Force Motion Pasco Lab
... The purpose of this laboratory activity is to investigate the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. THEORY Newton described the relationship between acceleration, force, and mass as follows: The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net ...
... The purpose of this laboratory activity is to investigate the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. THEORY Newton described the relationship between acceleration, force, and mass as follows: The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net ...
Review the study notes and homework for the hour tests and
... Know that kinetic energy (Equation 6.2) is the energy of motion and how to use the work-energy theorem (Equation (6.3)) to solve problems in mechanics. Be familiar with gravitational potential energy: PE mgh where h is the height of an object of mass m relative to an arbitrary reference level. Kno ...
... Know that kinetic energy (Equation 6.2) is the energy of motion and how to use the work-energy theorem (Equation (6.3)) to solve problems in mechanics. Be familiar with gravitational potential energy: PE mgh where h is the height of an object of mass m relative to an arbitrary reference level. Kno ...
Lab 7 - Collisions and Momentum - Newton`s Third Law
... It would be nice to be able to use Newton’s formulation of the second law of motion to find collision forces, but it is difficult to measure the rate of change of momentum during a rapid collision without special instruments. However, measuring the momenta of objects just before and just after a col ...
... It would be nice to be able to use Newton’s formulation of the second law of motion to find collision forces, but it is difficult to measure the rate of change of momentum during a rapid collision without special instruments. However, measuring the momenta of objects just before and just after a col ...
MasteringPhysics: Assignmen
... Your score on this assignment is 121.4%. You received 83.01 out of a possible total of 85 points, plus 20.13 points of extra credit. ...
... Your score on this assignment is 121.4%. You received 83.01 out of a possible total of 85 points, plus 20.13 points of extra credit. ...
atomic structure - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... Calculate the energy required to excite one litre of hydrogen gas at 1 atm and 298 K to the first excited state of atomic hydrogen. The energy for the dissociation of H–H bond is 436 kJ mol–1. Also calculate the minimum frequency of photon to break this bond. Ans :- ...
... Calculate the energy required to excite one litre of hydrogen gas at 1 atm and 298 K to the first excited state of atomic hydrogen. The energy for the dissociation of H–H bond is 436 kJ mol–1. Also calculate the minimum frequency of photon to break this bond. Ans :- ...
Reference Material in Physics Class IX
... When a body floats or immerses in a liquid, the pressure on the bottom surface is more than that the pressure on the top surface. Due to the difference in pressure, an upward force acts on the body. This upward force is called upthrust or buoyant force. The buoyant force is equal to the weight of th ...
... When a body floats or immerses in a liquid, the pressure on the bottom surface is more than that the pressure on the top surface. Due to the difference in pressure, an upward force acts on the body. This upward force is called upthrust or buoyant force. The buoyant force is equal to the weight of th ...
Balloon Racer Unit Overview Unit Title: Force and Motion Lesson
... we must find something else. Let’s see if we can find the affect that mass and force have on the balloon! ...
... we must find something else. Let’s see if we can find the affect that mass and force have on the balloon! ...
Chapter 6 Work and Kinetic Energy
... True or false: (a) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its speed must have changed. (b) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its velocity must have changed. (c) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its direction of motion ...
... True or false: (a) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its speed must have changed. (b) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its velocity must have changed. (c) If the net or total work done on a particle was not zero, then its direction of motion ...
Rotational Motion
... the notches in the rims of the pulleys. The height of the super pulley should be adjusted so that the string between the two pulleys is horizontal. The angle of the super pulley should be adjusted so that the string enters the super pulley parallel to the groove of the super pulley. The super pulley ...
... the notches in the rims of the pulleys. The height of the super pulley should be adjusted so that the string between the two pulleys is horizontal. The angle of the super pulley should be adjusted so that the string enters the super pulley parallel to the groove of the super pulley. The super pulley ...
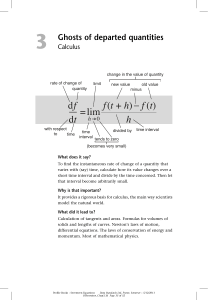
In Pursuit of the Unknown : 17 Equations That Changed
... had worked out the basics of calculus, some of Newton’s friends sparked a largely pointless but heated controversy about priority, accusing Leibniz of plagiarising Newton’s unpublished manuscripts. A few mathematicians from continental Europe responded with counter-claims of plagiarism by Newton. En ...
... had worked out the basics of calculus, some of Newton’s friends sparked a largely pointless but heated controversy about priority, accusing Leibniz of plagiarising Newton’s unpublished manuscripts. A few mathematicians from continental Europe responded with counter-claims of plagiarism by Newton. En ...