Name___________________________________ Test on
... The force that attracts a body toward the center of the earth or toward any other physical body having mass. ...
... The force that attracts a body toward the center of the earth or toward any other physical body having mass. ...
G080475-00 - DCC
... • It is very wet, probably not very good for “science”, is our test lab. • We built a computer hut and an instrument hut, then a small box inside it with a thin layer of concrete to fight against water. • We carried internet via 2 antennae that work as a directional radio bridge. ...
... • It is very wet, probably not very good for “science”, is our test lab. • We built a computer hut and an instrument hut, then a small box inside it with a thin layer of concrete to fight against water. • We carried internet via 2 antennae that work as a directional radio bridge. ...
Unit C UA pt B - LD Industries
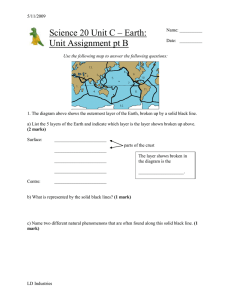
... ________ - relating to waves that travel through Earth as a result of explosions or earthquakes ________ - a large concentration of petroleum confined between layers of impermeable shale ________ - an instrument that records seismic waves ________ - a submerged ridge of rock, sand, or coral that ris ...
... ________ - relating to waves that travel through Earth as a result of explosions or earthquakes ________ - a large concentration of petroleum confined between layers of impermeable shale ________ - an instrument that records seismic waves ________ - a submerged ridge of rock, sand, or coral that ris ...
Seismology A shaky science
... Seismologist study seismograms and can tell a great deal about earthquakes. It can indicate how far way the epicenter is from the seismic station and the energy released by the earthquake. Magnitude- the amount of energy released by an earthquake. Arrival time- the time it takes for seismic waves to ...
... Seismologist study seismograms and can tell a great deal about earthquakes. It can indicate how far way the epicenter is from the seismic station and the energy released by the earthquake. Magnitude- the amount of energy released by an earthquake. Arrival time- the time it takes for seismic waves to ...
earthquakes - Cloudfront.net
... • Because of seismic waves from earthquakes • Seismic waves travel through solids faster than liquids • Seismic waves change direction when they change the material they are going through (from a solid to a liquid) ...
... • Because of seismic waves from earthquakes • Seismic waves travel through solids faster than liquids • Seismic waves change direction when they change the material they are going through (from a solid to a liquid) ...
Dynamic Earth
... -fossils of tropical plants found in continents now in polar regions -fossils of the same species found across oceans ...
... -fossils of tropical plants found in continents now in polar regions -fossils of the same species found across oceans ...
Module 5 - Earthquakes - IST Akprind Yogyakarta
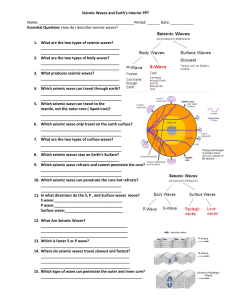
... Four types of seismic waves are generated when faulting triggers an earthquake. All the seismic waves are generated at the same time, but travel at different speeds and in different ways. Body waves penetrate the earth and travel through it, while surface waves travel along the surface of the ground ...
... Four types of seismic waves are generated when faulting triggers an earthquake. All the seismic waves are generated at the same time, but travel at different speeds and in different ways. Body waves penetrate the earth and travel through it, while surface waves travel along the surface of the ground ...
The Dangerous Earthquakes
... are. Earthquakes cause lots of damage. people get scared when it comes. ...
... are. Earthquakes cause lots of damage. people get scared when it comes. ...
Earthquakes
... 4. Complete the cause-events-effect chart to show how the different types of stress change the shape and volume of the rock. ...
... 4. Complete the cause-events-effect chart to show how the different types of stress change the shape and volume of the rock. ...
