Rock Review Sheet
... How do scientists decide if a rock is igneous, metamorphic or sedimentary? What are extrusive igneous rocks? What are intrusive igneous rocks? What term is used to describe the size and arrangement of crystals in an igneous rock? What process has a great effect on this term? Granite, pumice and scor ...
... How do scientists decide if a rock is igneous, metamorphic or sedimentary? What are extrusive igneous rocks? What are intrusive igneous rocks? What term is used to describe the size and arrangement of crystals in an igneous rock? What process has a great effect on this term? Granite, pumice and scor ...
Chapter 17 - MrFuglestad
... Scientists also found that there is more sediment on the sea floor as you move away from the Mid-Ocean ridge. Scientists map the age of the rocks on the ocean floor with isochrons. An isochron is line on a map that connects points that have the same age. ...
... Scientists also found that there is more sediment on the sea floor as you move away from the Mid-Ocean ridge. Scientists map the age of the rocks on the ocean floor with isochrons. An isochron is line on a map that connects points that have the same age. ...
Name: - Cobb Learning
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time B ...
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time B ...
Review 1 - Introduction and Minerals
... A. Nuclei of bonding atoms exchange electrons; the resulting ions are bonded together by the attractive forces between the negative and positive nucleons. B. Atoms of two different elements share electrons and protons; the resulting compound is bonded together by the strong, binding energy ofshared ...
... A. Nuclei of bonding atoms exchange electrons; the resulting ions are bonded together by the attractive forces between the negative and positive nucleons. B. Atoms of two different elements share electrons and protons; the resulting compound is bonded together by the strong, binding energy ofshared ...
Plate Tectonics – Guided Notes
... 5. _________________ _______________ type of convergent boundary created where one plate bends and sinks beneath the other. • Old Sea Floor being destroyed 6. The newly formed magma is forced upward along these plate boundaries, forming ___________________. Where Plates Collide 1. A subduction zone ...
... 5. _________________ _______________ type of convergent boundary created where one plate bends and sinks beneath the other. • Old Sea Floor being destroyed 6. The newly formed magma is forced upward along these plate boundaries, forming ___________________. Where Plates Collide 1. A subduction zone ...
Cells (Major Organelles and their Functions) Nucleus – contains
... breakage (cleavage or fracture). Rocks have 3 main types. Sedimentary – formed by weathering, erosion, deposition, cementation and compaction. Igneous – formed from melting into magma then cooling. Intrusive igneous cools inside the earth while extrusive igneous cools on the outside (lava that has c ...
... breakage (cleavage or fracture). Rocks have 3 main types. Sedimentary – formed by weathering, erosion, deposition, cementation and compaction. Igneous – formed from melting into magma then cooling. Intrusive igneous cools inside the earth while extrusive igneous cools on the outside (lava that has c ...
Name
... Wegener’s evidence was not disputed. He cited fossil evidence which included a fern-like plant called Glossopteris and freshwater reptiles called Mesosaurus and Lystrosaurus. Wegener also cited evidence of climate change such as glacial striations on Africa, and fossils of tropical plants in Spitsbe ...
... Wegener’s evidence was not disputed. He cited fossil evidence which included a fern-like plant called Glossopteris and freshwater reptiles called Mesosaurus and Lystrosaurus. Wegener also cited evidence of climate change such as glacial striations on Africa, and fossils of tropical plants in Spitsbe ...
ppt
... • began to break up ~750Myr ago • eventually reassembled >200Myr ago “Pangaea” • its breakup led to our continents today ...
... • began to break up ~750Myr ago • eventually reassembled >200Myr ago “Pangaea” • its breakup led to our continents today ...
Plate Tectonics Review & The Rock Cycle (11/3)
... Divergent plates – plates move apart Magma – flows up through the resulting cracks forms new rocks (seafloor spreading) Oceanic ridge – some of which have higher peaks and deeper canyons than earth’s continents ...
... Divergent plates – plates move apart Magma – flows up through the resulting cracks forms new rocks (seafloor spreading) Oceanic ridge – some of which have higher peaks and deeper canyons than earth’s continents ...
volcanic
... What happens when oceanic and continental plates collide? • The asthenosphere and the lithosphere are disrupted • The continental lithosphere subducts beneath the oceanic lithosphere • Mountains can be created through uplift and volcanic eruptions. • Valleys are created by the excessive energy rele ...
... What happens when oceanic and continental plates collide? • The asthenosphere and the lithosphere are disrupted • The continental lithosphere subducts beneath the oceanic lithosphere • Mountains can be created through uplift and volcanic eruptions. • Valleys are created by the excessive energy rele ...
Plate Tectonic Test Use the pictures above to answer questions 1
... ____ 23. Convection currents in the Earth’s mantle cause crustal plates to move. The drawing above shows a lab set up designed to model this process. If the two corks floating on the water represent the continents, which of the following outcomes is most likely to result from this investigation? ...
... ____ 23. Convection currents in the Earth’s mantle cause crustal plates to move. The drawing above shows a lab set up designed to model this process. If the two corks floating on the water represent the continents, which of the following outcomes is most likely to result from this investigation? ...
