Preview Sample 1
... throughout the known universe and describe all motion. Throughout the universe mass is a measure of inertia, and inertia exists everywhere. A change of motion, acceleration, always results from an unbalanced force everywhere in the known universe. Finally, forces of the universe always come in pair ...
... throughout the known universe and describe all motion. Throughout the universe mass is a measure of inertia, and inertia exists everywhere. A change of motion, acceleration, always results from an unbalanced force everywhere in the known universe. Finally, forces of the universe always come in pair ...
Essential Learning Outcomes (ELOs) Advanced Placement Physics (B & C)
... Systems of Two or More Bodies (Third Law) a. [B/C] Students should understand Newton's Third Law so that, for a given force, they can identify the body on which the reaction force acts and state the magnitude and direction of this reaction. b. [B/C] Students should be able to apply Newton's Third La ...
... Systems of Two or More Bodies (Third Law) a. [B/C] Students should understand Newton's Third Law so that, for a given force, they can identify the body on which the reaction force acts and state the magnitude and direction of this reaction. b. [B/C] Students should be able to apply Newton's Third La ...
Science Curriculum ~ Grade 5
... Organisms can survive only in environments in which their particular needs are met. A healthy ecosystem is one in which multiple species of different types are each able to meet their needs in a relatively stable web of life. Newly introduced species can damage the balance of an ecosystem. (F) T ...
... Organisms can survive only in environments in which their particular needs are met. A healthy ecosystem is one in which multiple species of different types are each able to meet their needs in a relatively stable web of life. Newly introduced species can damage the balance of an ecosystem. (F) T ...
Chapter 5 – Linking Forces to Momentum and Energy
... a child swinging on a playground swing. We’ll focus on a simple model, in which the total mechanical energy is constant. This is a reasonable starting point for most oscillating systems. Our own starting point, however, will be to consider how to incorporate springs into our force and energy perspec ...
... a child swinging on a playground swing. We’ll focus on a simple model, in which the total mechanical energy is constant. This is a reasonable starting point for most oscillating systems. Our own starting point, however, will be to consider how to incorporate springs into our force and energy perspec ...
Problem Solving—A General Approach | Summary
... drawn for each object involved, and it must show all the forces acting on a given object (and only on that object). Do not show forces that act on other objects. Choose a convenient xy coordinate system (one that makes your calculations easier, such as one axis in the direction of the acceleration). ...
... drawn for each object involved, and it must show all the forces acting on a given object (and only on that object). Do not show forces that act on other objects. Choose a convenient xy coordinate system (one that makes your calculations easier, such as one axis in the direction of the acceleration). ...
Scheme of work for chapter 9
... calculations are included: see ‘Try these’ p203 and the problem sets listed. The equation s = ut + ½ at2 also follows from graphical considerations of the area under a v-t graph. Three of the equations are provided on the formula sheet, the fourth, s = ½ (u+v)t, is not. This last equation is simply ...
... calculations are included: see ‘Try these’ p203 and the problem sets listed. The equation s = ut + ½ at2 also follows from graphical considerations of the area under a v-t graph. Three of the equations are provided on the formula sheet, the fourth, s = ½ (u+v)t, is not. This last equation is simply ...
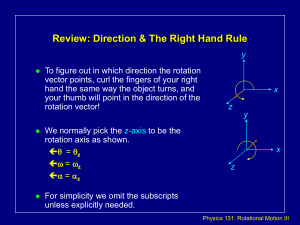
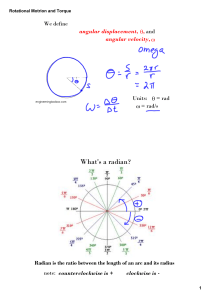
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
... will be correct. For each of these questions, you must select both correct choices to earn credit. No partial credit will be earned if only one correct choice is selected. Select the two that are best in each case. 63. A meteor of mass, M moves with a constant speed, v in a circular orbit of radius ...
... will be correct. For each of these questions, you must select both correct choices to earn credit. No partial credit will be earned if only one correct choice is selected. Select the two that are best in each case. 63. A meteor of mass, M moves with a constant speed, v in a circular orbit of radius ...
Kinetic Energy & Work
... • The simple methods we’ve learned using Newton’s laws are inadequate when the forces are not constant. • In this chapter, the introduction of the new concepts of work, energy, and the conservation of energy will allow us to deal with such problems. ...
... • The simple methods we’ve learned using Newton’s laws are inadequate when the forces are not constant. • In this chapter, the introduction of the new concepts of work, energy, and the conservation of energy will allow us to deal with such problems. ...


















![3. Higher Our Dynamic Universe Questions [ppt 8MB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001620458_1-64549958c5de6c7c6c0be1e1ccb97e89-300x300.png)