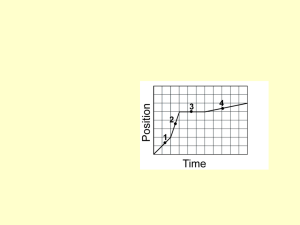
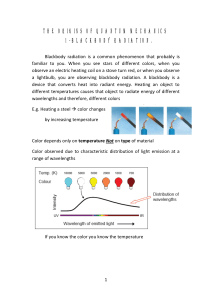
Date Specification Content Comments P2.2 The kinetic energy of
... f) Gravitational potential energy is the energy that an object has by virtue of its position in a gravitational field. Ep = m x g x h Ep is the change in gravitational potential energy in joules, J m is the mass in kilograms, kg g is the gravitational field strength in newtons per kilogram, N/kg h i ...
... f) Gravitational potential energy is the energy that an object has by virtue of its position in a gravitational field. Ep = m x g x h Ep is the change in gravitational potential energy in joules, J m is the mass in kilograms, kg g is the gravitational field strength in newtons per kilogram, N/kg h i ...
Lecture 5
... cp = specific heat at constant pressure Specific heat is the heat energy needed to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree. ...
... cp = specific heat at constant pressure Specific heat is the heat energy needed to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree. ...
Conservation of Energy Lab Challenge
... Challenge: Your task is to determine the amount of elastic potential energy stored in a toy “popper” using the law of conservation of energy. Since we do not have an equation for elastic potential energy in a popper, we must find another method. The only equipment available to you is a metric ruler, ...
... Challenge: Your task is to determine the amount of elastic potential energy stored in a toy “popper” using the law of conservation of energy. Since we do not have an equation for elastic potential energy in a popper, we must find another method. The only equipment available to you is a metric ruler, ...
Energy
... required for sustained physical activity ● SPEED: the rate at which an object moves All energy can be divided into two groups: potential energy and kinetic energy. ...
... required for sustained physical activity ● SPEED: the rate at which an object moves All energy can be divided into two groups: potential energy and kinetic energy. ...
More Energy Practice Problems
... 84 cm. With what speed must a female hurdler leave the ground to clear the hurdle at a speed of 1.0 m/s? 6. It is not uncommon on the service of a professional tennis player for the racquet to exert an average force of 150 N on the ball. If the ball has a mass of 0.600 kg, and is in contact with the ...
... 84 cm. With what speed must a female hurdler leave the ground to clear the hurdle at a speed of 1.0 m/s? 6. It is not uncommon on the service of a professional tennis player for the racquet to exert an average force of 150 N on the ball. If the ball has a mass of 0.600 kg, and is in contact with the ...
Ideas about Work and Energy
... The Potential Energy of gravity is a “conservative” form of energy. PE is path independent, it only depends on the starting and ending locations. PE is always a change in energy, meaning it has a reference point. This reference point is the location you are calling h = 0. ...
... The Potential Energy of gravity is a “conservative” form of energy. PE is path independent, it only depends on the starting and ending locations. PE is always a change in energy, meaning it has a reference point. This reference point is the location you are calling h = 0. ...
Thermal and Statistical Physics (Part II) Examples Sheet 1
... observed value of ⟨x2 ⟩ was 3.3×10−12 m2 in a 10-second interval. Use these data to determine a value of the Boltzmann constant, kB , and compare it with the modern value. 31. The famous ratchet and pawl machine, originally suggested by Smoluchowski in 1912 to be able to extract useful work from a t ...
... observed value of ⟨x2 ⟩ was 3.3×10−12 m2 in a 10-second interval. Use these data to determine a value of the Boltzmann constant, kB , and compare it with the modern value. 31. The famous ratchet and pawl machine, originally suggested by Smoluchowski in 1912 to be able to extract useful work from a t ...
Conservation of Energy - Rose
... 4. Given sufficient information, determine the change in specific internal energy ∆u and the change in ∆h for a substance that can be modeled using one of the following substance models: Ideal gas with room-temperature specific heats Incompressible substance with room-temperature specific heats and ...
... 4. Given sufficient information, determine the change in specific internal energy ∆u and the change in ∆h for a substance that can be modeled using one of the following substance models: Ideal gas with room-temperature specific heats Incompressible substance with room-temperature specific heats and ...
Forms of Energy Conversions
... Forms of Energy Conversions: use the back of this page for drawing if you need more room. There are six forms of energy: thermal (heat), electrical (moving electrons), electromagnetic (light), nuclear (energy that binds the nuclei of atoms), chemical and mechanical (a kind of kinetic energy of movin ...
... Forms of Energy Conversions: use the back of this page for drawing if you need more room. There are six forms of energy: thermal (heat), electrical (moving electrons), electromagnetic (light), nuclear (energy that binds the nuclei of atoms), chemical and mechanical (a kind of kinetic energy of movin ...
Jeopardy - Fair Lawn Schools
... The total momentum in a system cannot change as long as all the forces act only between the objects in the system. ...
... The total momentum in a system cannot change as long as all the forces act only between the objects in the system. ...
KE and PE Practice Problems Name Kinetic Energy Definition
... Definition: Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE) is the energy an object has due to its position. This position is due to gravity (So position change should only be in the vertical direction. The metric unit of GPE is Joules. 1. What is the Gravitational Potential Energy in a 75kg mass that is lifte ...
... Definition: Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE) is the energy an object has due to its position. This position is due to gravity (So position change should only be in the vertical direction. The metric unit of GPE is Joules. 1. What is the Gravitational Potential Energy in a 75kg mass that is lifte ...
Study Guide
... 9. Pieces of clear material that bends, ore refracts, light rays is ___________________. 10. Material that doesn’t carry electrons is called ____________________________. 11. Energy of motion is ____________________________________________. 12. Path along which electrons flow is ____________________ ...
... 9. Pieces of clear material that bends, ore refracts, light rays is ___________________. 10. Material that doesn’t carry electrons is called ____________________________. 11. Energy of motion is ____________________________________________. 12. Path along which electrons flow is ____________________ ...
Work - TeacherWeb
... A force does work on a body when it causes a displacement. There is no work done by a force if it causes no displacement. Forces perpendicular to displacement, such as the normal force, can do no work. For example, centripetal forces never do work. Calculating Work W = F • s = F s cos W = F(x) ...
... A force does work on a body when it causes a displacement. There is no work done by a force if it causes no displacement. Forces perpendicular to displacement, such as the normal force, can do no work. For example, centripetal forces never do work. Calculating Work W = F • s = F s cos W = F(x) ...
Physics Practice Exam 2 Solutions
... left with v. You see that if we divided KE by p, m would cancel out, and one v, and we would be left with ½ v, so v= 2KE/p. If we put the values from the table, you will see that C is the correct answer. 2. A In inelastic collisions, some energy is lost due to compressing, or sticking together, ther ...
... left with v. You see that if we divided KE by p, m would cancel out, and one v, and we would be left with ½ v, so v= 2KE/p. If we put the values from the table, you will see that C is the correct answer. 2. A In inelastic collisions, some energy is lost due to compressing, or sticking together, ther ...
Ch. 6 Section 6.1 Powerpoint
... •Heat: involves the transfer of energy between two objects due to a temperature difference. •Remember heat and temperature are different. •Temperature is a measure of the hotness or coldness of something and is proportional to the average molecular kinetic energy of the atoms, molecules, or ions pre ...
... •Heat: involves the transfer of energy between two objects due to a temperature difference. •Remember heat and temperature are different. •Temperature is a measure of the hotness or coldness of something and is proportional to the average molecular kinetic energy of the atoms, molecules, or ions pre ...