UNIT 1
... UNIT 1 - LIFE True or false: - Amoebas have a nucleus and a cytoplasm. - Bacteria have a cell membrane and a nucleus. - Bacteria have a cell wall. - Bacteria have mitochondria. - Amoebas and bacteria are one-celled organisms. - Plant cells have a cell wall. - Animal cells have chloroplasts. - Plant ...
... UNIT 1 - LIFE True or false: - Amoebas have a nucleus and a cytoplasm. - Bacteria have a cell membrane and a nucleus. - Bacteria have a cell wall. - Bacteria have mitochondria. - Amoebas and bacteria are one-celled organisms. - Plant cells have a cell wall. - Animal cells have chloroplasts. - Plant ...
C: CHON F: C: energy Store,Supply,Structure P: Structural
... pushed apart by H bonds. Cools density increases until 4˚c then density lowers ice forms on surface, insulates below, organism survive winter, don’t freeze, allows H2O to circulate cohesive-sticks to each other creates high surface tension charged will dissolve, - & + charges interact with H2O, H2O ...
... pushed apart by H bonds. Cools density increases until 4˚c then density lowers ice forms on surface, insulates below, organism survive winter, don’t freeze, allows H2O to circulate cohesive-sticks to each other creates high surface tension charged will dissolve, - & + charges interact with H2O, H2O ...
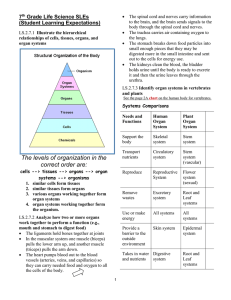
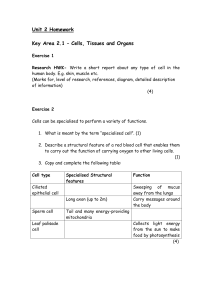
Tissues, Organs, Systems Review Answers
... become flaccid and close together. 18. Why do muscle cells need more mitochondria than skin cells? Muscle cells require a lot of energy for contraction and movement. While a skin cell still requires mitochondria for cellular respiration (converting glucose to useable ATP energy), they do not require ...
... become flaccid and close together. 18. Why do muscle cells need more mitochondria than skin cells? Muscle cells require a lot of energy for contraction and movement. While a skin cell still requires mitochondria for cellular respiration (converting glucose to useable ATP energy), they do not require ...
Evolution: Exhibition Notes 2
... cell, and the cell is without internal structures. Cells of this type, called prokaryotes, are represented by bacteria and some other single-celled organisms living at the present day. By 1,700 million years ago other cells had appeared, called eukaryotes. Most of the DNA of eukaryotes is contained ...
... cell, and the cell is without internal structures. Cells of this type, called prokaryotes, are represented by bacteria and some other single-celled organisms living at the present day. By 1,700 million years ago other cells had appeared, called eukaryotes. Most of the DNA of eukaryotes is contained ...
Human Body Systems PPT2013
... A cell is the simplest living thing that can have a "life of its own.“ An organism may be characterized as having different levels of organization built around the cell. ...
... A cell is the simplest living thing that can have a "life of its own.“ An organism may be characterized as having different levels of organization built around the cell. ...
Immunity 2
... higher temperature helps defense inhibits bacterial growth stimulates phagocytosis speeds up repair of tissues causes liver & spleen to store ...
... higher temperature helps defense inhibits bacterial growth stimulates phagocytosis speeds up repair of tissues causes liver & spleen to store ...
Document
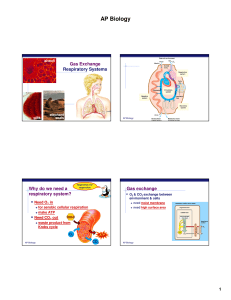
... The stomach breaks down food particles into small enough pieces that they may be digested more in the small intestine and sent out to the cells for energy use. The kidneys clean the blood, the bladder holds urine until the body is ready to excrete it and then the urine leaves through the urethra. ...
