4th Grade Science CRT Study Guide
... 2. Birds move as a group from one region to another and back again. When “birds fly south for the winter,” this is an example of an animal behavior known as __________________. 3. During the life cycle of a frog, at first a tadpole looks very different from the adult frog but soon changes and begins ...
... 2. Birds move as a group from one region to another and back again. When “birds fly south for the winter,” this is an example of an animal behavior known as __________________. 3. During the life cycle of a frog, at first a tadpole looks very different from the adult frog but soon changes and begins ...
Topic 1 - Manhasset Public Schools
... 8. The ability to grow in size is a characteristic of living organisms. Although an icicle may grow in size over time, it is considered nonliving because there is ...
... 8. The ability to grow in size is a characteristic of living organisms. Although an icicle may grow in size over time, it is considered nonliving because there is ...
Do not write on this paper
... 5. Which of the following work together to form tissues? A organs B organ systems C cells 1. Every living thing is made from a tiny building D muscles block called a(n) ___ . 2. Leaves make food through the process of __. 3. An amoeba, a giant squid, and an oak tree can each be described as a(n) ___ ...
... 5. Which of the following work together to form tissues? A organs B organ systems C cells 1. Every living thing is made from a tiny building D muscles block called a(n) ___ . 2. Leaves make food through the process of __. 3. An amoeba, a giant squid, and an oak tree can each be described as a(n) ___ ...
Biology Spring Review
... _________ Those individuals with unfavorable traits will be less likely to survive and reproduce- meaning they have a low fitness. 15. Bright coloration makes an organism easier to spot as prey. You would think this would be a disadvantage. What is the advantage of bright coloration in males of some ...
... _________ Those individuals with unfavorable traits will be less likely to survive and reproduce- meaning they have a low fitness. 15. Bright coloration makes an organism easier to spot as prey. You would think this would be a disadvantage. What is the advantage of bright coloration in males of some ...
Page 1
... Above right-cellular respiration-occurs in both plants AND animals; the mitochondria changes food into energy; food and oxygen combine to make energy, water, and carbon dioxide ( the water and carbon dioxide are waste products ) LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION IN AN ORGANISM: Order of least to most complex ( ...
... Above right-cellular respiration-occurs in both plants AND animals; the mitochondria changes food into energy; food and oxygen combine to make energy, water, and carbon dioxide ( the water and carbon dioxide are waste products ) LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION IN AN ORGANISM: Order of least to most complex ( ...
What`s in a Cell?
... could get it inside of a beach ball. That’s kind of what the ER is. Instead of newspaper…it’s a network of membranes. Substances like nutrients and wastes move along the surface to get from one place to another within a cell. There’s smooth ER and rough ER. The rough ER has ribosomes stuck in it. Ho ...
... could get it inside of a beach ball. That’s kind of what the ER is. Instead of newspaper…it’s a network of membranes. Substances like nutrients and wastes move along the surface to get from one place to another within a cell. There’s smooth ER and rough ER. The rough ER has ribosomes stuck in it. Ho ...
Study Guide for Science Unit 4
... They will not “wake up” during hibernation but get energy from the body fat stored on their bodies. *Natural events and living things can cause changes in an ecosystem. -Natural events-volcanoes, hurricanes, earthquakes -Living things-a new organism, over population of an organism, or when an organi ...
... They will not “wake up” during hibernation but get energy from the body fat stored on their bodies. *Natural events and living things can cause changes in an ecosystem. -Natural events-volcanoes, hurricanes, earthquakes -Living things-a new organism, over population of an organism, or when an organi ...
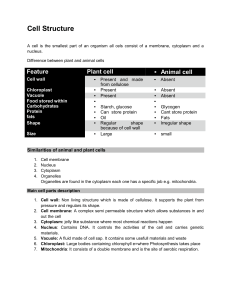
Cell Test 1 – Review Sheet
... 4) Explain the function(s) of the following organelles: (Be sure you can identify these in a picture!) a. Nucleus- directs all of the cell’s activities b. Mitochondria – the “powerhouses” of the cell that convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions c. Cell ...
... 4) Explain the function(s) of the following organelles: (Be sure you can identify these in a picture!) a. Nucleus- directs all of the cell’s activities b. Mitochondria – the “powerhouses” of the cell that convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions c. Cell ...
Cell Unit Test Study Guide
... 4. What is heredity? a. The passing of traits from one generation to the next 5. What is homeostasis? a. The maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment Chapter 3 1. What are the 3 parts of the cell theory? a. All organisms are made of one or more cells. b. The cell is the bas ...
... 4. What is heredity? a. The passing of traits from one generation to the next 5. What is homeostasis? a. The maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment Chapter 3 1. What are the 3 parts of the cell theory? a. All organisms are made of one or more cells. b. The cell is the bas ...
