Lecture 2
... Intensity is a qualitative measure of the actual shaking at a location during an earthquake and it is assigned in Roman Capital Letters There are many intensity scales. Two commonly used ones are 1) Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) Scale. 2) MSK Scale Both scales are quite similar and range from I( ...
... Intensity is a qualitative measure of the actual shaking at a location during an earthquake and it is assigned in Roman Capital Letters There are many intensity scales. Two commonly used ones are 1) Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) Scale. 2) MSK Scale Both scales are quite similar and range from I( ...
The Earth’s structure - Bishopston Comprehensive School
... • Earthquakes are caused when tension is released from inside the crust. • This happens because plates do not move smoothly - sometimes they get stuck. • When this happens a great deal of pressure builds up. • When this pressure is eventually released, an earthquake tends to occur. ...
... • Earthquakes are caused when tension is released from inside the crust. • This happens because plates do not move smoothly - sometimes they get stuck. • When this happens a great deal of pressure builds up. • When this pressure is eventually released, an earthquake tends to occur. ...
Ch. 11 Earthquakes
... plate scrapes across the top of the subducting plate. Divergent Oceanic environments – Make up the midocean ridges, plates are moving away from each other. ...
... plate scrapes across the top of the subducting plate. Divergent Oceanic environments – Make up the midocean ridges, plates are moving away from each other. ...
95AM-4
... 6. A single stay supports a derrick 16 m long. The angle between the derrick and the post is 60º while the included angle between stay and derrick is 30º. If the mass of the derrick is 500 Kg supporting a load of 2000 Kg. Find: (i) the force in the supporting stay (ii) the compressive force in the ...
... 6. A single stay supports a derrick 16 m long. The angle between the derrick and the post is 60º while the included angle between stay and derrick is 30º. If the mass of the derrick is 500 Kg supporting a load of 2000 Kg. Find: (i) the force in the supporting stay (ii) the compressive force in the ...
1: How far can seismic waves carry energy released from an
... 8: In what directions do surface waves move? Are they more or less destructive than body waves? ...
... 8: In what directions do surface waves move? Are they more or less destructive than body waves? ...
Notes 2.7 – Rational Functions
... figure 4.94, a wheel with a 10 cm radius turns with an angular velocity of 6π radians per second. A.) What is the frequency of the piston? ...
... figure 4.94, a wheel with a 10 cm radius turns with an angular velocity of 6π radians per second. A.) What is the frequency of the piston? ...
Geology_101_Homework_2
... 2) Explain the factors that affect the speed of a seismic wave as it travels through the Earth. Chap. 11 1) What is the difference between stress and strain? 2) What is the difference between ductile and brittle behavior for rocks? 3) There are two important brittle-ductile transitions in the upper ...
... 2) Explain the factors that affect the speed of a seismic wave as it travels through the Earth. Chap. 11 1) What is the difference between stress and strain? 2) What is the difference between ductile and brittle behavior for rocks? 3) There are two important brittle-ductile transitions in the upper ...
Deformation of the Crust
... • Need measurements from 3 stations • Difference in time P and S waves arrive ...
... • Need measurements from 3 stations • Difference in time P and S waves arrive ...
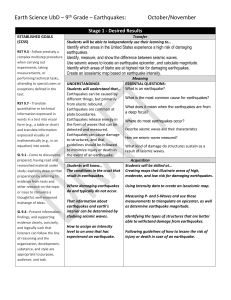
Earth Science UbD – 9th Grade – Earthquakes: October/November
... Use seismic waves to locate an earthquake epicenter, and calculate magnitude. Identify which areas of Idaho are at highest risk for damaging earthquakes. Create an isoseismic map based on earthquake intensity. UNDERSTANDINGS Students will understand that… Earthquakes can be caused by different thi ...
... Use seismic waves to locate an earthquake epicenter, and calculate magnitude. Identify which areas of Idaho are at highest risk for damaging earthquakes. Create an isoseismic map based on earthquake intensity. UNDERSTANDINGS Students will understand that… Earthquakes can be caused by different thi ...
Seismic Earth. Array Analysis of Broadband Seismograms. Volume 157. Brochure
... More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2496180/ ...
... More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2496180/ ...
Unit 1: Forces and Motion Study Guide
... 2. How are mass and weight different? 3. Does mass change gravity? 4. Do we weigh the same on other planets? -Foldable -Textbook pages on Haiku and Faculty Page Newton’s Laws of Motion: 1. Know and understand the difference between Newton’s three laws of motion. 2. Be ready to give an example of eac ...
... 2. How are mass and weight different? 3. Does mass change gravity? 4. Do we weigh the same on other planets? -Foldable -Textbook pages on Haiku and Faculty Page Newton’s Laws of Motion: 1. Know and understand the difference between Newton’s three laws of motion. 2. Be ready to give an example of eac ...