Forms of Energy
... Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic. ...
... Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic. ...
Z004 - THERMODYNAMICS
... -What is the change in internal energy of a gas if 2,000 joules of work are done on the gas and 6,000 joules of work is allowed to exit the system by cooling? -The enclosed gas in the previous question is .02 kg of atmospheric air. If the gas starts at 308 K what is its final temperature? -How much ...
... -What is the change in internal energy of a gas if 2,000 joules of work are done on the gas and 6,000 joules of work is allowed to exit the system by cooling? -The enclosed gas in the previous question is .02 kg of atmospheric air. If the gas starts at 308 K what is its final temperature? -How much ...
Work Energy Theorem & KE & PE
... force. For a round trip the frictional force generally opposes motion and only leads to a decrease in kinetic energy. ...
... force. For a round trip the frictional force generally opposes motion and only leads to a decrease in kinetic energy. ...
Pop Quiz pp. 151-155 What two forms of energy combine to make
... afternoon is growing cool. A vendor hands you a hot dog, and its heat helps warm your hands. Suddenly the stadium lights switch on. You can see the players more clearly now. ...
... afternoon is growing cool. A vendor hands you a hot dog, and its heat helps warm your hands. Suddenly the stadium lights switch on. You can see the players more clearly now. ...
Heat Chapter 12: Thermodynamics
... isometric – constant volume • W = 0; Q = U adiabatic – no heat is exchanged • Q = 0; U = W • The area under the curve on a P-V graph is equal to work. • Internal energy is linked to temperature. Recall from Chapter 10, for ideal monatomic gases: U = 3/2 nRT ...
... isometric – constant volume • W = 0; Q = U adiabatic – no heat is exchanged • Q = 0; U = W • The area under the curve on a P-V graph is equal to work. • Internal energy is linked to temperature. Recall from Chapter 10, for ideal monatomic gases: U = 3/2 nRT ...
Energy Notes with Answers energy_notes_with_answers
... Energy Notes Energy: The work that energy allows us to do can be divided into 5 main tasks. 1.) Produce ...
... Energy Notes Energy: The work that energy allows us to do can be divided into 5 main tasks. 1.) Produce ...
Thermochemistry ch 16 energy diagrams phase
... ENERGY AND CHEMICAL CHANGE CH. 16 •Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat and is found in two forms •potential energy is energy due to the composition of the substance •kinetic energy is the energy of motion (1/2 mv2) ...
... ENERGY AND CHEMICAL CHANGE CH. 16 •Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat and is found in two forms •potential energy is energy due to the composition of the substance •kinetic energy is the energy of motion (1/2 mv2) ...
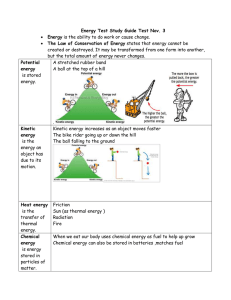
Energy Test Study Guide
... Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It may be transformed from one form into another, but the total amount of energy never changes. A stretched rubber band A ball at the top of a hill ...
... Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It may be transformed from one form into another, but the total amount of energy never changes. A stretched rubber band A ball at the top of a hill ...
Part VI
... • The work-kinetic energy theorem in rotational language states that the net work done by external forces in rotating a symmetrical rigid object about a fixed axis equals the change in the object’s rotational kinetic energy ...
... • The work-kinetic energy theorem in rotational language states that the net work done by external forces in rotating a symmetrical rigid object about a fixed axis equals the change in the object’s rotational kinetic energy ...
эритмалар. эритмалар назарияси. эритмаларнинг хоссалари
... When the process of isobaric pressure is constant: P = const For such a state of expression for the first law of thermodynamics Q = U + р V is rewritten as follows: QP = U2 -U1 + р(V2 -V1) = U2 - U1 + рV2 -рV1 QP = (U2 + рV2) - (U1 - рV1) The thermal effect at constant pressure is called the enth ...
