
File - Mr. Graham`s AP Physics 1 & AP Physics C
... The clay is now removed from the pan and the pan is returned to equilibrium at the end of the spring. A rubber ball, also of mass M, is dropped from the same height H onto the pan, and after the collision is caught in midair before hitting anything else. e) Indicate below whether the period of the ...
... The clay is now removed from the pan and the pan is returned to equilibrium at the end of the spring. A rubber ball, also of mass M, is dropped from the same height H onto the pan, and after the collision is caught in midair before hitting anything else. e) Indicate below whether the period of the ...
Work and Energy
... One can see from the work's definition 6.1.2 or 6.1.3, that it can be positive as well as negative. This depends on the angle between the directions of force and displacement in equation 6.1.2 or on the sign of the force's component in the equation 6.1.3. The force does positive work, if it has the ...
... One can see from the work's definition 6.1.2 or 6.1.3, that it can be positive as well as negative. This depends on the angle between the directions of force and displacement in equation 6.1.2 or on the sign of the force's component in the equation 6.1.3. The force does positive work, if it has the ...
Chapter 15– Oscillations
... • (a) The motion repeats every 0.500 s so the period must be T = 0.500 s. • (b) The frequency is the reciprocal of the period: • f = 1/T = 1/(0.500 s) = 2.00 Hz. • (c) The angular frequency ω is ω = 2πf = 2π(2.00 Hz) = 12.6 rad/s. • (d) The angular frequency is related to the spring constant k and t ...
... • (a) The motion repeats every 0.500 s so the period must be T = 0.500 s. • (b) The frequency is the reciprocal of the period: • f = 1/T = 1/(0.500 s) = 2.00 Hz. • (c) The angular frequency ω is ω = 2πf = 2π(2.00 Hz) = 12.6 rad/s. • (d) The angular frequency is related to the spring constant k and t ...
Work and Energy, Principle of Work and Energy, Principle of Work
... Another equation for working kinetics problems involving particles can be derived by integrating the equation of motion (F = ma) with respect to displacement By substituting at = v (dv/ds) into Ft = mat, the result is integrated to yield an equation known as the principle of work and energy (F ds = ...
... Another equation for working kinetics problems involving particles can be derived by integrating the equation of motion (F = ma) with respect to displacement By substituting at = v (dv/ds) into Ft = mat, the result is integrated to yield an equation known as the principle of work and energy (F ds = ...
Work/Energy Review KEY
... 25. An 800 kg block is pushed up a 5 m long ramp with an incline angle of 20 o. Find: a) the work needed to push the box up if the ramp is frictionless. b) the work needed to push the box up if the coefficient of friction is 0.20. c) the horsepower needed to do the work in part b above, assuming th ...
... 25. An 800 kg block is pushed up a 5 m long ramp with an incline angle of 20 o. Find: a) the work needed to push the box up if the ramp is frictionless. b) the work needed to push the box up if the coefficient of friction is 0.20. c) the horsepower needed to do the work in part b above, assuming th ...
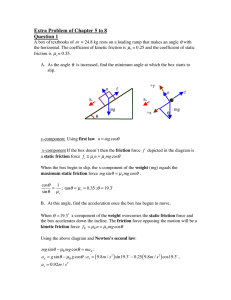
Chris Khan 2007 Physics Chapter 6 FF represents the force of
... and therefore, a = m2g / m1 + m2. Lastly, FT = m1a = m1(m2g / m1 + m2), where what is in parenthesis is what we found last step. To make an object move in a circle with constant force, a force must act on it that is directed towards the center of the circle. This means that the ball accelerates towa ...
... and therefore, a = m2g / m1 + m2. Lastly, FT = m1a = m1(m2g / m1 + m2), where what is in parenthesis is what we found last step. To make an object move in a circle with constant force, a force must act on it that is directed towards the center of the circle. This means that the ball accelerates towa ...
Laws - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... 11) If we double the mass of an object in motion, what would happen to its acceleration? Doubling the mass will divide the acceleration by two 12) If we apply three times the force to an object as the original force applied, what would happen to the object’s acceleration? Multiplying the force by 3 ...
... 11) If we double the mass of an object in motion, what would happen to its acceleration? Doubling the mass will divide the acceleration by two 12) If we apply three times the force to an object as the original force applied, what would happen to the object’s acceleration? Multiplying the force by 3 ...
here.
... physical quantities defined at each point along any trajectory. So they are functions of the instantaneous location and momentum (or velocity). Most often, our dynamical variables will be smooth functions on phase space. For e.g. the x-component of angular momentum is one such function L x = ypz − z ...
... physical quantities defined at each point along any trajectory. So they are functions of the instantaneous location and momentum (or velocity). Most often, our dynamical variables will be smooth functions on phase space. For e.g. the x-component of angular momentum is one such function L x = ypz − z ...
4.5 the law of conservation of Energy
... developer of the steam engine. One watt is equal to one joule per second. Note that the symbol for watt is not italicized (W), but the variable used for work is an italic W. Notice that power is the rate at which work is done. Work is a way to transfer energy from one system to another over time. As ...
... developer of the steam engine. One watt is equal to one joule per second. Note that the symbol for watt is not italicized (W), but the variable used for work is an italic W. Notice that power is the rate at which work is done. Work is a way to transfer energy from one system to another over time. As ...
AP Physics 1 Investigation 2: Newton`s Second Law
... uncertainty might be related to the measurements of time, length, or mass (or combinations of each). Students can minimize the uncertainties by taking measurements in multiple trials and averaging the results. See Resources for options of support in this area. The development of mathematical models ...
... uncertainty might be related to the measurements of time, length, or mass (or combinations of each). Students can minimize the uncertainties by taking measurements in multiple trials and averaging the results. See Resources for options of support in this area. The development of mathematical models ...
















![Laws - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009630889_1-f003c0238349cdcec84f792dc6fc934d-300x300.png)




