* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Animals
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Regional differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
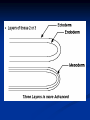
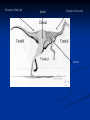
Introduction to Animals Heterotrophs 2. Multicellular 3. Most are Mobile 4. Most reproduce sexually/ few can asexually reproduce 5. No cell wall 6. Most (except sponges) have tissues. These are groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function. Ex: nerve tissue sends/receives signals 7. Formation of a Blastula (except sponges): a zygote that has gone through cell division until a ball of cells is formed. This ball of cells (blastula) keeps dividing until 3 distinct layers form. These layers will form into tissues and organs in the adult body. a. ectoderm: outer-layer- outer layer of skin, nervous system, sense organs b. endoderm: inner-layer- lining of digestive tract, respiratory system, urinary bladder, digestive organs such as liver, and many other glands. c. Mesoderm: Separates inner and outer layer- Most of the skeleton, muslcles, circulatory system, reproductive organs, and excretory organs. 8. atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism 1. Body Symmetry A. Three types of symmetry: body shape 1. Asymetrical: no specific shape/irregular (Sponges, coral) 2. Radial symmetry: body parts are arranged around a central axis, like spokes around a bicycle wheel. (Phylums Cnidarian, Echinodermata) These organisms resemble a pie where several cutting planes produce roughly identical pieces. An organism with radial symmetry exhibits no left or right sides. 3. Bilateral symmetry a. Have distinct right and left halves. A plane passing through the animal’s midline divides the animal into mirror image halves. The elaborate patterns on the wings of butterflies are one example of biological symmetry. Dissection/Position Terms Dorsal: The back of an organism Ventral: Stomach area Medial: middle Lateral: Side Anterior: Towards the head Posterior: Towards the back end or rear end area Caudal: tail Cranial: Head Posterior: hind end Medial Anterior: front end Lateral