Principals of General Zoology (Zoo-103)
... Homeostasis: is a term describe the physical and chemical parameters that an organism must maintain to allow proper functioning of its component cells, tissues, organs, and systems. Enzymes work best when a certain range of temperature and pH, that cells must maintain a balance between having to ...
... Homeostasis: is a term describe the physical and chemical parameters that an organism must maintain to allow proper functioning of its component cells, tissues, organs, and systems. Enzymes work best when a certain range of temperature and pH, that cells must maintain a balance between having to ...
File
... - Unicellular – organism that exists as a singular, independent cell - Multicellular – organism that exists as specialized groups of cells; cells are organized into tissues that perform the same function; tissues form organs and organs make up an organ system - Prokaryote – has nuclear material in t ...
... - Unicellular – organism that exists as a singular, independent cell - Multicellular – organism that exists as specialized groups of cells; cells are organized into tissues that perform the same function; tissues form organs and organs make up an organ system - Prokaryote – has nuclear material in t ...
DNA viruses: herpes simplex virus
... Humulin was the first medication produced using modern genetic engineering techniques in which actual human DNA is inserted into a host cell. The host cells are then allowed to grow and reproduce normally, and due to the inserted human DNA, they produce a synthetic version of human insulin. Humulin ...
... Humulin was the first medication produced using modern genetic engineering techniques in which actual human DNA is inserted into a host cell. The host cells are then allowed to grow and reproduce normally, and due to the inserted human DNA, they produce a synthetic version of human insulin. Humulin ...
... Humulin was the first medication produced using modern genetic engineering techniques in which actual human DNA is inserted into a host cell. The host cells are then allowed to grow and reproduce normally, and due to the inserted human DNA, they produce a synthetic version of human insulin. Humulin ...
Biology EOC review
... - Unicellular – organism that exists as a singular, independent cell - Multicellular – organism that exists as specialized groups of cells; cells are organized into tissues that perform the same function; tissues form organs and organs make up an organ system - Prokaryote – has nuclear material in t ...
... - Unicellular – organism that exists as a singular, independent cell - Multicellular – organism that exists as specialized groups of cells; cells are organized into tissues that perform the same function; tissues form organs and organs make up an organ system - Prokaryote – has nuclear material in t ...
Organization of Regulation of the Human Body I. Organization of Life
... Above 112 F is lethal. Enzymes DENATURE (change their shape) E. Atmospheric Pressure - for proper absorption of oxygen ...
... Above 112 F is lethal. Enzymes DENATURE (change their shape) E. Atmospheric Pressure - for proper absorption of oxygen ...
P4A1 INVESTIGATOR Name James Priess Address Fred
... Nance, J., Munro, E.M., and Priess, J.R. (2003). C. elegans PAR-3 and PAR-6 are required for apicobasal asymmetries associated with cell adhesion and gastrulation. Development 130, 5339-5350. Harrell, J.R., and Goldstein, B. (2011). Internalization of multiple cells during C. elegans gastrulation de ...
... Nance, J., Munro, E.M., and Priess, J.R. (2003). C. elegans PAR-3 and PAR-6 are required for apicobasal asymmetries associated with cell adhesion and gastrulation. Development 130, 5339-5350. Harrell, J.R., and Goldstein, B. (2011). Internalization of multiple cells during C. elegans gastrulation de ...
Online Onion Root Tips
... http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/cell_cycle.html ...
... http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/cell_cycle.html ...
EOCT REVIEW
... a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. b.Explain how enzymes function as catalysts. c. Identify the function of the four major macromolecules (i.e., carbohydrates, proteins, lipi ...
... a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. b.Explain how enzymes function as catalysts. c. Identify the function of the four major macromolecules (i.e., carbohydrates, proteins, lipi ...
Cell Membrane
... XX = female XY = male Sex linked traits are traits that are carried on the X chromosome. Therefore, it is easier for a male to express a recessive sex linked trait because if he inherits one gene from his mother than he will show the trait. Ex- XHXh = carrier female of hemophilia Xh Y = male with th ...
... XX = female XY = male Sex linked traits are traits that are carried on the X chromosome. Therefore, it is easier for a male to express a recessive sex linked trait because if he inherits one gene from his mother than he will show the trait. Ex- XHXh = carrier female of hemophilia Xh Y = male with th ...
Ch. 3 Cells
... ► Interphase- is a period of cell growth and new molecules are synthesized ► S phase- DNA of cell is replicated to prepare for cell division ► G1 & G2 phases- cell grows and other structures are duplicated ...
... ► Interphase- is a period of cell growth and new molecules are synthesized ► S phase- DNA of cell is replicated to prepare for cell division ► G1 & G2 phases- cell grows and other structures are duplicated ...
