* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physical Science ALDs Organized by GPS
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamic temperature wikipedia , lookup
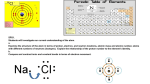
Physical Science – GPS vs. ALD’s GPS Beginning Learner Developing Learner Proficient Learner SPS1. Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. a. Examine the structure of the atom in terms of proton, electron, and neutron locations. atomic mass and atomic number. atoms with different numbers of neutrons (isotopes). explain the relationship of the proton number to the element’s identity. b. Compare and contrast ionic and covalent bonds in terms of electron movement. recognize the differences between atoms and molecules identify the structure of the atom examine the structure of the atom in terms of proton, electron, and neutron locations, atomic mass and atomic number, and atoms with different numbers of neutrons (isotopes) and explain the relationship of the proton number to the element’s identity recognize that electrons are involved in bonding compare and contrast ionic and covalent bonds in terms of electron movement identify methods of electron transfer Distinguished Learner GPS Beginning Learner SPS2. Students will explore the nature of matter, its classifications, and its system for naming types of matter. a. Calculate density when given a means to determine a substance’s mass and volume. b. Predict formulas for stable binary ionic compounds based on balance of charges. c. Use IUPAC nomenclature for transition between chemical names and chemical formulas of binary ionic compounds (containing representative elements). binary covalent compounds (i.e. carbon dioxide, carbon tetrachloride). d. Demonstrate the Law of Conservation of Matter in a chemical reaction. e. Apply the Law of Conservation of Matter by balancing the following types of chemical equations: Synthesis Decomposition Single Replacement Double Replacement Developing Learner Proficient Learner Distinguished Learner explore the nature of matter, its classifications, and the system for naming types of matter calculate density when given a means to determine a substance’s mass and volume predict formulas for stable binary ionic compounds based on balance of charges use IUPAC nomenclature for transitions between chemical names and chemical formulas of binary ionic compounds (containing representative elements) and binary covalent compounds (carbon dioxide, carbon tetrachloride) describe the Law of Conservation of Matter identify reactants and products in a chemical reaction recognize a balanced equation apply the Law of Conservation of Matter in a chemical reaction balance chemical equations (synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement) GPS Beginning Learner Developing Learner Proficient Learner Distinguished Learner SPS3. Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. a. Differentiate among alpha and beta particles and gamma radiation. b. Differentiate between fission and fusion. c. Explain the process halflife as related to radioactive decay. d. Describe nuclear energy, its practical application as an alternative energy source, and its potential problems. identify the types of radioactivity and differentiate between fission and fusion explain the process of halflife as it relates to radioactive decay differentiate between alpha and beta particles and gamma radiation determine the half-life given a graph of radioactive decay describe nuclear energy, its practical application as an alternative energy source, and its potential problems GPS Beginning Learner Developing Learner Proficient Learner SPS4. Students will investigate the arrangement of the Periodic Table. a. Determine the trends of the use the Periodic Table of the following: Elements to locate metals, nonmetals, and metalloids Number of valence electrons Types of ions formed by representative elements Location of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids Phases at room temperature b. Use the Periodic Table to predict the above properties for representative elements. determine the trends in the number of valence electrons, types of ions formed by representative elements, and phases at room temperature use the Periodic Table of the Elements to predict the properties for representative elements Distinguished Learner GPS Beginning Learner Developing Learner Proficient Learner SPS5. Students will compare and contrast the phases of matter as they relate to atomic and molecular motion. a. Compare and contrast the atomic/molecular motion of solids, liquids, gases and plasmas. b. Relate temperature, pressure, and volume of gases to the behavior of gases. describe the movement of particles in solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas compare and contrast the atomic/molecular motion of solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas relate temperature, pressure, and volume of gases to the behavior of gases Distinguished Learner GPS Beginning Learner Developing Learner Proficient Learner Distinguished Learner describe solutions in terms of solute/solvent describe solutions in terms of concentration and conductivity SPS6. Students will investigate the properties of solutions. a. Describe solutions in terms of solute/solvent conductivity concentration b. Observe factors affecting the rate a solute dissolves in a specific solvent. c. Demonstrate that solubility is related to temperature by constructing a solubility curve. d. Compare and contrast the components and properties of acids and bases. e. Determine whether common household substances are acidic, basic, or neutral. investigate properties of solutions by observing factors affecting the rate at which a solute dissolves in a specific solvent demonstrate that solubility is related to temperature by constructing a solubility curve compare and contrast the components and