CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY
... Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. ...
... Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. ...
multicellular organisms
... In vascular plants, transport of water and mineral nutrients from the roots occurs via xylem involving root pressure, capillary action transpiration (adhesion and cohesion of water molecules); transport of the products of photosynthesis and some mineral nutrients occurs by translocation in the phloe ...
... In vascular plants, transport of water and mineral nutrients from the roots occurs via xylem involving root pressure, capillary action transpiration (adhesion and cohesion of water molecules); transport of the products of photosynthesis and some mineral nutrients occurs by translocation in the phloe ...
Transport Across Cell Membranes
... conditions change – Homes – furnace, a/c – Cells – membrane transport – Organisms – have systems that help maintain relatively constant conditions inside the organism • Examples? ...
... conditions change – Homes – furnace, a/c – Cells – membrane transport – Organisms – have systems that help maintain relatively constant conditions inside the organism • Examples? ...
here - Perspectives in Environmental and Systems Biology
... Phoshotransfer networks as communication modalité in cellular energetics and metabolic signaling Prof. Petras Dzeja (Rochester) ...
... Phoshotransfer networks as communication modalité in cellular energetics and metabolic signaling Prof. Petras Dzeja (Rochester) ...
Variety of Life - Madras College
... was called Penicillium notatum. • The substance killing the bacteria was penicillin. ...
... was called Penicillium notatum. • The substance killing the bacteria was penicillin. ...
Human Herpes Virus 8
... and genital warts caused by infection with the HPV types 6, 11, 16 or 18 in women between the ages of 16 and 26. ...
... and genital warts caused by infection with the HPV types 6, 11, 16 or 18 in women between the ages of 16 and 26. ...
In Action 82
... A cell is the basic unit of life, because their individual cells carry out all the functions carried out by living things. Two scientists (Matthias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann) who studied cells combined their observations to make a hypothesis … all living things are made up of cells. Rudolf Virc ...
... A cell is the basic unit of life, because their individual cells carry out all the functions carried out by living things. Two scientists (Matthias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann) who studied cells combined their observations to make a hypothesis … all living things are made up of cells. Rudolf Virc ...
In a garden bed of tomato plants, some plants were observed
... Store, modify and package casein into vesicles for transport from the cell. (1) ...
... Store, modify and package casein into vesicles for transport from the cell. (1) ...
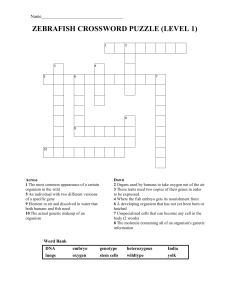
Zebrafish Crossword Puzzles
... 1 Tool used to pull small things out of water 4 Surrounds and protects the fish embryo 7 An individual with two identical copies of the same gene 12 How we test our ideas in science 14 Pumps blood through the body 15 The study of biological inheritance of traits 16 The most common appearance of a ce ...
... 1 Tool used to pull small things out of water 4 Surrounds and protects the fish embryo 7 An individual with two identical copies of the same gene 12 How we test our ideas in science 14 Pumps blood through the body 15 The study of biological inheritance of traits 16 The most common appearance of a ce ...
name: period - Spring Branch ISD
... functions. Compare the shape of the neuron and red blood cells in figure 1.1 on page 816. How the shape of the red blood cell and neuron (nerve cell) fit its function, specifically? 2. In terms of DNA, in what way are all of the cells in the body alike? What accounts for the differences in these two ...
... functions. Compare the shape of the neuron and red blood cells in figure 1.1 on page 816. How the shape of the red blood cell and neuron (nerve cell) fit its function, specifically? 2. In terms of DNA, in what way are all of the cells in the body alike? What accounts for the differences in these two ...
Skeletal System(Bones), Muscular System (Muscles), and
... relay electrical signals through the body. The nervous system directs behavior and movement and, along with the ...
... relay electrical signals through the body. The nervous system directs behavior and movement and, along with the ...
Chapter 24 guided notes the origin of species answers
... discussed in Chapter. ORIGIN OF SPECIES ———— DARWIN. LONDON. JOHN MURRAY. [front cover] [inside front cover] THE ORIGIN OF SPECIES. [page ii] ~~~~~ "But with regard to the. Creationism is the religious belief that the universe and life originated "from specific acts of divine creation," as opposed t ...
... discussed in Chapter. ORIGIN OF SPECIES ———— DARWIN. LONDON. JOHN MURRAY. [front cover] [inside front cover] THE ORIGIN OF SPECIES. [page ii] ~~~~~ "But with regard to the. Creationism is the religious belief that the universe and life originated "from specific acts of divine creation," as opposed t ...
Bio-Assess
... Game Instructions: The following instructions are based on using one set of cards for every 6 people. Each deck (white, yellow, blue) represents a stream sampling site. If more those 6 people per set are playing, divide players evenly among the sets. 1. Each group uses one deck of bioassessment card ...
