a bacterial operon 4 understand the limitations of evolution and perhaps augment biology with additional ...
Prokaryotic cells, Eukaryotic cells and viruses differ
... Structure and function of cell membranes Roles of Golgi and ER in the production and secretion of proteins ...
... Structure and function of cell membranes Roles of Golgi and ER in the production and secretion of proteins ...
The paradox of model organisms
... cellular processes once their biology is well understood Animal rights activists have seized on this argument, but show little interest in appreciating the huge contribution that model organisms have made to molecular biology. Indeed, it is not an exaggeration to say that research on animals has tau ...
... cellular processes once their biology is well understood Animal rights activists have seized on this argument, but show little interest in appreciating the huge contribution that model organisms have made to molecular biology. Indeed, it is not an exaggeration to say that research on animals has tau ...
Multicellular organisms meet their needs in different ways.
... increases the chance of an organism’s surviving and producing offspring that also reproduce. An adaptation may have to do with the way an organism gets its energy or processes materials. An adaptation may relate to the shape or structure of an organism’s body. An adaptation can even be a form of beh ...
... increases the chance of an organism’s surviving and producing offspring that also reproduce. An adaptation may have to do with the way an organism gets its energy or processes materials. An adaptation may relate to the shape or structure of an organism’s body. An adaptation can even be a form of beh ...
Cells - Images
... S7L2. Students will describe the structure and function of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. a. Explain that cells take in nutrients in order to grow and divide and to make needed materials. b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic ...
... S7L2. Students will describe the structure and function of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. a. Explain that cells take in nutrients in order to grow and divide and to make needed materials. b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic ...
Levels of Organization
... The cornerstone of modern biology is evolutionary theory For example, it predicts and explains… ...
... The cornerstone of modern biology is evolutionary theory For example, it predicts and explains… ...
Year 8 Praising stars 2 revision Electrical circuits
... In order to survive in a habitat, organisms need various resources. An animal needs food, water, oxygen, shelter and it needs to find a mate to reproduce. Plants need light, water and carbon dioxide in order to make food. They also need mineral salts (nutrients), oxygen and space to grow. ...
... In order to survive in a habitat, organisms need various resources. An animal needs food, water, oxygen, shelter and it needs to find a mate to reproduce. Plants need light, water and carbon dioxide in order to make food. They also need mineral salts (nutrients), oxygen and space to grow. ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.