Section 3 What is energy? Energy “Ability to do work” Anything that
... Energy stored by objects due to their position above Earth’s surface Anything that can fall has stored energy Increased by increasing its height If two objects = height, larger mass more GPE ...
... Energy stored by objects due to their position above Earth’s surface Anything that can fall has stored energy Increased by increasing its height If two objects = height, larger mass more GPE ...
Chapter 5
... Energy- is defined as the ability to do work. Work is done when a force causes something to move https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xBnS23U_ao4 Energy can also be defined as the ability to cause change. Energy moves from place to place and changes forms. Work can be calculated by using the fo ...
... Energy- is defined as the ability to do work. Work is done when a force causes something to move https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xBnS23U_ao4 Energy can also be defined as the ability to cause change. Energy moves from place to place and changes forms. Work can be calculated by using the fo ...
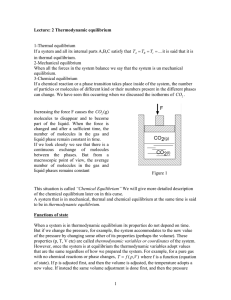
1 Lecture: 2 Thermodynamic equilibrium 1
... This situation is called “Chemical Equilibrium” We will give more detailed description of the chemical equilibrium later on in this curse. A system that is in mechanical, thermal and chemical equilibrium at the same time is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium. Functions of state When a system is ...
... This situation is called “Chemical Equilibrium” We will give more detailed description of the chemical equilibrium later on in this curse. A system that is in mechanical, thermal and chemical equilibrium at the same time is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium. Functions of state When a system is ...
Forces and Motion Vocabulary Words
... Forces that have a net force of zero (the object is still) Forces that have a net force that is not zero (object will move) Objects in motion stay in motion, objects at rest stay at rest unless acted on by an outside force ...
... Forces that have a net force of zero (the object is still) Forces that have a net force that is not zero (object will move) Objects in motion stay in motion, objects at rest stay at rest unless acted on by an outside force ...
Lecture 21 (6.1)
... • An isolated system can be viewed as a “small universe” (q = 0 and w = 0) ∆E = q + w = 0 ⇒ E = constant • 1st Law – The internal energy of an isolated system is constant (energy can not be created or destroyed within an isolated system) ...
... • An isolated system can be viewed as a “small universe” (q = 0 and w = 0) ∆E = q + w = 0 ⇒ E = constant • 1st Law – The internal energy of an isolated system is constant (energy can not be created or destroyed within an isolated system) ...
Temperature and Kinetic Energy
... Temperature and Kinetic Energy Particles of matter moving at different speeds have different kinetic energies because kinetic energy depends on speed. It is not possible to know the kinetic energy of each particle in an object. However, the average kinetic energy of all the particles in an object ca ...
... Temperature and Kinetic Energy Particles of matter moving at different speeds have different kinetic energies because kinetic energy depends on speed. It is not possible to know the kinetic energy of each particle in an object. However, the average kinetic energy of all the particles in an object ca ...
Work and Power
... work in the same amount of time as something that is not as powerful. • Ex: An old microwave can heat up a hot pocket in about 3 minutes. A new microwave can heat up the hot pocket to the same temperature in about 2 and a half minutes. • The new microwave is more powerful. ...
... work in the same amount of time as something that is not as powerful. • Ex: An old microwave can heat up a hot pocket in about 3 minutes. A new microwave can heat up the hot pocket to the same temperature in about 2 and a half minutes. • The new microwave is more powerful. ...
Energy can
... You can measure the amount of kinetic energy given to the can as well as figure out how much energy is stored as potential energy in the rubber band. To calculate the kinetic or potential energy: 1. Weigh your can in kg. 2. Determine its deceleration as it rolls away from you. To do this, you will n ...
... You can measure the amount of kinetic energy given to the can as well as figure out how much energy is stored as potential energy in the rubber band. To calculate the kinetic or potential energy: 1. Weigh your can in kg. 2. Determine its deceleration as it rolls away from you. To do this, you will n ...
