Reading Record Assessment
... (The key to understanding how earthquakes happen is knowing that Earth is made up of different layers.) ...
... (The key to understanding how earthquakes happen is knowing that Earth is made up of different layers.) ...
The Layers of Earth
... Heat maintained by insulation of outer layers Powers all geologic activity ...
... Heat maintained by insulation of outer layers Powers all geologic activity ...
50 PLATE TECTONICS I. Introduction A. General 1. The theory of
... Model: the lower or inner portion of the mantle, near the core, is hotter than the upper mantle, this unequal distribution of heat results in circulation of heated, semiplastic mantle material...warm, less dense material of lower mantle rises very slowly in regions of spreading centers, spreads late ...
... Model: the lower or inner portion of the mantle, near the core, is hotter than the upper mantle, this unequal distribution of heat results in circulation of heated, semiplastic mantle material...warm, less dense material of lower mantle rises very slowly in regions of spreading centers, spreads late ...
Geology - s3.amazonaws.com
... So how do scientist know what is inside the Earth? Making inferences (conclusion based on evidence)… • Make scale models • Drill into the Earth • Study energy waves from earthquake • Study rocks that spew from volcanoes ...
... So how do scientist know what is inside the Earth? Making inferences (conclusion based on evidence)… • Make scale models • Drill into the Earth • Study energy waves from earthquake • Study rocks that spew from volcanoes ...
IgneousPet423-13Intro
... magmatic liquids. They represent aliquots of liquid that have escaped to the surface. The compositional variation observed in the liquids that the volcanic rocks represent is produced by varying degrees of crystal fractionation of a largely “gabbroic” mineral assemblage that now comprises plutonic i ...
... magmatic liquids. They represent aliquots of liquid that have escaped to the surface. The compositional variation observed in the liquids that the volcanic rocks represent is produced by varying degrees of crystal fractionation of a largely “gabbroic” mineral assemblage that now comprises plutonic i ...
Inside the Earth
... • 5-100 km thick • 2 types of crust – Oceanic (very dense, made of basalt) – Continental (less dense, made of granite) ...
... • 5-100 km thick • 2 types of crust – Oceanic (very dense, made of basalt) – Continental (less dense, made of granite) ...
無投影片標題
... isostatic equilibrium, a process analogous to a ship floating in water. • Some seismic waves – energy associated with earthquakes – can pass through the Earth. Analysis of how these waves are changed, and the time required for their passage, has told researchers much about conditions inside Earth. ...
... isostatic equilibrium, a process analogous to a ship floating in water. • Some seismic waves – energy associated with earthquakes – can pass through the Earth. Analysis of how these waves are changed, and the time required for their passage, has told researchers much about conditions inside Earth. ...
Chapter 4.2 Plate Tectonics Theory
... Lithosphere—the oceanic and continental crust and the rigid upper mantle. Asthenosphere—a layer of slowly flowing, deformable rock under the lithosphere. Lithosphere is broken into separate plates that “float” on the denser asthenosphere. The continents and oceans are carried along on the moving l ...
... Lithosphere—the oceanic and continental crust and the rigid upper mantle. Asthenosphere—a layer of slowly flowing, deformable rock under the lithosphere. Lithosphere is broken into separate plates that “float” on the denser asthenosphere. The continents and oceans are carried along on the moving l ...
06SC_TEST7 - Secondary Science Wiki
... 4. The movement of tectonic plates changes the surface of the Earth. Which type of plate boundary would most likely form a mountain range? A. convergent boundary without subduction B. convergent boundary with subduction C. divergent boundary D. transform boundary ...
... 4. The movement of tectonic plates changes the surface of the Earth. Which type of plate boundary would most likely form a mountain range? A. convergent boundary without subduction B. convergent boundary with subduction C. divergent boundary D. transform boundary ...
6th Grade Science Formative Assessment 5 Multiple Choice
... 4. The movement of tectonic plates changes the surface of the Earth. Which type of plate boundary would most likely form a mountain range? A. convergent boundary without subduction B. convergent boundary with subduction C. divergent boundary D. transform boundary ...
... 4. The movement of tectonic plates changes the surface of the Earth. Which type of plate boundary would most likely form a mountain range? A. convergent boundary without subduction B. convergent boundary with subduction C. divergent boundary D. transform boundary ...
The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... spreading and Earth’s plates into a single scientific theory, or a well-tested concept that explains a wide range of observations. Theory of plate tectonics explains the formation, movement and subduction of Earth’s plates. Theory highlights: ...
