Chapter 5 Lecture
... Doubling the force causes double the reading on the spring. When both forces are applied, the reading is three times the initial reading. ...
... Doubling the force causes double the reading on the spring. When both forces are applied, the reading is three times the initial reading. ...
Force and Laws of Motion
... Earth in the direction of motion of the ball increases the speed of the ball. 4. A force may change the direction of a moving body. For example, when a moving cricket ball is hit by a bat, the cricket ball moves in a different direction. The force applied by the bat changes the direction of the movi ...
... Earth in the direction of motion of the ball increases the speed of the ball. 4. A force may change the direction of a moving body. For example, when a moving cricket ball is hit by a bat, the cricket ball moves in a different direction. The force applied by the bat changes the direction of the movi ...
PPT
... am confused about is direction. So Torque will point along the axis in either direction. I am just confused on how I can see the apply in real life. Like does a force pointing along the axis of rotation do anything? I bet you're going to say this can all be figured out with F = ma huh? My wish for " ...
... am confused about is direction. So Torque will point along the axis in either direction. I am just confused on how I can see the apply in real life. Like does a force pointing along the axis of rotation do anything? I bet you're going to say this can all be figured out with F = ma huh? My wish for " ...
Unit 4 Practice Test: Rotational Motion
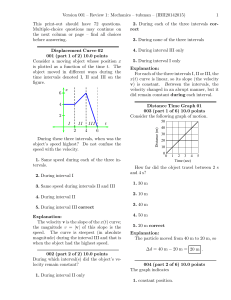
... horizontal component of this force, Fh, is the centripetal force and this force Fc = mrω2. However, if F increases so does its vertical component. When F is large enough so that its vertical component is equal to the weight of the child, the child’s feet leave the ground. 36. Mass resists changes in ...
... horizontal component of this force, Fh, is the centripetal force and this force Fc = mrω2. However, if F increases so does its vertical component. When F is large enough so that its vertical component is equal to the weight of the child, the child’s feet leave the ground. 36. Mass resists changes in ...
Chapter 06 Test B
... 6. An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion in a straight line summarizes a portion of Newton’s ____________________ law. 7. If the net force on an object is zero, the forces acting on it are ____________________. 8. The property of an object that resis ...
... 6. An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion in a straight line summarizes a portion of Newton’s ____________________ law. 7. If the net force on an object is zero, the forces acting on it are ____________________. 8. The property of an object that resis ...
Powerpoint
... energy. Ideally, when the foot is leaving the ground, the cycle of the motion will have advanced so that potential energy is being converted to kinetic energy. What fraction of an oscillation period should the time between landing and lift off correspond to? Given the period you calculated above, wh ...
... energy. Ideally, when the foot is leaving the ground, the cycle of the motion will have advanced so that potential energy is being converted to kinetic energy. What fraction of an oscillation period should the time between landing and lift off correspond to? Given the period you calculated above, wh ...
Experiment 4 The Simple Pendulum Reading:
... complete cycle is from when it’s going right at the lowest point of the swing until when it returns to the bottom twice and is again going right. 3.2 From these five measurements of the period, calculate the mean period and the standard deviation of the mean period using Kgraph or Excel. Do not roun ...
... complete cycle is from when it’s going right at the lowest point of the swing until when it returns to the bottom twice and is again going right. 3.2 From these five measurements of the period, calculate the mean period and the standard deviation of the mean period using Kgraph or Excel. Do not roun ...
Rotational speed
... center of gravity is A) displaced from its center. B) in the same place as its center of mass. C) stabilized by its structure. D) relatively low for such a tall building. E) above a place of support. ...
... center of gravity is A) displaced from its center. B) in the same place as its center of mass. C) stabilized by its structure. D) relatively low for such a tall building. E) above a place of support. ...
Static Equilibrium
... all of the object’s weight (Mg) is concentrated at the center of gravity. That is, if you were blindfolded and supported an object at its center of gravity on your finger, weightwise you would not be able to tell if it were perhaps a rod or a block of equal mass. If an object’s weight were concentra ...
... all of the object’s weight (Mg) is concentrated at the center of gravity. That is, if you were blindfolded and supported an object at its center of gravity on your finger, weightwise you would not be able to tell if it were perhaps a rod or a block of equal mass. If an object’s weight were concentra ...
Quiz3 Solutions
... = R F sin , where R is the distance from the part's center of gravity to the pivot point (here, the streetlight base) and F is the gravity force on that part, and θ is the angle between the two. For the vertical rod, θ is 180°, because the vector from the lamp base to the center of gravity of th ...
... = R F sin , where R is the distance from the part's center of gravity to the pivot point (here, the streetlight base) and F is the gravity force on that part, and θ is the angle between the two. For the vertical rod, θ is 180°, because the vector from the lamp base to the center of gravity of th ...
Experiment 5 The Simple Pendulum Reading:
... few times. Figure out how the gate works by moving the bob through the gate slowly, by hand. How many periods does the photo-gate measure? (Write it in your lab book!) 4.1. From three measurements of the period with the photo-gate, again calculate the mean and the standard deviation of the mean. Cal ...
... few times. Figure out how the gate works by moving the bob through the gate slowly, by hand. How many periods does the photo-gate measure? (Write it in your lab book!) 4.1. From three measurements of the period with the photo-gate, again calculate the mean and the standard deviation of the mean. Cal ...
Torque and Rotational Motion
... Rotational Inertia or Moment of Inertia • If you remember inertia is an object’s resistance to change. It is directly proportional to mass. • An object’s rotational inertia or moment of inertia is the object’s resistance to rotations. These are impacted by the size, shape and axis of rotation of th ...
... Rotational Inertia or Moment of Inertia • If you remember inertia is an object’s resistance to change. It is directly proportional to mass. • An object’s rotational inertia or moment of inertia is the object’s resistance to rotations. These are impacted by the size, shape and axis of rotation of th ...