Earthquakes
... 2) Normal: Tension causes horizontal and vertical movement 3) Strike-Slip – shear causes horizontal and vertical movement ...
... 2) Normal: Tension causes horizontal and vertical movement 3) Strike-Slip – shear causes horizontal and vertical movement ...
Deep crustal structure of the northeastern margin of the Arabian
... information on deeper structure remains little. Moreover, the mechanisms by which dense oceanic crustal and mantle rocks are emplaced onto less dense and more buoyant continental crust are still controversial and remain poorly understood. The focus here is on an active-source seismic and gravity E-W ...
... information on deeper structure remains little. Moreover, the mechanisms by which dense oceanic crustal and mantle rocks are emplaced onto less dense and more buoyant continental crust are still controversial and remain poorly understood. The focus here is on an active-source seismic and gravity E-W ...
Lecture 27 April 3, 2006
... What is EarthScope?EarthScope is a bold undertaking to apply modern observational, analytical and telecommunications technologies to investigate the structure and evolution of the North American continent and the physical processes controlling earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.EarthScope will prov ...
... What is EarthScope?EarthScope is a bold undertaking to apply modern observational, analytical and telecommunications technologies to investigate the structure and evolution of the North American continent and the physical processes controlling earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.EarthScope will prov ...
ISNS 4359 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES Spring 2005
... 4 easy steps to mitigation Step 1. Determine areas of highest risk (incorporate historical earthquake data) & prepare Seismic Hazard Maps incorporating soil & bedrock data (do not suggest/permit development in hazard zones). Step 2. Retrofit existing structures, build seismically isolated buildings ...
... 4 easy steps to mitigation Step 1. Determine areas of highest risk (incorporate historical earthquake data) & prepare Seismic Hazard Maps incorporating soil & bedrock data (do not suggest/permit development in hazard zones). Step 2. Retrofit existing structures, build seismically isolated buildings ...
Course Review 2
... In a circus act Bimbo, The Human Cannonball, is fired from the muzzle of a cannon that is angled at 600 to the horizontal and sits 3.0 m from the floor. If Bimbo has a mass of 65 kg and leaves the muzzle of the cannon at a velocity of 20 m/s the mechanical energy his body will possess at any time du ...
... In a circus act Bimbo, The Human Cannonball, is fired from the muzzle of a cannon that is angled at 600 to the horizontal and sits 3.0 m from the floor. If Bimbo has a mass of 65 kg and leaves the muzzle of the cannon at a velocity of 20 m/s the mechanical energy his body will possess at any time du ...
M - Otterbein University
... Newton II: calculate motion from force • If we know which force is acting on an object of known mass we can calculate (predict) its motion • Qualitatively: – objects subject to a constant force will speed up (slow down) in that direction – Objects subject to a force perpendicular to their motion (v ...
... Newton II: calculate motion from force • If we know which force is acting on an object of known mass we can calculate (predict) its motion • Qualitatively: – objects subject to a constant force will speed up (slow down) in that direction – Objects subject to a force perpendicular to their motion (v ...
Sects. 12.3 through 12.4
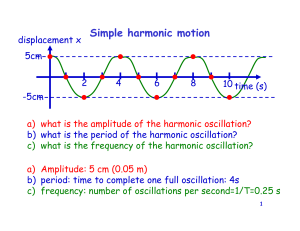
... object at rest when it is pulled 0.200 m from its equilibrium position (the origin of the x axis). The object is now released from rest with an initial position of xi = 0.200 m, and it subsequently undergoes simple harmonic oscillations. Find (a) the force constant of the spring, (b) the frequency o ...
... object at rest when it is pulled 0.200 m from its equilibrium position (the origin of the x axis). The object is now released from rest with an initial position of xi = 0.200 m, and it subsequently undergoes simple harmonic oscillations. Find (a) the force constant of the spring, (b) the frequency o ...
Unit 4 - Dynamic Crust Earthquakes & Volcanoes
... (Remember what that is?...hint: think crust) is divided into solid sections of rock called “plates.” These plates move in relation to one Another. Tectonics are the forces that cause the Earth’s crust to continually move and create new landforms such as mountains, mid-ocean ridges, trenches, or faul ...
... (Remember what that is?...hint: think crust) is divided into solid sections of rock called “plates.” These plates move in relation to one Another. Tectonics are the forces that cause the Earth’s crust to continually move and create new landforms such as mountains, mid-ocean ridges, trenches, or faul ...
5 - PowerPoint - Earthquakes
... The Focus and Epicenter of an Earthquake • The point within Earth where faulting begins is the focus, or hypocenter • The point directly above the focus on the surface is the epicenter ...
... The Focus and Epicenter of an Earthquake • The point within Earth where faulting begins is the focus, or hypocenter • The point directly above the focus on the surface is the epicenter ...
1) Whereas Aristotle relied on logic in explaining nature, Galileo
... C) later than the lighter object. 12) A 500-N parachutist opens his chute and experiences an air resistance force of 800 N. The net force on the parachutist is A) 800 N downward. B) 300 N downward. C) 500 N downward. D) 300 N upward. 13) A freight train rolls along a track with considerable momentum ...
... C) later than the lighter object. 12) A 500-N parachutist opens his chute and experiences an air resistance force of 800 N. The net force on the parachutist is A) 800 N downward. B) 300 N downward. C) 500 N downward. D) 300 N upward. 13) A freight train rolls along a track with considerable momentum ...
19.1 Forces Within Earth
... 1. Determine P and S wave arrival time to seismographs 2. Calculate the difference between P & S wave arrival times 3. Determine epicentral distance 4. Minimum of three stations needed to determine epicenter ...
... 1. Determine P and S wave arrival time to seismographs 2. Calculate the difference between P & S wave arrival times 3. Determine epicentral distance 4. Minimum of three stations needed to determine epicenter ...
Conversations with the Earth
... • 6.1-6.9 - Can be destructive in areas up to about 100 kilometers across where people live. • 7.0-7.9 - Major earthquake. Can cause serious damage over larger areas. • 8 or greater - Great earthquake. Can cause serious damage in areas several hundred kilometers across. ...
... • 6.1-6.9 - Can be destructive in areas up to about 100 kilometers across where people live. • 7.0-7.9 - Major earthquake. Can cause serious damage over larger areas. • 8 or greater - Great earthquake. Can cause serious damage in areas several hundred kilometers across. ...