... When the process of isobaric pressure is constant: P = const For such a state of expression for the first law of thermodynamics Q = U + р V is rewritten as follows: QP = U2 -U1 + р(V2 -V1) = U2 - U1 + рV2 -рV1 QP = (U2 + рV2) - (U1 - рV1) The thermal effect at constant pressure is called the enth ...
Energy and Radiation Reading: p. 25
... and same mass. If we combine them into one, then the internal energy will be 2X, but T=40 degrees still. Note the difference between T and Internal Energy. If you place a cold marble in your hand, the marble “heats up”==energy is transferred from the warm object to the colder one. This is always the ...
... and same mass. If we combine them into one, then the internal energy will be 2X, but T=40 degrees still. Note the difference between T and Internal Energy. If you place a cold marble in your hand, the marble “heats up”==energy is transferred from the warm object to the colder one. This is always the ...
1 7.3 Heat capacities: extensive state variables (Hiroshi Matsuoka
... Molar heat capacity is actually more physical than specific heat because molar heat capacity corresponds to Avogadro’s number of atoms or molecules and is therefore proportional to heat capacity per atom or molecule so that by comparing molar heat capacities of various systems, we can gain some insi ...
... Molar heat capacity is actually more physical than specific heat because molar heat capacity corresponds to Avogadro’s number of atoms or molecules and is therefore proportional to heat capacity per atom or molecule so that by comparing molar heat capacities of various systems, we can gain some insi ...
Thermal Energy from Chemical Reactions
... • The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1°C • The higher the specific heat, the more effectively the substance will store heat • Has the unit Jg–1°C –1 Temperature Energy needed Specific X mass (g) X ...
... • The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1°C • The higher the specific heat, the more effectively the substance will store heat • Has the unit Jg–1°C –1 Temperature Energy needed Specific X mass (g) X ...
241 Lecture 11
... In thermodynamics, equilibrium means not only the absence of change but the absence of any tendency toward change on a macroscopic scale. Different kinds of driving forces bring about different kinds of change. For example: imbalance of mechanical forces tend to cause energy ...
... In thermodynamics, equilibrium means not only the absence of change but the absence of any tendency toward change on a macroscopic scale. Different kinds of driving forces bring about different kinds of change. For example: imbalance of mechanical forces tend to cause energy ...
Vocabulary
... b. It transforms to an equal amount of some other form of energy. c. Much of it is lost d. It is used to overcome friction ...
... b. It transforms to an equal amount of some other form of energy. c. Much of it is lost d. It is used to overcome friction ...
SC.4.P.11.1-11.2 - Energy Transfer and Transformation
... • A change in thermal energy can lead to a change in phase or state of matter. • Temperature is a measure of thermal energy. ...
... • A change in thermal energy can lead to a change in phase or state of matter. • Temperature is a measure of thermal energy. ...
Technology Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology
... Chemical energy: energy stored within a chemical substance. Electrical energy: energy associated with electrons moving along a conductor. Energy: the ability to do work. Exhaustible energy resources: materials that cannot be replaced. Fission: the process of splitting atoms to release vast quantitie ...
... Chemical energy: energy stored within a chemical substance. Electrical energy: energy associated with electrons moving along a conductor. Energy: the ability to do work. Exhaustible energy resources: materials that cannot be replaced. Fission: the process of splitting atoms to release vast quantitie ...
Unit 11 Energy, Changes of State, Solids and Liquids
... Unit 11 Energy, Changes of State, Solids and Liquids Thermodynamics – the study of energy Energy – the ability to do work or produce heat Units of energy: calorie (cal) – amount of energy required to rise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 ˚C Joule (J) – SI unit – 1 calorie = 4.184 J ...
... Unit 11 Energy, Changes of State, Solids and Liquids Thermodynamics – the study of energy Energy – the ability to do work or produce heat Units of energy: calorie (cal) – amount of energy required to rise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 ˚C Joule (J) – SI unit – 1 calorie = 4.184 J ...