... Game Instructions: The following instructions are based on using one set of cards for every 6 people. Each deck (white, yellow, blue) represents a stream sampling site. If more those 6 people per set are playing, divide players evenly among the sets. 1. Each group uses one deck of bioassessment card ...
Chapter 24 guided notes the origin of species answers
... Creationism is the religious belief that the universe and life originated "from specific acts of divine creation," as opposed to the scientific conclusion that they. CHAPTER I. THE PERIOD BEFORE THE LAW. The following two positions will be admitted without question, it is believed, by all Christians ...
... Creationism is the religious belief that the universe and life originated "from specific acts of divine creation," as opposed to the scientific conclusion that they. CHAPTER I. THE PERIOD BEFORE THE LAW. The following two positions will be admitted without question, it is believed, by all Christians ...
Bio 405 – Ecology – Fall 2002
... If your final total across all grading components is less than or equal to one point below a higher grade, rounding up to the higher grade will occur if two of the three tests scored at the higher grade. For example, if your test scores were 84, 91, and 92 with a total of 267 (a B with 270 needed to ...
... If your final total across all grading components is less than or equal to one point below a higher grade, rounding up to the higher grade will occur if two of the three tests scored at the higher grade. For example, if your test scores were 84, 91, and 92 with a total of 267 (a B with 270 needed to ...
Big Picture
... Match the body system in the first column with the correct function in the second column: 1. respiratory system 2. muscular system 3. digestive system 4. circulatory system 5. endocrine system ...
... Match the body system in the first column with the correct function in the second column: 1. respiratory system 2. muscular system 3. digestive system 4. circulatory system 5. endocrine system ...
Jack Bowers` Chapter 2 Biology Notes
... Fertilization: Fusion of an egg and sperm cell Mendel: Scientist who studied pea plants and provided the basis of modern genetics Homologous chromosomes: Chromosomes that have the same length, appearance, and copies of genes, although the alleles may differ Crossing Over: Exchange of chromosome segm ...
... Fertilization: Fusion of an egg and sperm cell Mendel: Scientist who studied pea plants and provided the basis of modern genetics Homologous chromosomes: Chromosomes that have the same length, appearance, and copies of genes, although the alleles may differ Crossing Over: Exchange of chromosome segm ...
2014 Biology STAAR EOC Review
... Regulate transport in & out of cell (selectively permeable- only lets some things in and out of the cell; specifically, small molecules and larger hydrophobic molecules move through easily. e.g. O 2, CO2, H2O. Ions, hydrophilic molecules larger than water, and large molecules such as proteins do not ...
... Regulate transport in & out of cell (selectively permeable- only lets some things in and out of the cell; specifically, small molecules and larger hydrophobic molecules move through easily. e.g. O 2, CO2, H2O. Ions, hydrophilic molecules larger than water, and large molecules such as proteins do not ...
NGSS Levels of Organization
... Learning Goals! 1. Describe and sequence the 5 levels of biological organization. ! 2. What must happen in the body to maintain homeostasis? Give an example of this.! 3. Describe the outcome of the two types of feedback, and give an example for each.! ...
... Learning Goals! 1. Describe and sequence the 5 levels of biological organization. ! 2. What must happen in the body to maintain homeostasis? Give an example of this.! 3. Describe the outcome of the two types of feedback, and give an example for each.! ...
BI 215 - Butler Community College
... New Spring 2016 Implement Fall 2016 Textbook Update Fall 2016 ...
... New Spring 2016 Implement Fall 2016 Textbook Update Fall 2016 ...
key
... 1 Define anatomy. Anatomy is the study of structure and structural relationships of the body and / or its parts. 2 Define cellular anatomy. Cellular anatomy is the study of the structure of the cell. 3 Define cytology. Cytology is the study of the structure, function, pathology, life cycles, and lif ...
... 1 Define anatomy. Anatomy is the study of structure and structural relationships of the body and / or its parts. 2 Define cellular anatomy. Cellular anatomy is the study of the structure of the cell. 3 Define cytology. Cytology is the study of the structure, function, pathology, life cycles, and lif ...
Human Body Systems Graphic Organizer
... 1. How do the different components of the body work together to enable humans to survive and interact with their environment? ...
... 1. How do the different components of the body work together to enable humans to survive and interact with their environment? ...
The Cell
... nucleolus produces rRNA this rRNA isjoined with proteins at the nucleolus to form the subunits of ribosomes Explain the following three phrases. (6 marks: 2 marks each) a) Many different proteins can be constructed from just a few amino acids. Only 20 amino acids exist but attraction and bonding ...
... nucleolus produces rRNA this rRNA isjoined with proteins at the nucleolus to form the subunits of ribosomes Explain the following three phrases. (6 marks: 2 marks each) a) Many different proteins can be constructed from just a few amino acids. Only 20 amino acids exist but attraction and bonding ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.