Chapter 1 Quick Review
... kinetic energy of the particle b. it obeys Newton’s second law c. it obeys Newton’s third law d. its work depends on the end points of every motion, not on the path between e. it is not a frictional force 2. A ball is held at a height H above a floor. It is then released and falls to the floor. If a ...
... kinetic energy of the particle b. it obeys Newton’s second law c. it obeys Newton’s third law d. its work depends on the end points of every motion, not on the path between e. it is not a frictional force 2. A ball is held at a height H above a floor. It is then released and falls to the floor. If a ...
THERMODYNAMICS Ideal Gases. Also for gases we concentrate on
... State variables and conservation of energy. Saying that heat is a form of energy allows to express a more general form of conservation of energy. Even in presence of viscosity the part of energy transformed into heat remains mechanical energy, only it is 'confused', passing at the microscopic level ...
... State variables and conservation of energy. Saying that heat is a form of energy allows to express a more general form of conservation of energy. Even in presence of viscosity the part of energy transformed into heat remains mechanical energy, only it is 'confused', passing at the microscopic level ...
Define electrical energy
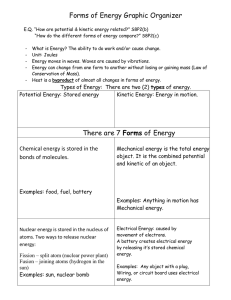
... object has due to position, condition, or chemical composition. -Gravitational potential energy increases as the object’s height increases. ...
... object has due to position, condition, or chemical composition. -Gravitational potential energy increases as the object’s height increases. ...
FE Review Common Pitfalls in Thermodynamics
... 3. Algebra—Simple algebraic mistakes often occur in the solutions to thermodynamics problems. These mistakes unnecessarily lead to a great deal of student frustration that is not related to the thermodynamics theory applied to the problem solution. 4. System sketches—Students often omit sketches of ...
... 3. Algebra—Simple algebraic mistakes often occur in the solutions to thermodynamics problems. These mistakes unnecessarily lead to a great deal of student frustration that is not related to the thermodynamics theory applied to the problem solution. 4. System sketches—Students often omit sketches of ...
BR. HMWK 2012-03-07 11052
... 3. A spring scale calibrate in kg is used to determine the density of a rock specimen. The reading on the spring scale is 0.45 kg when the specimen is suspended in air and 0.36 kg when the specimen is fully submerged in water. If the density of water is 1000 kg/m3, the density of the rock specimen ...
... 3. A spring scale calibrate in kg is used to determine the density of a rock specimen. The reading on the spring scale is 0.45 kg when the specimen is suspended in air and 0.36 kg when the specimen is fully submerged in water. If the density of water is 1000 kg/m3, the density of the rock specimen ...
Study Guide
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? ____________ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? ____________ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _________ ...
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? ____________ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? ____________ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _________ ...
Conservation of Energy 2015
... = KEf - KEi = ½ mvf2 - ½ mvi2 Work = the change in kinetic energy ...
... = KEf - KEi = ½ mvf2 - ½ mvi2 Work = the change in kinetic energy ...
File - Ms. Conger*6th Grade Science
... • If you do not have an iPad please raise your hand so I can give you a notecard. • Once you are logged in please answer the questions at your own pace. ...
... • If you do not have an iPad please raise your hand so I can give you a notecard. • Once you are logged in please answer the questions at your own pace. ...
The angular momentum of particle subject to no torque is conserved.
... Conservative Forces (cont’d) • Potential energy is thus NOT an absolute quantity: it does not have an absolute value. • Likewise, the Kinetic Energy is also NOT an absolute quantity: it depends on the specific rest frame used to measure the velocity. ...
... Conservative Forces (cont’d) • Potential energy is thus NOT an absolute quantity: it does not have an absolute value. • Likewise, the Kinetic Energy is also NOT an absolute quantity: it depends on the specific rest frame used to measure the velocity. ...
Thermodynamics - SeyedAhmad.com
... Thermodynamics is the study of energy relationships that involve heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and heat transfer. Central Heating ...
... Thermodynamics is the study of energy relationships that involve heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and heat transfer. Central Heating ...
Chapter 8 Potential Energy and Conservative Forces
... • Nonconservative forces are path dependent, i.e. the work done by a nonconservative force depends on the precise path followed by an object. That work may be either positive, negative, or zero depending on the force and the path. Nonconservative forces do not store energy. Examples are: friction, t ...
... • Nonconservative forces are path dependent, i.e. the work done by a nonconservative force depends on the precise path followed by an object. That work may be either positive, negative, or zero depending on the force and the path. Nonconservative forces do not store energy. Examples are: friction, t ...
Unit_Phys_2_Forces__Momentum
... m is the mass in kilograms, kg g is the gravitational field strength in newtons per kilogram, N/kg h is the change in height in metres, m Candidates should understand that when an object is raised vertically work is done against gravitational force and the object gains gravitational potential energy ...
... m is the mass in kilograms, kg g is the gravitational field strength in newtons per kilogram, N/kg h is the change in height in metres, m Candidates should understand that when an object is raised vertically work is done against gravitational force and the object gains gravitational potential energy ...