... The stomach breaks down food particles into small enough pieces that they may be digested more in the small intestine and sent out to the cells for energy use. The kidneys clean the blood, the bladder holds urine until the body is ready to excrete it and then the urine leaves through the urethra. ...
BIOLOGY CLASS NOTES UNIT 9 Human Body_Body Organization
... Lesson Objectives: Learners will be able to… Identify organs and the system to which they belong. Identify the functions of the various systems of the human body. Explain how cells and tissues are specialized for specific functions. Explain how the different organs within an organ system work toget ...
... Lesson Objectives: Learners will be able to… Identify organs and the system to which they belong. Identify the functions of the various systems of the human body. Explain how cells and tissues are specialized for specific functions. Explain how the different organs within an organ system work toget ...
Marine Biology Final Review Outline
... Upper and lower parts of the intertidal Characteristics used to classify intertidal communities How organisms deal with dessication Adaptations to life on the rocky shore Predominate methods of feeding in each intertidal area Limiting resources Vertical zonation – what is it? What caus ...
... Upper and lower parts of the intertidal Characteristics used to classify intertidal communities How organisms deal with dessication Adaptations to life on the rocky shore Predominate methods of feeding in each intertidal area Limiting resources Vertical zonation – what is it? What caus ...
Science4CE Biology notes
... side of a leaf and packed with chloroplasts, these plant cells are designed for photosynthesis. Red blood cells: contain haemoglobin to absorb and carry oxygen around the body. ...
... side of a leaf and packed with chloroplasts, these plant cells are designed for photosynthesis. Red blood cells: contain haemoglobin to absorb and carry oxygen around the body. ...
AP Biology - TeacherWeb
... moisture maintains cell membrane structure gases diffuse only dissolved in water High surface area? High surface area! Where have we heard that before? ...
... moisture maintains cell membrane structure gases diffuse only dissolved in water High surface area? High surface area! Where have we heard that before? ...
2017 RC 4 Student Notes PPT
... In humans, body temperature is controlled through various feedback mechanisms. On a warm day, physical activity of the muscular and skeletal system causes the endocrine system to signal the integumentary system to perspire until body temperature returns to normal. Animals obtain nutrients and energy ...
... In humans, body temperature is controlled through various feedback mechanisms. On a warm day, physical activity of the muscular and skeletal system causes the endocrine system to signal the integumentary system to perspire until body temperature returns to normal. Animals obtain nutrients and energy ...
KS4 Introducing Biological Classification
... First we will look at the main features of each group, and then show how they are related ...
... First we will look at the main features of each group, and then show how they are related ...
No Slide Title
... Taxonomy The scientific classification of organisms is known as taxonomy. More than 200 years ago Carolus Linnaeus proposed the first classification scheme that divided organisms into two kingdoms, plants and animals. The Linnean system has since developed into a five-kingdom system that is the mos ...
... Taxonomy The scientific classification of organisms is known as taxonomy. More than 200 years ago Carolus Linnaeus proposed the first classification scheme that divided organisms into two kingdoms, plants and animals. The Linnean system has since developed into a five-kingdom system that is the mos ...
Assessment of JiTT on Student Learning
... %Gain (%G) = Percent of class correct on post-test - % of class correct on pre-test Average normalized gain: = % correct on post-test - % correct on pre-test / 100-(%Gain possible)
We used the results from a 20-question pre-class and post-class test, calculating the average normalized gain as
de ...
... %Gain (%G) = Percent of class correct on post-test - % of class correct on pre-test Average normalized gain:
Directions for Use HistoChoice® MB (Molecular Biology) Tissue
... to the increased number of preserved antigenic sites, saving cost on every slide that is processed. HistoChoice® MB provides superior sensitivity, allowing markers to be observed at lower antibody levels. It makes an excellent transport medium and can be safely washed down the drain upon neutralizat ...
