* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Dangerous Earthquakes
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
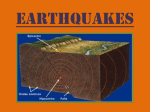
The Dangerous Earthquakes Bala R. The Dangerous Earthquakes Bala R. Table of Contents How Earthquakes Work . . . . . Page 1 Key Concept: Form/Function Where Most Damage Occur. . . Page 3 Key Concept: Change Causes Of Earthquake. . . . . . . Page 5 Key Concept: perspective Rough Roads. . . . . . . . . . . . . Page 7 Key Concept: Responsibility How Earthquakes Work Do you know how earthquakes form? Well, imagine how it feels when you are standing on a moving surface. It’s shaky and scary. Earthquakes happen when the ground shakes and moves. Showing a earthquake and how it is cracked up. What is a Tectonic Plate? A tectonic plate is broken pieces of earth’s crust that fit like a puzzle.These puzzle pieces move every year. They move about 0-6 inches per-year.Tectonic plates move on hot magma. The tectonic plates are in outer surface of earth’s crust called lithosphere. Showing broken pieces of earth’s crust. Where Most Damage Occurs Most damages occur where most people are and where they live. They also occur where most buildings are and where homes are. Earthquakes cause lots of damage. people get scared when it comes. Showing what damage from an earthquake. What Damage There Is People homes run down, glass breaking, cars smashing. People also losing lives. Trees will be falling down.It feels shaky, and when an earthquake comes, the ground will come apart. Surface waves cause ground movement, and the ground will break apart. People can get stuck in house open cracks. Showing damage. Chapter 3: Causes of Earthquakes Forces build up slowly and eventually become so strong that they cause rocks to break underground.That’s how it makes the ground to break underground. These forces are called seismic waves. Showing how ground breaks underground What Are Tectonic Plates? Tectonic plates are segments of lithosphere. Lithosphere is the outer part of the earth,consisting of the crust and upper mantle. They are also broken pieces of earth’s crust. Showing house cracked Rough Roads There will be cracks open on roads. These cracks are called faults. People can get stuck in crack open roads. They can be so dangerous. Cracks on roads Measuring Earthquakes Scientists use a tool called Seismograph to measure an earthquake. They are measured on a Richter Scale. That’s how we know how big an earthquake is. Showing damage of buildings About the Author Bala loves to play games with her little brother. Her favorite sport is swimming. Her talents are in gymnastics always. She collects cool rocks. She also likes going to school. She has a 5 year old brother that goes to Lindsey Elementary school.Her dad is always funny. He’s name is Phani and her mom’s name is Jaya, and her brother’s name is Abhinav. She loves her family so much. She loves hanging out with new friends. She loves making crafts with best friends. She loves making people happy. She loves being so nice and friendly .She always tries her best on some talents. She is 9 years old and she loves playing around. She is most talented in swimming. Her favorite subject is math because it is fun. It is also science because of the experiments. Glossary Richter Scale (noun) A scale to measure an earthquake Lithosphere (noun) The outer part of Earth’s crust (verb) Tectonic plates Fault Line (noun) Seismograph Damage (verb) Seismic Waves It means broken pieces of Earth’s crust A break in Earth’s crust (noun) THe tool to measure Earthquake To ruin things that we need (noun) The energy that is released Normal Fault (noun) Go’s up and down the ground Reverse Fault (noun) Go’s reverse way from normal fault Strike-Slip Fault (noun) It go’s side ways by ground References Lauber, Patricia. Volcanoes and Earthquakes. New York: Scholastic Inc, 1985. Branley, Franklyn. Earthquakes. New York: Harper Collins, 1990. USGS. 2 0 1 1 . < h t t p : / / g a l l e r y. u s g s . g o v / s e t s / 1989_Loma_Prieta,_California_Earthquake>.