What are the six main forms of energy?
... • Energy = mass x speed of light – Energy and mass are equivalent and can be converted into one another. – 1 gram of matter turned entirely into energy = 90,000,000,000,000 J – 1 gram of explosive produces 2931 J This is because it is not entirely turned into energy, there is some matter ...
... • Energy = mass x speed of light – Energy and mass are equivalent and can be converted into one another. – 1 gram of matter turned entirely into energy = 90,000,000,000,000 J – 1 gram of explosive produces 2931 J This is because it is not entirely turned into energy, there is some matter ...
The Energy of Life - AVC Distance Education: Learn
... Less-usable energy is disorganized. Entropy is the measure of this disorder. Usable energy has low entropy. Disorganized energy such as heat has high entropy. Entropy is continuously increasing in the universe in all natural processes. ...
... Less-usable energy is disorganized. Entropy is the measure of this disorder. Usable energy has low entropy. Disorganized energy such as heat has high entropy. Entropy is continuously increasing in the universe in all natural processes. ...
Ch 14, 15, 16
... absorb the same energy? The metal has a lower specific heat than the wood, so its temp increases more as thermal energy is absorbed ...
... absorb the same energy? The metal has a lower specific heat than the wood, so its temp increases more as thermal energy is absorbed ...
Energy and its Conservation
... • “ the work it does on an object that moves between two points depends only on the position of these two points and not on the path.” • “the work it does on an object that moves through a round trip is zero.” ...
... • “ the work it does on an object that moves between two points depends only on the position of these two points and not on the path.” • “the work it does on an object that moves through a round trip is zero.” ...
Kinetic Energy
... The total Mechanical Energy must always be equal to the sum of Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy ...
... The total Mechanical Energy must always be equal to the sum of Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy ...
UNIT 2 Energy and Momentum Test Review
... theorem and the law of conservation of energy, and solve related problems in one and two dimensions use an inquiry process to analyse, in qualitative and quantitative terms, situations involving work, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, thermal energy, and elastic potential energy, in ...
... theorem and the law of conservation of energy, and solve related problems in one and two dimensions use an inquiry process to analyse, in qualitative and quantitative terms, situations involving work, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, thermal energy, and elastic potential energy, in ...
AP Physics C IC
... Ex. A 15 kg crate is moved along a horizontal surface by a warehouse worker who is pulling on it with a rope that makes an angle of 30.0° with the horizontal. The tension in the rope is 100.0 N and the crate slides a distance of 10.0 m. a) How much work is done on the crate by the rope? b) How much ...
... Ex. A 15 kg crate is moved along a horizontal surface by a warehouse worker who is pulling on it with a rope that makes an angle of 30.0° with the horizontal. The tension in the rope is 100.0 N and the crate slides a distance of 10.0 m. a) How much work is done on the crate by the rope? b) How much ...
Law of Conservation of Energy
... potential and kinetic energy in a system that can be expressed by the following equation Mechanical energy = Potential energy+ Kinetic energy *Mechanical energy is energy due to the position and the motion of an object or the objects ...
... potential and kinetic energy in a system that can be expressed by the following equation Mechanical energy = Potential energy+ Kinetic energy *Mechanical energy is energy due to the position and the motion of an object or the objects ...
Forces Test Review - Ms. Rousseau`s Classroom
... theorem and the law of conservation of energy, and solve related problems in one and two dimensions use an inquiry process to analyse, in qualitative and quantitative terms, situations involving work, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, thermal energy, and elastic potential energy, in ...
... theorem and the law of conservation of energy, and solve related problems in one and two dimensions use an inquiry process to analyse, in qualitative and quantitative terms, situations involving work, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy, thermal energy, and elastic potential energy, in ...
5.2 Physics section 5.2
... How fast would a 65 g bullet have to travel to have the same amount of kinetic energy as a 140 g bullet with a velocity of 180 m/s? ...
... How fast would a 65 g bullet have to travel to have the same amount of kinetic energy as a 140 g bullet with a velocity of 180 m/s? ...