Momentum & Collisions
... • In many situations, such as a bullet hitting a carrot, we cannot use Newton’s second law to solve problems because we know very little about the complicated forces involved. • In this chapter, we shall introduce momentum and impulse, and the conservation of momentum, to solve such problems. ...
... • In many situations, such as a bullet hitting a carrot, we cannot use Newton’s second law to solve problems because we know very little about the complicated forces involved. • In this chapter, we shall introduce momentum and impulse, and the conservation of momentum, to solve such problems. ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... D. 200 N 4th Item Specification: Given a scenario, predict outcomes based on application of Newton’s Three Laws of Motion. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 13. A bat strikes a ball into the outfield. If the action force is the bat hitting the ball, the reaction force is A. the ball hitting the bat. B. the ...
... D. 200 N 4th Item Specification: Given a scenario, predict outcomes based on application of Newton’s Three Laws of Motion. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 13. A bat strikes a ball into the outfield. If the action force is the bat hitting the ball, the reaction force is A. the ball hitting the bat. B. the ...
PDF (English
... Here you see footage of hurricanes that formed in the Atlantic Ocean during 2009. Do you see that every single hurricane rotates counterclockwise? All hurricanes formed in the Northern hemisphere rotate counterclockwise. In this video, we'll provide you with the tools to explain why hurricanes rotat ...
... Here you see footage of hurricanes that formed in the Atlantic Ocean during 2009. Do you see that every single hurricane rotates counterclockwise? All hurricanes formed in the Northern hemisphere rotate counterclockwise. In this video, we'll provide you with the tools to explain why hurricanes rotat ...
Physics 1111 - Term A 2014 Important Facts
... 4- Approach and method are correct, but there are minor numerical or algebraic errors. If you substitute numbers for letters at the start of the calculation, rather than working the problem symbolically and plugging in numbers at the end, and get the right answer, you will usually get a 4, because ...
... 4- Approach and method are correct, but there are minor numerical or algebraic errors. If you substitute numbers for letters at the start of the calculation, rather than working the problem symbolically and plugging in numbers at the end, and get the right answer, you will usually get a 4, because ...
IntroTHT_2e_SM_Chap01
... 1-10C Pound-mass lbm is the mass unit in English system whereas pound-force lbf is the force unit. One pound-force is the force required to accelerate a mass of 32.174 lbm by 1 ft/s 2. In other words, the weight of a 1-lbm mass at sea level is 1 lbf. ...
... 1-10C Pound-mass lbm is the mass unit in English system whereas pound-force lbf is the force unit. One pound-force is the force required to accelerate a mass of 32.174 lbm by 1 ft/s 2. In other words, the weight of a 1-lbm mass at sea level is 1 lbf. ...
Wed Apr 6 2016 06:00 PM EDT
... The object is in equilibrium if the net torque on the object is zero. The object is in equilibrium if the net force and the net torque on the object are both zero. The object cannot be in equilibrium because more than one force acts on it. The object is in equilibrium if the forces are equal in magn ...
... The object is in equilibrium if the net torque on the object is zero. The object is in equilibrium if the net force and the net torque on the object are both zero. The object cannot be in equilibrium because more than one force acts on it. The object is in equilibrium if the forces are equal in magn ...
Problem set 11
... constant k = 4 and external force FE = 10 cos (3t). Determine the position of the mass at any time. 4. A body of mass 4 kg will stretch a spring 80 centimeters. This same body is attached to such a spring with an accompanying dashpot. Suppose the damping constant is 49 N. At t = 0, the mass is given ...
... constant k = 4 and external force FE = 10 cos (3t). Determine the position of the mass at any time. 4. A body of mass 4 kg will stretch a spring 80 centimeters. This same body is attached to such a spring with an accompanying dashpot. Suppose the damping constant is 49 N. At t = 0, the mass is given ...
Pure Unit 06
... 6.2 Work Gravitational potential energy and work done Potential energy is stored energy • Gravitational potential energy (G.P.E) is the energy a body has due to its position • To find G.P.E. of an object near surface of Earth, we need to consider its mass and its height above the ground. ...
... 6.2 Work Gravitational potential energy and work done Potential energy is stored energy • Gravitational potential energy (G.P.E) is the energy a body has due to its position • To find G.P.E. of an object near surface of Earth, we need to consider its mass and its height above the ground. ...
ch2_osc_waves
... One has to be wary in using numerical method because you are not always confident that the results are accurate. The approximation method used in this simulations only gives reasonable results when the time increment is very small so that during any time step the acceleration does not change very mu ...
... One has to be wary in using numerical method because you are not always confident that the results are accurate. The approximation method used in this simulations only gives reasonable results when the time increment is very small so that during any time step the acceleration does not change very mu ...
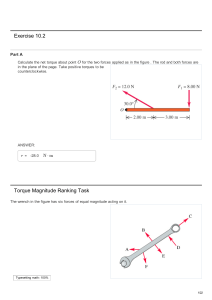
Exercise 10.2 Torque Magnitude Ranking Task
... axis of the disk is vertical and the disk is supported by frictionless bearings. The motor of the turntable is off, so there is no external torque being applied to the axis. Another disk (a record) is dropped onto the first such that it lands coaxially (the axes coincide). The moment of inertia of t ...
... axis of the disk is vertical and the disk is supported by frictionless bearings. The motor of the turntable is off, so there is no external torque being applied to the axis. Another disk (a record) is dropped onto the first such that it lands coaxially (the axes coincide). The moment of inertia of t ...