Plates move apart
... ocean ridges, rift valleys form along divergent boundary, as the sea floor spreads apart. ...
... ocean ridges, rift valleys form along divergent boundary, as the sea floor spreads apart. ...
How are mountains formed?
... They move because a plume of magma is rising deep within the earth’s mantle (the outer layer of the earth) As it moves, pressure builds up which forces the plates to move. As they move against each other, they cause are sites of intense geologic activity, such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and ...
... They move because a plume of magma is rising deep within the earth’s mantle (the outer layer of the earth) As it moves, pressure builds up which forces the plates to move. As they move against each other, they cause are sites of intense geologic activity, such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and ...
Slide 1
... What is the main cause of plate movement? Convection currents How do convection currents work? Core heats up molten rock making it less dense. The molten rock rises up towards the crust, where it cools down. As it cools it gets more dense and begins to sink back down through the mantle. This cycle w ...
... What is the main cause of plate movement? Convection currents How do convection currents work? Core heats up molten rock making it less dense. The molten rock rises up towards the crust, where it cools down. As it cools it gets more dense and begins to sink back down through the mantle. This cycle w ...
Study Guide - ab032.k12.sd.us
... -Another runs along the Mediterranean Sea through Iran and then continues through Indonesia and the Pacific -Over 80% of land volcanoes occur in these two belts -Most are along plate boundaries Rift Volcanoes-volcanoes that form where plates are moving apart leaving gaps at the edges of the spreadin ...
... -Another runs along the Mediterranean Sea through Iran and then continues through Indonesia and the Pacific -Over 80% of land volcanoes occur in these two belts -Most are along plate boundaries Rift Volcanoes-volcanoes that form where plates are moving apart leaving gaps at the edges of the spreadin ...
End of unit exam study guide
... • When mining diamonds deep in the earth’s crust, what do you think will happen to the temperature? Goes up due to close proximity to the asthenosphere • What are the layers of the earth? In order Use 6th ...
... • When mining diamonds deep in the earth’s crust, what do you think will happen to the temperature? Goes up due to close proximity to the asthenosphere • What are the layers of the earth? In order Use 6th ...
Plate Tectonics - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... Volcanoes are formed by: - Subduction - Rifting - Hotspots ...
... Volcanoes are formed by: - Subduction - Rifting - Hotspots ...
Geology Lecture 8 Plate Tectonics and Hotspots
... • Plates exist • Plates move • Plates interact and generate geologic ...
... • Plates exist • Plates move • Plates interact and generate geologic ...
4. What are two examples of hot spots from the
... generation in the legends of Pele, the fiery Goddess of Volcanoes. Pele originally lived on Kauai. When her older sister Namakaokahai, the Goddess of the Sea, attacked her, Pele fled to the Island of Oahu. When she was forced by Namakaokahai to flee again, Pele moved southeast to Maui and finally to ...
... generation in the legends of Pele, the fiery Goddess of Volcanoes. Pele originally lived on Kauai. When her older sister Namakaokahai, the Goddess of the Sea, attacked her, Pele fled to the Island of Oahu. When she was forced by Namakaokahai to flee again, Pele moved southeast to Maui and finally to ...
Lab 3 Presentation slides
... • Associated with deep trenches and volcanic island arcs that are parallel to the trench e.g., Tonga, Aleutians Ocean-Continent Convergence • Subduction of more dense oceanic plate beneath continental plate • Associated with deep ocean trenches near continental volcanic arcs e.g., Andes, Cascades Co ...
... • Associated with deep trenches and volcanic island arcs that are parallel to the trench e.g., Tonga, Aleutians Ocean-Continent Convergence • Subduction of more dense oceanic plate beneath continental plate • Associated with deep ocean trenches near continental volcanic arcs e.g., Andes, Cascades Co ...
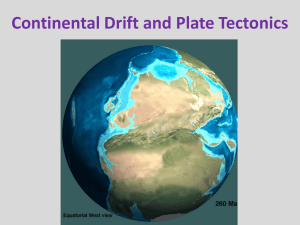
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
... • Oceanic ridges • Abysall plain • Denser than continental • < 150 my old ...
... • Oceanic ridges • Abysall plain • Denser than continental • < 150 my old ...
Class notes ()
... What do we know about the shape of magmatic bodies? Are they sheets? Blobs? Spheres? ...
... What do we know about the shape of magmatic bodies? Are they sheets? Blobs? Spheres? ...
Rock_Cycle_and_Igneous_Rocks
... magma/lava • Igneous rocks can be classified based on LOCATION (which tells the texture) and COMPOSITION (which tells the color) ...
... magma/lava • Igneous rocks can be classified based on LOCATION (which tells the texture) and COMPOSITION (which tells the color) ...
Section 1 Review
... 300 million years ago and that began to break up 200 million years ago Panthalassa the single, large ocean that ...
... 300 million years ago and that began to break up 200 million years ago Panthalassa the single, large ocean that ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.