EXPERIMENT 1- Measurements and Accuracy
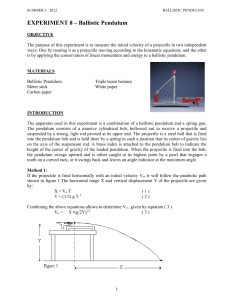
... Method 2: The initial velocity Vo of the projectile can also be determined by using the ballistic pendulum (Fig 2). It consists of a spring gun that fires a metallic ball of mass m which is caught by a catcher at the end of a pendulum of mass M. The collision between the ball and pendulum is perfect ...
... Method 2: The initial velocity Vo of the projectile can also be determined by using the ballistic pendulum (Fig 2). It consists of a spring gun that fires a metallic ball of mass m which is caught by a catcher at the end of a pendulum of mass M. The collision between the ball and pendulum is perfect ...
gravitational potential energy
... horizontal. Assuming that all three bears throw with the same speed, which rock will be traveling fastest when it hits the water?” Three students meet after the exam and discuss their answers. Emma: “Baby Bear’s rock will be going the fastest because it starts with a downward component of velocity.” ...
... horizontal. Assuming that all three bears throw with the same speed, which rock will be traveling fastest when it hits the water?” Three students meet after the exam and discuss their answers. Emma: “Baby Bear’s rock will be going the fastest because it starts with a downward component of velocity.” ...
simple harmonic motion
... mg Looks like spring force F mg s L L mg Like the spring ( Fs kx) k constant L Now, consider the angular frequency of the spring ...
... mg Looks like spring force F mg s L L mg Like the spring ( Fs kx) k constant L Now, consider the angular frequency of the spring ...
Chapter 1. Newton`s Laws of Motion
... rest in another frame sees that the body is not moving in a uniform motion, then this second frame of reference cannot be inertial. This may due, for example, to the fact that this frame of reference is itself accelerating in some fashion, which would account for the apparent non-uniform motion of t ...
... rest in another frame sees that the body is not moving in a uniform motion, then this second frame of reference cannot be inertial. This may due, for example, to the fact that this frame of reference is itself accelerating in some fashion, which would account for the apparent non-uniform motion of t ...
Force is not stored or used up. Because energy can be stored and
... Forces need not be exerted by living things or machines. Transforming energy from one form into another usually requires some kind of living or mechanical mechanism. The concept is not applicable to forces, which are an interaction between objects, not a thing to be transferred or transformed. Incor ...
... Forces need not be exerted by living things or machines. Transforming energy from one form into another usually requires some kind of living or mechanical mechanism. The concept is not applicable to forces, which are an interaction between objects, not a thing to be transferred or transformed. Incor ...
Work, Power, Kinetic Energy
... of a definite mechanical system through the action of a mechanical force acting on that system along a finite trajectory. By conservation of energy, work done on a system enhances its energy while work done by a system depletes it. If we can calculate this energy, we can often use it to then calcula ...
... of a definite mechanical system through the action of a mechanical force acting on that system along a finite trajectory. By conservation of energy, work done on a system enhances its energy while work done by a system depletes it. If we can calculate this energy, we can often use it to then calcula ...
fan cart physics
... Question: What happens to the cart when there is no force? 4. Form hypothesis: What will the motion of the cart be like when there is no force at all? (There is no friction in this model.) _____________________________________________ 5. Predict: Suppose a cart with no fans has a starting velocity o ...
... Question: What happens to the cart when there is no force? 4. Form hypothesis: What will the motion of the cart be like when there is no force at all? (There is no friction in this model.) _____________________________________________ 5. Predict: Suppose a cart with no fans has a starting velocity o ...
Lecture 9 Power
... m = 6.0 kg runs onto the left end of a curved ramp with speed v0 = 7.8 m/s at height y0 = 8.5 m above the floor. It then slides to the right and comes to a momentary stop when it reaches a height y = 11.1 m from the floor. The ramp is not frictionless. What is the increase ∆Eth in the thermal energy ...
... m = 6.0 kg runs onto the left end of a curved ramp with speed v0 = 7.8 m/s at height y0 = 8.5 m above the floor. It then slides to the right and comes to a momentary stop when it reaches a height y = 11.1 m from the floor. The ramp is not frictionless. What is the increase ∆Eth in the thermal energy ...
phys34210_13 - University of Surrey
... of time) by plotting the x-position of the object (Armadillo!) at different time intervals on an (x , t) plot. The average SPEED is simply the total distance travelled (independent of the direction or travel) divided by the time taken. Note speed is a SCALAR quantity, i.e., only its magnitude is imp ...
... of time) by plotting the x-position of the object (Armadillo!) at different time intervals on an (x , t) plot. The average SPEED is simply the total distance travelled (independent of the direction or travel) divided by the time taken. Note speed is a SCALAR quantity, i.e., only its magnitude is imp ...
2014 Exam and Revision Advice
... Common Errors: Momentum and energy of photons and electrons Examples: Comparing diffraction patterns between electrons and X-rays. Error: Assume that if momenta of both are the same, then their energies are also the same. Method: Draw up concept map linking quantities with relationships. ...
... Common Errors: Momentum and energy of photons and electrons Examples: Comparing diffraction patterns between electrons and X-rays. Error: Assume that if momenta of both are the same, then their energies are also the same. Method: Draw up concept map linking quantities with relationships. ...
AH (SHM) - mrmackenzie
... (a) Determine the value for the amplitude (A), period (T), frequency (f) and angular frequency (ω ω) of the motion. (b) Use values from part (a) to obtain an expression in the form y = A cos ωt for the displacement y from the equilibrium position of the object undergoing simple harmonic motion. (c) ...
... (a) Determine the value for the amplitude (A), period (T), frequency (f) and angular frequency (ω ω) of the motion. (b) Use values from part (a) to obtain an expression in the form y = A cos ωt for the displacement y from the equilibrium position of the object undergoing simple harmonic motion. (c) ...
無投影片標題
... Planck postulated that thermal radiation is emitted from a heated surface in discrete energy called quanta. The energy of these quanta is given by E = h, h = 6.625 x 10-34 J-sec (Planck’s constant) According to the photoelectric results, Einstein suggested that the energy in a light wave is als ...
... Planck postulated that thermal radiation is emitted from a heated surface in discrete energy called quanta. The energy of these quanta is given by E = h, h = 6.625 x 10-34 J-sec (Planck’s constant) According to the photoelectric results, Einstein suggested that the energy in a light wave is als ...
Ch#7 - KFUPM Faculty List
... acts on the block between A and B, as shown in Fig.2. If the kinetic energy of the block at A is 10 J, what is its kinetic energy at B? (Ans: 24 J) . Q#3 A 2.0-kg object moves along the +x-axis with a speed of 5 m/s under the influence of a force F= (3i+4j) N. What is the power delivered by this for ...
... acts on the block between A and B, as shown in Fig.2. If the kinetic energy of the block at A is 10 J, what is its kinetic energy at B? (Ans: 24 J) . Q#3 A 2.0-kg object moves along the +x-axis with a speed of 5 m/s under the influence of a force F= (3i+4j) N. What is the power delivered by this for ...