Force, Net Force, and Inertia
... Newton’s First Law of Motion • Also Known as The Law of Inertia • You may have heard the phrase, “An object in motion tends to stay in motion, and an object at rest will tend to stay at rest.” • In Physics we say, “A body moving at a constant velocity will stay at that velocity, and a body at rest ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion • Also Known as The Law of Inertia • You may have heard the phrase, “An object in motion tends to stay in motion, and an object at rest will tend to stay at rest.” • In Physics we say, “A body moving at a constant velocity will stay at that velocity, and a body at rest ...
4.3 PPT_EQ & Waves
... Travel only through solids Move through solids at different speeds depending on the density Cause rock particles to move from side to side & up and down ...
... Travel only through solids Move through solids at different speeds depending on the density Cause rock particles to move from side to side & up and down ...
Earthquake Basics
... • Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks • Continuing adjustment of stress results in aftershocks • Most earthquakes are small and harmless, but rare much larger ones can cause enormous damage and loss of lives. • California has dozens of earthquakes every day, so we need to learn to ...
... • Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks • Continuing adjustment of stress results in aftershocks • Most earthquakes are small and harmless, but rare much larger ones can cause enormous damage and loss of lives. • California has dozens of earthquakes every day, so we need to learn to ...
Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy Sir Isaac Newton
... To every action there is always opposed an equal reaction; or, the mutual actions of two bodies upon each other are always equal, and directed to the contrary parts. ...
... To every action there is always opposed an equal reaction; or, the mutual actions of two bodies upon each other are always equal, and directed to the contrary parts. ...
Warm-up
... 1. If a toy train has a mass of 1.5 kg & accelerates at a rate of 20 m/s2, what is the amount of force acting on it? 2. Make a Venn diagram comparing/contrasting gravity & friction. ...
... 1. If a toy train has a mass of 1.5 kg & accelerates at a rate of 20 m/s2, what is the amount of force acting on it? 2. Make a Venn diagram comparing/contrasting gravity & friction. ...
Physics 422 - Spring 2013 - Midterm Exam, March 6
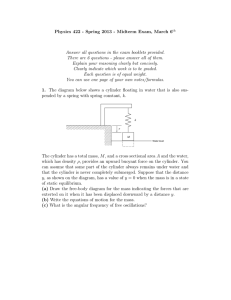
... (a) Draw the free-body diagram for the mass indicating the forces that are exterted on it when it has been displaced downward by a distance y. (b) Write the equations of motion for the mass. (c) What is the angular frequency of free oscillations? ...
... (a) Draw the free-body diagram for the mass indicating the forces that are exterted on it when it has been displaced downward by a distance y. (b) Write the equations of motion for the mass. (c) What is the angular frequency of free oscillations? ...
Newton*s Three Laws of Motion
... • Galileo was born in 1564 and died in 1642 • Galileo proved the Copernican hypothesis • He made us understand how objects moved on the surface of Earth and of gravity. ...
... • Galileo was born in 1564 and died in 1642 • Galileo proved the Copernican hypothesis • He made us understand how objects moved on the surface of Earth and of gravity. ...
Convergent Boundaries
... lithosphere. Two kinds of body waves exist: P-waves and Swaves. • Both of these waves produce a sharp jolt or shaking. •P-waves or primary waves are formed by the alternate expansion and contraction of bedrock. • P-waves also have the ability to travel through solid, liquid, and gaseous materials. • ...
... lithosphere. Two kinds of body waves exist: P-waves and Swaves. • Both of these waves produce a sharp jolt or shaking. •P-waves or primary waves are formed by the alternate expansion and contraction of bedrock. • P-waves also have the ability to travel through solid, liquid, and gaseous materials. • ...
1 - Hingham Schools
... A. The force on the apple is greater than the force on the Earth because the Earth is more massive. B. The force on the Earth is greater than the force on the apple because the Earth is more massive. C. The force on the apple is less than the force on the Earth because the tree is supporting the app ...
... A. The force on the apple is greater than the force on the Earth because the Earth is more massive. B. The force on the Earth is greater than the force on the apple because the Earth is more massive. C. The force on the apple is less than the force on the Earth because the tree is supporting the app ...