... to the increased number of preserved antigenic sites, saving cost on every slide that is processed. HistoChoice® MB provides superior sensitivity, allowing markers to be observed at lower antibody levels. It makes an excellent transport medium and can be safely washed down the drain upon neutralizat ...
Contents - Macmillan Caribbean
... self-contained units of living material, which are enclosed by a barrier of the cell membrane that separates the cell from the surrounding environment. Some organisms, for example the amoeba and bacteria, are unicellular, that is each organism is made of a single cell. However, there are more comple ...
... self-contained units of living material, which are enclosed by a barrier of the cell membrane that separates the cell from the surrounding environment. Some organisms, for example the amoeba and bacteria, are unicellular, that is each organism is made of a single cell. However, there are more comple ...
I. Student misconceptions
... Students often misunderstand the significance of individuals and individual variation to the theory of evolution by natural selection. a. The term adaptation is used to describe changes in an individual over its lifetime (such as physiological adaptation). It is also used to describe changes in trai ...
... Students often misunderstand the significance of individuals and individual variation to the theory of evolution by natural selection. a. The term adaptation is used to describe changes in an individual over its lifetime (such as physiological adaptation). It is also used to describe changes in trai ...
File
... b. Assist in making new cell parts c. Control almost every process in a cell • Organic catalysts – affects the rate or speed of a chemical reaction without itself being changed • Highly specific in its action and can be used over and over again Nucleic Acids • Organic compound containing carbon, oxy ...
... b. Assist in making new cell parts c. Control almost every process in a cell • Organic catalysts – affects the rate or speed of a chemical reaction without itself being changed • Highly specific in its action and can be used over and over again Nucleic Acids • Organic compound containing carbon, oxy ...
Chapter 1
... 2. Eukaryotic are the largest cells, but are still microscopic. They are about 10 times larger than most bacteria cells. -They have a nucleus. -They also have membrane bound organelles. All living things are not bacteria or archaebacteria are made of one or more eukaryotic cells. These organisms are ...
... 2. Eukaryotic are the largest cells, but are still microscopic. They are about 10 times larger than most bacteria cells. -They have a nucleus. -They also have membrane bound organelles. All living things are not bacteria or archaebacteria are made of one or more eukaryotic cells. These organisms are ...
Concept 1: sponges are basal animals that lack true tissues
... They compose of a pseudocoelom, and it transports nutrients through the body (because they lack a circulatory system). They contain 25000 known species and a lot more unknown, one of them is studied carefully and became a model in biological studies such as aging in humans, its called C.elegans. Nem ...
... They compose of a pseudocoelom, and it transports nutrients through the body (because they lack a circulatory system). They contain 25000 known species and a lot more unknown, one of them is studied carefully and became a model in biological studies such as aging in humans, its called C.elegans. Nem ...
Answer Key for Final Exam Practice Problems
... Various tissue types combine to make a structural unit called an organ (e.g. heart, brain, liver, etc.), several organs that collectively perform a similar function are called an organ system (digestive system, respiratory system, etc.). All organ systems functioning cooperatively make up an organis ...
... Various tissue types combine to make a structural unit called an organ (e.g. heart, brain, liver, etc.), several organs that collectively perform a similar function are called an organ system (digestive system, respiratory system, etc.). All organ systems functioning cooperatively make up an organis ...
Biology, High School
... only with nearby cells. 4.8 Recognize that the body’s systems interact to maintain homeostasis. Describe the basic function of a physiological feedback loop. 5. Evolution and Biodiversity Central Concepts: Evolution is the result of genetic changes that occur in constantly changing environments. Ove ...
... only with nearby cells. 4.8 Recognize that the body’s systems interact to maintain homeostasis. Describe the basic function of a physiological feedback loop. 5. Evolution and Biodiversity Central Concepts: Evolution is the result of genetic changes that occur in constantly changing environments. Ove ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.