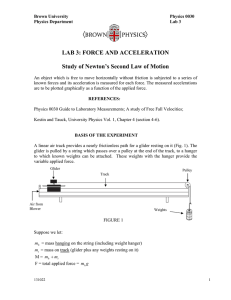
Physics - Higher Level - Paper Two
... kinetic energy of the rocket varies as it moves from the ground to its maximum height. ...
... kinetic energy of the rocket varies as it moves from the ground to its maximum height. ...
Introduction to Modern Physics PHYX 2710
... • Multiply both sides of Newton’s second law by the time interval over which the force acts: • The left side of the equation is impulse, the (average) force acting on an object multiplied by the time interval over which the force acts. ...
... • Multiply both sides of Newton’s second law by the time interval over which the force acts: • The left side of the equation is impulse, the (average) force acting on an object multiplied by the time interval over which the force acts. ...
ODU-Mechanics-Questions
... Section 1: Equations of motion ............................................................ 6 Equations of motion ........................................................................ 6 Motion – time graphs ...................................................................... 8 Section 2: Forces ...
... Section 1: Equations of motion ............................................................ 6 Equations of motion ........................................................................ 6 Motion – time graphs ...................................................................... 8 Section 2: Forces ...
chapter7
... The sign of the acceleration does not have to be the same as the sign of the angular speed The instantaneous angular acceleration is defined as the limit of the average acceleration as the ...
... The sign of the acceleration does not have to be the same as the sign of the angular speed The instantaneous angular acceleration is defined as the limit of the average acceleration as the ...
File
... 1. A tube is been placed upon the 1 m-high table and shaped into a three-quarters circle. A golf ball is pushed into the tube at one end at high speed. The ball rolls through the tube and exits at the opposite end. Describe the path of the golf ball as it exits the tube. 2. If the 50g golf ball leav ...
... 1. A tube is been placed upon the 1 m-high table and shaped into a three-quarters circle. A golf ball is pushed into the tube at one end at high speed. The ball rolls through the tube and exits at the opposite end. Describe the path of the golf ball as it exits the tube. 2. If the 50g golf ball leav ...
Physics 231 Topic 7: Oscillations Wade Fisher October 5-10 2012
... It must traverse the circumference of the orbit: D = 2 π R Thus, the speed S = D/T = 2 π R / T We can also express this in terms of an angular frequency: The angular frequency = / t = 2 π / T = the speed at which the angle is changing Units = 1/s or Radians/s MSU Physics 231 Fall 2012 ...
... It must traverse the circumference of the orbit: D = 2 π R Thus, the speed S = D/T = 2 π R / T We can also express this in terms of an angular frequency: The angular frequency = / t = 2 π / T = the speed at which the angle is changing Units = 1/s or Radians/s MSU Physics 231 Fall 2012 ...
1 - CSUN.edu
... 7. Calculate the percent error in table C. 8. Repeat the steps above for table D,E,F. Be sure to keep NET FORCE CONSTANT and increase mass while experimenting to find the answer for question b. You will need to recalculate the kinetic friction every time you add more mass. ...
... 7. Calculate the percent error in table C. 8. Repeat the steps above for table D,E,F. Be sure to keep NET FORCE CONSTANT and increase mass while experimenting to find the answer for question b. You will need to recalculate the kinetic friction every time you add more mass. ...
Lab 9: Newton`s Third Law and Conservation
... INVESTIGATION 2: NEWTON'S LAWS AND MOMENTUM CONSERVATION Your previous work should have shown that interaction forces between two objects are equal in magnitude and opposite in sign (direction) on a moment by moment basis for all the interactions you might have studied. This is a testimonial to the ...
... INVESTIGATION 2: NEWTON'S LAWS AND MOMENTUM CONSERVATION Your previous work should have shown that interaction forces between two objects are equal in magnitude and opposite in sign (direction) on a moment by moment basis for all the interactions you might have studied. This is a testimonial to the ...
Circular Motion
... finds that the body is at rest. This is because the body is lying at the same distance all the time as the body remains at rest. He concludes that the body is acted upon by a radially outward force which is equal and opposite of the tension in the string. This pseudo force which is equal and opposit ...
... finds that the body is at rest. This is because the body is lying at the same distance all the time as the body remains at rest. He concludes that the body is acted upon by a radially outward force which is equal and opposite of the tension in the string. This pseudo force which is equal and opposit ...