properties of acids and bases determine whether common household substances are acidic, basic, or neutral GPS Beginning Learner Developing Learner Proficient Learner Distinguished Learner differentiate between conduction, convection, and radiation describe molecular motion as it relates to thermal energy changes in terms of conduction, convection, and radiation SPS7. Students will relate transformations and flow of energy within a system. a. Identify energy transformations within a system (e.g. lighting of a match). b. Investigate molecular motion as it relates to thermal energy changes in terms of conduction, convection, and radiation. c. Determine the heat capacity of a substance using mass, specific heat, and temperature. d. Explain the flow of energy in phase changes through the use of a phase diagram. describe energy transformations identify three types of heat transfer identify energy transformations within a system, such as lighting a match describe the three types of heat energy transfer (radiation, conduction, convection) determine the heat capacity of a substance using mass, specific heat, and temperature identify phase changes compare phase changes explain the flow of energy in phase changes through the use of a phase diagram GPS Beginning Learner Developing Learner Proficient Learner Distinguished Learner SPS8. Students will determine relationships among force, mass, and motion. a. Calculate velocity and acceleration. b. Apply Newton’s three laws to everyday situations by explaining the following: Inertia Relationship between force, mass and acceleration Equal and opposite forces c. Relate falling objects to gravitational force d. Explain the difference in mass and weight. e. Calculate amounts of work and mechanical advantage using simple machines. recognize examples of forces recognize balanced and unbalanced forces calculate velocity and acceleration demonstrate the effect of balanced and unbalanced forces on an object apply Newton’s three laws to everyday situations recognize simple machines that make work easier identify simple machines relate falling objects to gravitational force explain the difference between mass and weight calculate amounts of work and mechanical advantage for simple machines calculate the velocity of a falling object predict which machine would have the greatest mechanical advantage GPS Beginning Learner Developing Learner Proficient Learner Distinguished Learner SPS9. Students will investigate the properties of waves. a. Recognize that all waves transfer energy. b. Relate frequency and wavelength to the energy of different types of electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves. c. Compare and contrast the characteristics of electromagnetic and mechanical (sound) waves. d. Investigate the phenomena of reflection, refraction, interference, and diffraction. e. Relate the speed of sound to different mediums. f. Explain the Doppler Effect in terms of everyday interactions. recognize that all waves transfer energy explain that colors are distinguished by differences in wavelengths/frequencies relate frequency and wavelength to the energy of different types of electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves explain how the parts of a wave are affected by changes in amplitude and pitch describe electromagnetic and mechanical waves describe how the behavior of waves is affected by medium (air, liquid water, solids) compare and contrast the characteristics of electromagnetic and mechanical (sound) waves investigate the phenomena of reflection, refraction, interference, and diffraction relate the speed of sound to different mediums explain the Doppler Effect in terms of everyday interactions GPS Beginning Learner Developing Learner Proficient Learner Distinguished Learner SPS10. Students will investigate the properties of electricity and magnetism. a. Investigate static electricity in terms of friction induction conduction b. Explain the flow of electrons in terms of alternating and direct current. the relationship among voltage, resistance and current. simple series and parallel circuits. c. Investigate applications of magnetism and/or its relationship to the movement of electrical charge as it relates to electromagnets simple motors permanent magnets recognize that many electrons produce electricity demonstrate series and parallel circuits investigate static electricity in terms of friction, induction, and conduction define voltage, resistance, and current explain the flow of electrons in terms of alternating and direct current apply alternating and direct current in a real-world scenario explain the relationships between voltage, resistance, and current solve problems related to voltage, resistance, and current compare and contrast simple series and parallel circuits describe an electromagnet predict outcomes given series and parallel circuits explain magnetism and/or its relationship to the movement of electrical charge as it relates to electromagnets, including simple motors and permanent magnets identify types of circuits describe a permanent magnet explain how factors affect the strength of an electromagnet GPS Beginning Learner Developing Learner Proficient Learner recognize appropriate laboratory techniques recognize appropriate solutions for solving scientific problems recognize that different explanations can be used to explain a single set of data Distinguished Learner Characteristics of Science suggest reasonable hypotheses for identified problems recognize possible effects of measurement and calculation errors use technology to develop tables and graphs use dimensional analysis to solve problems use data as evidence to support scientific claims solve scientific problems by substituting quantitative values or using dimensional analysis and/or simple use technology to develop and algebraic formulas as test experimental or appropriate mathematical models