* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 Quick Review
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
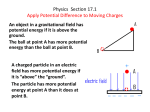
TA: Tomoyuki Nakayama February 15th – February 16th, 2010 PHY 2048: Physics 1 with Calculus, Spring 2010 Review: Chapter 8.1-8.8 The purpose of this review is to refresh your memory. Physics is a cumulative subject, so make it sure that you understand basic concepts and typical problem solving techniques in previous chapters before moving on to a new chapter. ________________________________________________________________________________ A. Work-Energy Theorem 1. Write down the work-energy theorem in two ways. 2. A figure on the right shows a mass m attached to a string of negligible mass. What initial velocity do you need to give at the lowest point for the mass to take a circular path? 3. Two blocks of masses M = 2.0 kg and 2M are connected to a spring of spring constant k = 150 N/m. The horizontal surface is frictionless. The blocks are released from rest with the spring relaxed. What maximum distance does the hanging block fall before it momentarily stops? B. Potential Energy Function 1. The figure on the right shows a plot of potential energy U versus position x of 1-kg particle that can travel only along an x axis, where UA = 15 J, UB = 35 J and UC = 45 J. The particle is released at x = 0 with an initial velocity of 4 m/s, headed in the +x direction. What is the turning point of the particle? C. Thermal Energy 1. Express thermal energy in terms of work done by friction. 2. A 1-kg block with an initial velocity v = 5 m/s slides along a track that descends through a vertical distance h = 1 m. The track is frictionless except for the lower section; there the block slides to a stop in a distance D = 4 m due to friction. What is the change in thermal energy of the system? What is the coefficient of kinetic friction? TA: Tomoyuki Nakayama February 15th – February 16th, 2010 PHY 2048: Physics 1 with Calculus, Spring 2010 Practice Exam Problems (Chapter 8.1-8.8) Working on this problem set is optional, but it is strongly recommended. It is highly likely that some of these problems will appear in the exams. Do it on a weekly basis. Cramming is tiring and sometimes it ends up in a disaster. ________________________________________________________________________________ 1. A force on a particle is conservative if (Conservative Force) a. its work equals the change in the kinetic energy of the particle b. it obeys Newton’s second law c. it obeys Newton’s third law d. its work depends on the end points of every motion, not on the path between e. it is not a frictional force 2. A ball is held at a height H above a floor. It is then released and falls to the floor. If air resistance is negligible, which of the five graphs below correctly gives the mechanical energy E of the Earth-ball system as a function of the altitude y of the ball? (Mechanical Energy) 3. A 0.50-kg block attached to an ideal spring with a spring constant of 80 N/m oscillates on a horizontal frictionless surface. When the spring is 4.0 cm longer its equilibrium length, the speed of the block is 0.50 m/s. The greatest speed of the block is (Spring Potential Energy) a. 0.23 m/s b. 0.32 m/s c. 0.55 m/s d. 0.71 m/s e. 0.93 m/s 4. A small ball of mass ma starts from rest at the position shown and slide along the frictionless loop-the-loop track of radius R. What is the smallest value of y such that the object will slide without losing contact with the track? (Gravitational Potential Energy) a. R/4 b. R/2 c. R d. 2R e. zero 4. A 700-N man jumps out of a window into a fire net 10 m below. The net stretches 2 m before bringing the man to rest and tossing him back into the air. The maximum potential energy of the net, compared to its unstretched potential is: (Conservation of Energy) a. 300 J b. 710 J c. 850 J d. 7000 J e. 8400 6. The potential energy of a 0.20-kg particle moving along the x axis is given by U(x) = (8.0J/m2)x2+(2.0J/m4)x4. When the particle is at x = 1.0 m it is traveling in the positive x direction with a speed of 5.0 m/s. It next stops momentarily to turn around at x = : (Potential Energy Function) a. 0 b. -1.1 m c. 1.1 m d. -2.3 m e. 2.3 m 7. A 0.75-kg block slides on a rough horizontal table top. Just before it hits a horizontal ideal spring its speed is 3.5 m/s. It compresses the spring 5.7 cm before coming to rest. If the spring constant is 1200 N/m, the thermal energy of the block and the table top must have: (Thermal Energy) a. not changed b. decreased by 1.9 J c. decreased by 2.6 J c. increased by 1.9 J e. increased by 2.6 J Answers: 1-d 2-e 3-d 4-b 5- e 6-c 7-e