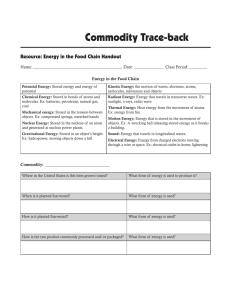
Energy Cont`d - Fulton County Schools
... match is struck against the side of a matchbox and bursts into flames? What causes you to hear something? What kind of energy is sound? ...
... match is struck against the side of a matchbox and bursts into flames? What causes you to hear something? What kind of energy is sound? ...
Heat Energy - Waconia High School
... called atoms. Heat energy is the motion of atoms. The faster the atoms move, the more heat that is produced. Causes a temperature change or phase ...
... called atoms. Heat energy is the motion of atoms. The faster the atoms move, the more heat that is produced. Causes a temperature change or phase ...
…And Energy
... • (ME or E) of an object is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of that object ...
... • (ME or E) of an object is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of that object ...
ME, PE, and KE part 2 - Kleins
... Therefore, the Kinetic energy formula uses both mass and velocity ...
... Therefore, the Kinetic energy formula uses both mass and velocity ...
Test #3 Review
... Open Systems In open systems, matter may flow in and out of the system boundaries. The first law of thermodynamics for open systems states: the increase in the internal energy of a system is equal to the amount of energy added to the system by matter flowing in and by heating, minus the amount lost ...
... Open Systems In open systems, matter may flow in and out of the system boundaries. The first law of thermodynamics for open systems states: the increase in the internal energy of a system is equal to the amount of energy added to the system by matter flowing in and by heating, minus the amount lost ...
Chapter 13
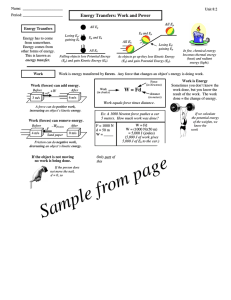
... Work, Power, and Machines • Work is conducted only when an applied ( net ) force results in the change in position of an object • Work is measured in Joules ( J ) ...
... Work, Power, and Machines • Work is conducted only when an applied ( net ) force results in the change in position of an object • Work is measured in Joules ( J ) ...
Class notes on Work Potential Energy and
... Work is scalar and can be positive or negative. Work is measured in newton meters or joules. Energy is the capacity for doing work, which is inherent to an object or physical system. Energy is measured in joules and can neither be created nor destroyed, but is always conserved through a given system ...
... Work is scalar and can be positive or negative. Work is measured in newton meters or joules. Energy is the capacity for doing work, which is inherent to an object or physical system. Energy is measured in joules and can neither be created nor destroyed, but is always conserved through a given system ...
Unit 6 Mechanical Principles and Applications
... In the first diagram a mass is raised on a pulley. Work is done and the energy of the mass increases. This energy is stored in the mass as potential energy. In the second diagram a truck is accelerated along a surface. A force is needed to do this and work is done. The energy used to accelerate the ...
... In the first diagram a mass is raised on a pulley. Work is done and the energy of the mass increases. This energy is stored in the mass as potential energy. In the second diagram a truck is accelerated along a surface. A force is needed to do this and work is done. The energy used to accelerate the ...
Physics 11 Unit Test – Energy and Society KNOWLEDGE 20 Marks
... 10. _______________________ is the rate at which work is done. 11. ___________________ is the energy of motion or the kinetic energy of matter at the atomic and molecular levels. ...
... 10. _______________________ is the rate at which work is done. 11. ___________________ is the energy of motion or the kinetic energy of matter at the atomic and molecular levels. ...
What are the units of power?
... Deyjah pushes a shopping cart with a force of 40N directed at an angle of 40o down from the horizontal. Find the work done by Deyjah on the cart as the shopper walks 65m across the parking lot. ...
... Deyjah pushes a shopping cart with a force of 40N directed at an angle of 40o down from the horizontal. Find the work done by Deyjah on the cart as the shopper walks 65m across the parking lot. ...
Text Questions
... 53. By “standard conditions,” we usually mean a pressure of ______ and a temperature of _____. 54. How do we define standard enthalpy change? ...
... 53. By “standard conditions,” we usually mean a pressure of ______ and a temperature of _____. 54. How do we define standard enthalpy change? ...
Review for Chapter 5 and 6 Test
... The average passenger's mass is 65 kg. Determine the power requirement of the escalator in order to move this number of passengers in this amount of time. 650N×8m=5200J 5200J/60s=86.7W 9. Two physics students, Will N.Andable and Ben Pumpiniron, are in the weightlifting room. Will lifts the 100-pound ...
... The average passenger's mass is 65 kg. Determine the power requirement of the escalator in order to move this number of passengers in this amount of time. 650N×8m=5200J 5200J/60s=86.7W 9. Two physics students, Will N.Andable and Ben Pumpiniron, are in the weightlifting room. Will lifts the 100-pound ...
9. Entropy 2nd and 3rd laws/ Thermodynamic processes / Droplet
... 9.1 Entropy in second and third laws of thermodynamics (2pts) 1. Explain the statistical definition of entropy (4pts) 2. Consider a “thermodynamic system” of two dices and let the energy of a certain throw (state of the system) be the sum of the two values of the dices. Calculate the respective entr ...
... 9.1 Entropy in second and third laws of thermodynamics (2pts) 1. Explain the statistical definition of entropy (4pts) 2. Consider a “thermodynamic system” of two dices and let the energy of a certain throw (state of the system) be the sum of the two values of the dices. Calculate the respective entr ...