* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces and Motion Review
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
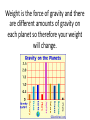
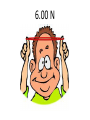
Forces and Motion Review 1. What does an object have that will cause it to resist a change in motion? Inertia 2. What are the two elastic forces called? Tension and Compression 3. The weight of an object is dependent on its _________________. Mass 4. What are forces measured in? Newtons 5.Calculate the kinetic energy of a beagle that weighs 30 kg and is running at a speed of 4 m/s. 240 J 6. If Shelby’s mass is 16 kg, what will be her mass on the moon? 16 kg – Mass does NOT change on different planets. 7. What about you is going to change on different planets? Weight 8. Why does your weight change on different planets? Weight is the force of gravity and there are different amounts of gravity on each planet so therefore your weight will change. 9. Anything that has mass and takes up space is known as what? Matter 10. If the north pole of one magnet is brought near the north pole of another magnet, what is going to happen? Repulsion 11. Give an example of Newton’s First Law of Motion. When you roll a ball and it a hits a wall, the wall is the unbalanced force that stops the ball’s motion. 12. What has the greatest impact on the friction of a block pulled across a surface? The type of surface in contact with the block. 13. What is the energy associated with the mousetrap car, the fan car, the rollercoaster or any other moving object called? Kinetic Energy 14. If I put my dachshund, Greta, who weighs 10 kg on top of a table that is 2 meters high. What is her gravitational potential energy? (Don’t forget to multiply by the force of gravity: 9.8 N/kg) 10 kg x 2 m x 9.8 N/kg = 196 J 15. What kind of force are you exerted when you rub your hands together? Frictional Force 16. The amount of matter in an object is _________________. Mass 17. Explain the motion of the mousetrap car and the fan car. Fan Car – speed is constant Mousetrap car – great acceleration and an abrupt stop. 18. If a car travels 30 meters in 10 seconds, what is the average speed? 3 meters/second 19. You pull a wooden block at a steady speed across a tabletop with a spring scale. The scale registers 2.00 N. If you place another block (just like the first one) on top of the block and pull the two blocks with the spring scale at a steady speed, what will the scale register? 4.00 N 20. A rubber band is stretched 2.0 cm with a spring scale, and the spring scale registers 3.0 N. If you stretched the rubber band twice as far (to 4.0 cm), what would you expect the spring scale to register? 6.00 N 21. Earth’s ___________ attracts objects near it, just like magnets attract objects near them. Gravity