Number Name Honors Section 5-1
... 10. Is the coefficient of friction the same between two identical surfaces in a lab on Earth and in a lab in a space colony on the moon? Explain __________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ...
... 10. Is the coefficient of friction the same between two identical surfaces in a lab on Earth and in a lab in a space colony on the moon? Explain __________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ...
Earthquakes "I can..." Review
... How does Earthquake energy move? How are earthquakes measured? How are earthquakes located? How can we make earthquake proof buildings? What happens at plate boundaries? What affects the strength of an earthquake? How do we know what it is like inside the earth? How and why do the plates move? ...
... How does Earthquake energy move? How are earthquakes measured? How are earthquakes located? How can we make earthquake proof buildings? What happens at plate boundaries? What affects the strength of an earthquake? How do we know what it is like inside the earth? How and why do the plates move? ...
Laws of Motion Test Name
... mass of 0.78 kg, which ball will have the greater acceleration? (F=ma) a. The one with a mass of .78 kg will have the greatest acceleration. b. The one with a mass of .52 kg will have the greatest acceleration. c. They will both accelerate at the same rate. d. Neither will accelerate. Use the pictur ...
... mass of 0.78 kg, which ball will have the greater acceleration? (F=ma) a. The one with a mass of .78 kg will have the greatest acceleration. b. The one with a mass of .52 kg will have the greatest acceleration. c. They will both accelerate at the same rate. d. Neither will accelerate. Use the pictur ...
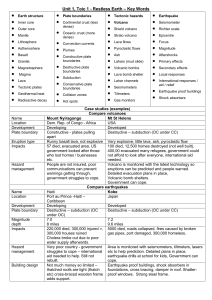
Our own Earth`s interior structure, and surface features will be
... nebula) comprised of mostly hydrogen and helium. Condensation of material is temperature sensitive. Only denser, heavier elements condensed and became trapped in the forming terrestrial planets. Farther from the forming Sun, ices could condense along with rocky and metallic grains. The composition, ...
... nebula) comprised of mostly hydrogen and helium. Condensation of material is temperature sensitive. Only denser, heavier elements condensed and became trapped in the forming terrestrial planets. Farther from the forming Sun, ices could condense along with rocky and metallic grains. The composition, ...
Earthquakes-1
... Earthquake Intensity • Richter Scale – measures the strength of an earthquake – increase of one unit of magnitude (for example, from 4.6 to 5.6) represents a 10-fold increase in wave amplitude on a seismogram – or approximately a 32-fold increase in the ...
... Earthquake Intensity • Richter Scale – measures the strength of an earthquake – increase of one unit of magnitude (for example, from 4.6 to 5.6) represents a 10-fold increase in wave amplitude on a seismogram – or approximately a 32-fold increase in the ...
Name: ___________________________ Chapter 6 Notes: Earthquakes Stress
... Moment Magnitude Scale: rating that estimates the _________ released by an earthquake. Scientists study _______________ Seismograph: instrument that _______________ and measures seismic waves These show the ____________ of waves present and how __________ they were. Comparing Magnitude F ...
... Moment Magnitude Scale: rating that estimates the _________ released by an earthquake. Scientists study _______________ Seismograph: instrument that _______________ and measures seismic waves These show the ____________ of waves present and how __________ they were. Comparing Magnitude F ...
Forces and Motion Review
... Weight is the force of gravity and there are different amounts of gravity on each planet so therefore your weight will change. ...
... Weight is the force of gravity and there are different amounts of gravity on each planet so therefore your weight will change. ...
to Unit 5 Topic 5-6
... which can make it bend and stretch - when the pressure is too great, the rock breaks suddenly creating a fault • There are three types of movement, of the tectonic plates, along a fault (see Figure 5.54, p. 403) ...
... which can make it bend and stretch - when the pressure is too great, the rock breaks suddenly creating a fault • There are three types of movement, of the tectonic plates, along a fault (see Figure 5.54, p. 403) ...