Why don`t we learn these…
... Tiny air sacs, located at both ends of the lungs, through which gases are exchanged with the blood? ...
... Tiny air sacs, located at both ends of the lungs, through which gases are exchanged with the blood? ...
Classifying Living Organisms
... 5. Why are the bat and the bird not classified as the same species? 6. Scientists have identified more than ___________ different types of living things. Will this be all the organisms that are discovered? Why or why not? ...
... 5. Why are the bat and the bird not classified as the same species? 6. Scientists have identified more than ___________ different types of living things. Will this be all the organisms that are discovered? Why or why not? ...
Tissues and organs continued
... Cells specialize by suppressing some of their genes and activating others. A zygote must contain all the information necessary for an organism to be created. This information is passed on by differentiation and put to use during specialization. ...
... Cells specialize by suppressing some of their genes and activating others. A zygote must contain all the information necessary for an organism to be created. This information is passed on by differentiation and put to use during specialization. ...
Recognize and apply the definition of diffusion
... Compare sexual and asexual reproduction Asexual: is the ability for an organism to reproduce itself w/out egg or ...
... Compare sexual and asexual reproduction Asexual: is the ability for an organism to reproduce itself w/out egg or ...
Biology Week 1
... evolving different traits but hat the basic plan or a creatures beginning remains the same. FOSSILS: Are important for estimating when various lineages developed in geologic time. As fossilization is an uncommon occurrence. Usually requiring hard body parts and death near a site where sediments are ...
... evolving different traits but hat the basic plan or a creatures beginning remains the same. FOSSILS: Are important for estimating when various lineages developed in geologic time. As fossilization is an uncommon occurrence. Usually requiring hard body parts and death near a site where sediments are ...
GCSE Cells Topic Learning Checklist
... Recall that stem cells from human embryos and adult bone marrow can be cloned and made to ...
... Recall that stem cells from human embryos and adult bone marrow can be cloned and made to ...
Chapter 1 Biology: The Study of Life
... to continue to exist, reproduction must occur. Reproduction can be asexual or sexual. ...
... to continue to exist, reproduction must occur. Reproduction can be asexual or sexual. ...
Chapter 1 Biology: The Study of Life
... to continue to exist, reproduction must occur. Reproduction can be asexual or sexual. ...
... to continue to exist, reproduction must occur. Reproduction can be asexual or sexual. ...
BIO 1101 - Makerere University Courses
... SEMESTER WHEN OFFERED: Semester One of Year One VENUE: DOSATE Biology Laboratory COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed to acquaint biology student-teachers with knowledge about the cell theory and origin of life. It also describes the functions, structures and division processes of biological c ...
... SEMESTER WHEN OFFERED: Semester One of Year One VENUE: DOSATE Biology Laboratory COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed to acquaint biology student-teachers with knowledge about the cell theory and origin of life. It also describes the functions, structures and division processes of biological c ...
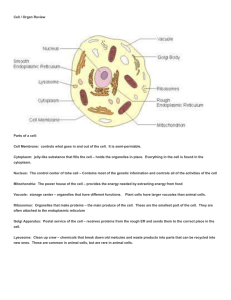
Cell / Organ Review Parts of a cell: Cell Membrane: controls what
... Mitochondria: The power house of the cell – provides the energy needed by extracting energy from food Vacuole: storage center – organelles that have different functions. ...
... Mitochondria: The power house of the cell – provides the energy needed by extracting energy from food Vacuole: storage center – organelles that have different functions. ...
right here - TeacherWeb
... Spontaneous Generation – mistaken idea that life can arise from nonliving materials; sometimes called Abiogenesis - Francesco Redi performed controlled experiments that tested spontaneous generation of maggots from decaying meat – disproved idea. - Louis Pasteur performed controlled experiments that ...
... Spontaneous Generation – mistaken idea that life can arise from nonliving materials; sometimes called Abiogenesis - Francesco Redi performed controlled experiments that tested spontaneous generation of maggots from decaying meat – disproved idea. - Louis Pasteur performed controlled experiments that ...
Review Facts for the Biology SOL
... Mendel's laws of heredity are based on his mathematical analysis of observations of patterns of inheritance of traits. The laws of probability govern simple genetic recombinations. Genotype describes the genetic make-up of an organism and phenotype describes the organism's appearance based on ...
... Mendel's laws of heredity are based on his mathematical analysis of observations of patterns of inheritance of traits. The laws of probability govern simple genetic recombinations. Genotype describes the genetic make-up of an organism and phenotype describes the organism's appearance based on ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.