Motion in accelerated reference frames
... We again have a law of addition of velocities: the velocity of P in the O-system is the vector sum of the velocity VA of the fixed point of the A-system that coincides with P and the velocity vA of P relative to the A-system. This is illustrated for a special case in figure 1.2 discussed in the exampl ...
... We again have a law of addition of velocities: the velocity of P in the O-system is the vector sum of the velocity VA of the fixed point of the A-system that coincides with P and the velocity vA of P relative to the A-system. This is illustrated for a special case in figure 1.2 discussed in the exampl ...
Physics 1010: The Physics of Everyday Life
... object in vacuum minus weight of fluid having volume equal to that of object ...
... object in vacuum minus weight of fluid having volume equal to that of object ...
Gravitational potential
... careful here. This is a relationship between a vector and scalar quantity. We have taken the advantage by considering eld in one direction only and expressed the relation in scalar form, where sign indicates the direction with respect to assumed positive reference direction. In three dimensional re ...
... careful here. This is a relationship between a vector and scalar quantity. We have taken the advantage by considering eld in one direction only and expressed the relation in scalar form, where sign indicates the direction with respect to assumed positive reference direction. In three dimensional re ...
3. rotational motion - Mahesh Tutorials Science
... Friction is responsible for the motion but work done or dissipation of energy against friction is zero as there is no relative motion between body and surface at the point of contact. ...
... Friction is responsible for the motion but work done or dissipation of energy against friction is zero as there is no relative motion between body and surface at the point of contact. ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion Conclusion
... The concept of forces acting on a mass (one object) is intimately related to the concept of ENERGY production or storage. • A mass accelerated to a non-zero speed carries energy (mechanical) • A mass raised up carries energy (gravitational) • The atom in a molecule carries energy (chemical) • The mo ...
... The concept of forces acting on a mass (one object) is intimately related to the concept of ENERGY production or storage. • A mass accelerated to a non-zero speed carries energy (mechanical) • A mass raised up carries energy (gravitational) • The atom in a molecule carries energy (chemical) • The mo ...
Torque
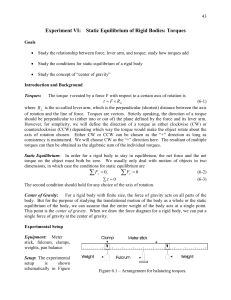
... concept of center of gravity we can still regard the entire weight acting at a single point, center of gravity, and it is the torque generated by this entire weight acting at center of gravity that is balanced by the torque from the hanging weight on the other side. Use the second condition for equi ...
... concept of center of gravity we can still regard the entire weight acting at a single point, center of gravity, and it is the torque generated by this entire weight acting at center of gravity that is balanced by the torque from the hanging weight on the other side. Use the second condition for equi ...
Chapter 6 - TeacherWeb
... Terminal Velocity: Because the air resistance _______________ as an object’s speed _________________, eventually the _______________ force of air resistance will equal the __________________ force of gravity and the acceleration will be ___________. The object will then fall at _______________ velo ...
... Terminal Velocity: Because the air resistance _______________ as an object’s speed _________________, eventually the _______________ force of air resistance will equal the __________________ force of gravity and the acceleration will be ___________. The object will then fall at _______________ velo ...
15.02.09PhysicsWeek23
... we are going to extend our new knowledge to find the exact acceleration due to gravity in South Gate and we’ll compare it to Mou ...
... we are going to extend our new knowledge to find the exact acceleration due to gravity in South Gate and we’ll compare it to Mou ...
Slide - Fort Lewis College
... If there are no external forces on an object, then: • If it is at rest, it will stay that way - forever. • If it is moving, it will keep doing so at constant velocity, in a straight line - forever. ...
... If there are no external forces on an object, then: • If it is at rest, it will stay that way - forever. • If it is moving, it will keep doing so at constant velocity, in a straight line - forever. ...
Textbook Practice Problems
... ” I CAN” statements highlighted in yellow should be displayed for students. draw an object and all the forces working on that object when the object is still or moving. From that drawing I can determine what is happening to the object as a result of the force (4E). describe how Newton’s laws app ...
... ” I CAN” statements highlighted in yellow should be displayed for students. draw an object and all the forces working on that object when the object is still or moving. From that drawing I can determine what is happening to the object as a result of the force (4E). describe how Newton’s laws app ...
Chapter 15 - KFUPM Faculty List
... its motion its kinetic energy is K = 5 J and its potential energy measured with U = 0 at x = 0) is U = 3 J. When it is at x = xm, the kinetic and potential energies are: (Ans: K = 0 and U = 8J) Q#29: A 0.25-kg block oscillates at the end of the spring with a spring constant of 200N/m. If the system ...
... its motion its kinetic energy is K = 5 J and its potential energy measured with U = 0 at x = 0) is U = 3 J. When it is at x = xm, the kinetic and potential energies are: (Ans: K = 0 and U = 8J) Q#29: A 0.25-kg block oscillates at the end of the spring with a spring constant of 200N/m. If the system ...