... spreading and Earth’s plates into a single scientific theory, or a well-tested concept that explains a wide range of observations. Theory of plate tectonics explains the formation, movement and subduction of Earth’s plates. Theory highlights: ...
rocks - OCW Usal
... • The more general is based in the quantity of The more general is based in the quantity of the forming minerals that are organized as • Primary: Pi – Essential: more than 5% in volume – Accessory: less than 5% in volume • Secondary: formed after any primary • This general system is mainly working ...
... • The more general is based in the quantity of The more general is based in the quantity of the forming minerals that are organized as • Primary: Pi – Essential: more than 5% in volume – Accessory: less than 5% in volume • Secondary: formed after any primary • This general system is mainly working ...
Unit 4-Dynamic Crust PowerPoint
... with gases, begins to rise up through cracks and weak spots in the crust. 2. When this molten material, along with gases from inside earth, break through the surface, it may flow out on the surface, and then it is called _____. --Where do they form? 1. __________________________________ ____________ ...
... with gases, begins to rise up through cracks and weak spots in the crust. 2. When this molten material, along with gases from inside earth, break through the surface, it may flow out on the surface, and then it is called _____. --Where do they form? 1. __________________________________ ____________ ...
Dynamic Earth WebQuest
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time B ...
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time B ...
Volcanoes - School District 27J
... examples in Indonesia) ˃ Where two oceanic plates diverge (Iceland) ˃ Where a hot blob of magma within the mantle rises to the surface (Hawaiian islands) ˃ Where an oceanic plate subducts under a continental plate (Mt. St. Helens, WA) ...
... examples in Indonesia) ˃ Where two oceanic plates diverge (Iceland) ˃ Where a hot blob of magma within the mantle rises to the surface (Hawaiian islands) ˃ Where an oceanic plate subducts under a continental plate (Mt. St. Helens, WA) ...
Constraints on the evolution of oceanic lithosphere from surface
... Plate tectonic manifests itself most simply in ocean basins. A plate-cooling model has been used extensively to describe the evolution of oceanic lithosphere and is able to predict the observed age-dependent trend of seafloor topography. Various global and basin-wide seismic models also suggest that ...
... Plate tectonic manifests itself most simply in ocean basins. A plate-cooling model has been used extensively to describe the evolution of oceanic lithosphere and is able to predict the observed age-dependent trend of seafloor topography. Various global and basin-wide seismic models also suggest that ...
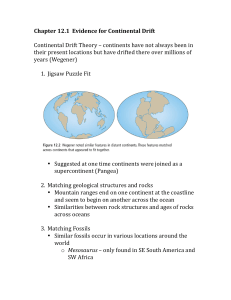
Chapter 12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift Continental Drift Theory
... Chapter 12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift ...
... Chapter 12.1 Evidence for Continental Drift ...
Plate Tectonics and Continental Accretion
... seen in subduction zones where on oceanic plate descends beneath a continental plate. Fragments of rocks forming the upper layers of the oceanic plate are scraped off the downgoing oceanic plate and become smeared onto the bottom and leading edge of the overriding continental plate. This process wor ...
... seen in subduction zones where on oceanic plate descends beneath a continental plate. Fragments of rocks forming the upper layers of the oceanic plate are scraped off the downgoing oceanic plate and become smeared onto the bottom and leading edge of the overriding continental plate. This process wor ...
S024: Plate Tectonics
... Volcanoes form in the middle of Volcanoes form below the surface of tectonic A. B. a tectonic plate. plates. Volcanoes form where tectonic Volcanoes form where earthquakes are least C. D. plates meet other plates. likely to occur. Source: MCAS: 2006, Science and Technology/Engineering – Grade 8 http ...
... Volcanoes form in the middle of Volcanoes form below the surface of tectonic A. B. a tectonic plate. plates. Volcanoes form where tectonic Volcanoes form where earthquakes are least C. D. plates meet other plates. likely to occur. Source: MCAS: 2006, Science and Technology/Engineering – Grade 8 http ...
10-2
... 28. A narrow valley that forms where the plates separate at a divergent boundary is called a _______________________________________. 29. Where are most divergent boundaries located? _______________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ...
... 28. A narrow valley that forms where the plates separate at a divergent boundary is called a _______________________________________. 29. Where are most divergent boundaries located? _______________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ...
Earth Resources
... Convergent—plates pushed together Oceanic plate runs into continental—continental over oceanic Subduction—distinct subduction zones ...
... Convergent—plates pushed together Oceanic plate runs into continental—continental over oceanic Subduction—distinct subduction zones ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.