CHAP NUM="1" ID="CH
... fruit fly cell. Systems biologists develop such models from huge databases of information about molecules and their interactions in the cell. A major goal of this systems approach is to use the models to predict how one change, such as an increase in the activity of a particular protein, can ripple ...
... fruit fly cell. Systems biologists develop such models from huge databases of information about molecules and their interactions in the cell. A major goal of this systems approach is to use the models to predict how one change, such as an increase in the activity of a particular protein, can ripple ...
Bio01 Intro
... Regulation involves altering the rate of processes. The process of maintaining a constant internal environment is called homeostasis. ...
... Regulation involves altering the rate of processes. The process of maintaining a constant internal environment is called homeostasis. ...
Benchmarks by Topic - maineindianeducation
... C. The Scientific and Technological Enterprise: Students understand the history and nature of scientific knowledge and technology, the process of inquiry and technological design, and the impacts science and technology have on society and the environment. C1. Understandings of Inquiry Students descr ...
... C. The Scientific and Technological Enterprise: Students understand the history and nature of scientific knowledge and technology, the process of inquiry and technological design, and the impacts science and technology have on society and the environment. C1. Understandings of Inquiry Students descr ...
Water Cycle
... 34. How are non-vascular plants different from vascular plants? Xylem/phloem in vascular plants 35. How are gymnosperms different from angiosperms? Gymnosperms = naked seeds in cones, needle like leaves; Angiosperm = flowering and seeds are in fruits, blade-like leaves 36. Where are the sugars made ...
... 34. How are non-vascular plants different from vascular plants? Xylem/phloem in vascular plants 35. How are gymnosperms different from angiosperms? Gymnosperms = naked seeds in cones, needle like leaves; Angiosperm = flowering and seeds are in fruits, blade-like leaves 36. Where are the sugars made ...
Category 4
... Use the equation to answer the questions that follow: 3. What are the reactants of photosynthesis? _______________________________________________ 4. What are the products of photosynthesis? ________________________________________________ 5. What is missing from the equation above that must be pr ...
... Use the equation to answer the questions that follow: 3. What are the reactants of photosynthesis? _______________________________________________ 4. What are the products of photosynthesis? ________________________________________________ 5. What is missing from the equation above that must be pr ...
Keystone Biology Practice Questions copy.pages
... B. Translocation can cause duplication of certain sections of chromosomes.! C. Translocation can cause the exchange of genetic material between homologous! chromosomes.! D. Translocation can result in the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during! meiosis.! 38. Scientists have been able t ...
... B. Translocation can cause duplication of certain sections of chromosomes.! C. Translocation can cause the exchange of genetic material between homologous! chromosomes.! D. Translocation can result in the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during! meiosis.! 38. Scientists have been able t ...
I. INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY (pg. 16)
... *Some organisms obtain energy directly from the __________ and use it to make its own food, this process is called _______________________. ______________, some bacteria & protists use this process. *Other organisms have to obtain their energy fro the food they eat like, humans, other animals, and f ...
... *Some organisms obtain energy directly from the __________ and use it to make its own food, this process is called _______________________. ______________, some bacteria & protists use this process. *Other organisms have to obtain their energy fro the food they eat like, humans, other animals, and f ...
I have put together a recommendation for teacher assignments
... closely at genes. What is a gene? Genes are really packages of information that tell a cell how to make proteins. Proteins are polymers, or long chains, of amino acids. As you learned already, there are 20 different types of amino acids. The order in which the amino acids are joined determines which ...
... closely at genes. What is a gene? Genes are really packages of information that tell a cell how to make proteins. Proteins are polymers, or long chains, of amino acids. As you learned already, there are 20 different types of amino acids. The order in which the amino acids are joined determines which ...
Unit 03 - fixurscore
... Specialization of cells 1-4 (plants) 5-9 (animal) 1. Root hair cell: It has long hairs to increase surface area of the cell. It has a large number of mitochondria to provide energy for active up take. 2. Xylem vessels: It transports water and minerals to the plant. The xylem cells are dead and are ...
... Specialization of cells 1-4 (plants) 5-9 (animal) 1. Root hair cell: It has long hairs to increase surface area of the cell. It has a large number of mitochondria to provide energy for active up take. 2. Xylem vessels: It transports water and minerals to the plant. The xylem cells are dead and are ...
GHSGT BIOLOGY REVIEW
... 1809. This theory said that organisms changed to meet the needs of their environment such as a giraffe’s neck stretching as it reached to get food. He said that these useful characteristics would be passed on to the next generation. He also said that traits not used would “waste away” This theory ha ...
... 1809. This theory said that organisms changed to meet the needs of their environment such as a giraffe’s neck stretching as it reached to get food. He said that these useful characteristics would be passed on to the next generation. He also said that traits not used would “waste away” This theory ha ...
Name: Period:______ Date:_____ Biology Spring Final 2016 The
... c. Body parts d. All of the above ...
... c. Body parts d. All of the above ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.