Identification of large-scale human-specific copy number
... variety of micro-duplications and micro-deletions also contribute to the totality of the genomic differences between humans and the great apes (Britten 2002; Frazer et al. 2003; Liu et al. 2003; Fortna et al. 2004). Furthermore, copy number differences (CNDs) on the scale of up to hundreds of kilobase ...
... variety of micro-duplications and micro-deletions also contribute to the totality of the genomic differences between humans and the great apes (Britten 2002; Frazer et al. 2003; Liu et al. 2003; Fortna et al. 2004). Furthermore, copy number differences (CNDs) on the scale of up to hundreds of kilobase ...
Study questions - Pre-lab
... phenomenon further and to find an 4. explanation for why only one of them could taste PTC while the other could not. They then gathered hundreds of people and had them sample PTC. They found that about 25% of respondents said they did not taste anything. Through further experimentation they ultimate ...
... phenomenon further and to find an 4. explanation for why only one of them could taste PTC while the other could not. They then gathered hundreds of people and had them sample PTC. They found that about 25% of respondents said they did not taste anything. Through further experimentation they ultimate ...
Genetic Services-Intellectual Disability Project
... [1]). Rearrangements involving the subtelomeric regions of human chromosomes, have been identified as a significant cause of learning disability [2]. As these regions are of high gene density [3], abnormalities of copy number in genes at these loci, have a more pronounced phenotypic effect than at o ...
... [1]). Rearrangements involving the subtelomeric regions of human chromosomes, have been identified as a significant cause of learning disability [2]. As these regions are of high gene density [3], abnormalities of copy number in genes at these loci, have a more pronounced phenotypic effect than at o ...
DNA Tribes Digest for October 28, 2010
... African Panel: A listing of your DNA match scores for all individual Sub-Saharan African populations in our database. Central Asian Panel: A listing of your DNA match scores for individual native Central Asian and Siberian populations in our database, also including Roma (European Gypsy) match score ...
... African Panel: A listing of your DNA match scores for all individual Sub-Saharan African populations in our database. Central Asian Panel: A listing of your DNA match scores for individual native Central Asian and Siberian populations in our database, also including Roma (European Gypsy) match score ...
Loss of Heterozygosity at 6q Is Frequent and Concurrent with 3p
... recent findings of Gijtenbeek et al, who suggested that the molecular mechanisms underlying sporadic and familial hemangioblastomas may be different (48). However, in the present study, 3p loss was more common in sporadic hemangioblastomas than previously reported, thus suggesting its role in the tu ...
... recent findings of Gijtenbeek et al, who suggested that the molecular mechanisms underlying sporadic and familial hemangioblastomas may be different (48). However, in the present study, 3p loss was more common in sporadic hemangioblastomas than previously reported, thus suggesting its role in the tu ...
1305077113_457396
... Using PCR amplification, minute amounts of DNA evidence can be used to solve crimes. DNA contains within its noncoding regions many repeated sequences, including STRs, which vary in number among individuals; these differences are used to produce a DNA profile of a person. DNA profiling has dramatica ...
... Using PCR amplification, minute amounts of DNA evidence can be used to solve crimes. DNA contains within its noncoding regions many repeated sequences, including STRs, which vary in number among individuals; these differences are used to produce a DNA profile of a person. DNA profiling has dramatica ...
Ch 07 Overview - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Using PCR amplification, minute amounts of DNA evidence can be used to solve crimes. DNA contains within its noncoding regions many repeated sequences, including STRs, which vary in number among individuals; these differences are used to produce a DNA profile of a person. DNA profiling has dramatica ...
... Using PCR amplification, minute amounts of DNA evidence can be used to solve crimes. DNA contains within its noncoding regions many repeated sequences, including STRs, which vary in number among individuals; these differences are used to produce a DNA profile of a person. DNA profiling has dramatica ...
Single-molecule studies of DNA replication Geertsema, Hylkje
... replication proteins are stably bound and re-used for many cycles of Okazakifragment synthesis. Such a mechanism provides an attractive model for coordinated synthesis of both strands. Dilution experiments of T7 DNA replication reactions showed that both leading- and lagging-strand synthesis are res ...
... replication proteins are stably bound and re-used for many cycles of Okazakifragment synthesis. Such a mechanism provides an attractive model for coordinated synthesis of both strands. Dilution experiments of T7 DNA replication reactions showed that both leading- and lagging-strand synthesis are res ...
overview - El Paso High School
... • Silent mutations do not affect protein function. • Loss of function mutations affect protein function and may lead to structural proteins or enzymes that no longer work—almost always recessive. (LINK Silent mutations are a source of neutral alleles in evolution; see Concept 15.2) (See Figure 8.1) ...
... • Silent mutations do not affect protein function. • Loss of function mutations affect protein function and may lead to structural proteins or enzymes that no longer work—almost always recessive. (LINK Silent mutations are a source of neutral alleles in evolution; see Concept 15.2) (See Figure 8.1) ...
Presentation
... fragment—referred to as amplifying the sequence. Primers are 15–20 bases, made in the laboratory. The base sequence at the 3′ end of the DNA fragment must be known. ...
... fragment—referred to as amplifying the sequence. Primers are 15–20 bases, made in the laboratory. The base sequence at the 3′ end of the DNA fragment must be known. ...
Lesson Plan - beyond benign
... Restriction Enzymes Background Information In the previous activity you extracted DNA from your cheek cells. DNA extraction is the first step towards DNA analysis. In order for Gena’s DNA to be analyzed for the presence of cancer genes her extracted DNA must be prepared, or “chopped up”, into piece ...
... Restriction Enzymes Background Information In the previous activity you extracted DNA from your cheek cells. DNA extraction is the first step towards DNA analysis. In order for Gena’s DNA to be analyzed for the presence of cancer genes her extracted DNA must be prepared, or “chopped up”, into piece ...
Construction of an arabidopsis BAC library and isolation of clones
... clones containing the ATTS0477 sequence, and ATTS0477-1ike sequences. We wished to identify the latter clones because many disease-resistance genes are members of clustered multi-gene families (Martin et al., 1993; Song et al., 1995), and we wished to determine if ATTS0477 was similar in this regard ...
... clones containing the ATTS0477 sequence, and ATTS0477-1ike sequences. We wished to identify the latter clones because many disease-resistance genes are members of clustered multi-gene families (Martin et al., 1993; Song et al., 1995), and we wished to determine if ATTS0477 was similar in this regard ...
Genetics Review
... Animation: Crossing-over in an Inversion Heterozygote 1. Inversion results when a chromosome segment excises and reintegrates oriented 1800 from the original orientation. There are two types: a. Pericentric inversions include the centromere. b. Paracentric inversions do not include the centromere. 2 ...
... Animation: Crossing-over in an Inversion Heterozygote 1. Inversion results when a chromosome segment excises and reintegrates oriented 1800 from the original orientation. There are two types: a. Pericentric inversions include the centromere. b. Paracentric inversions do not include the centromere. 2 ...
Lab 6: Electrophoresis
... Restriction endonucleases recognize specific DNA sequences in the double-stranded DNA and digest the DNA at the sites. The result is the production of fragments of DNA of various lengths corresponding to the distance between identical DNA sequences within the chromosome. Some restriction enzymes cut ...
... Restriction endonucleases recognize specific DNA sequences in the double-stranded DNA and digest the DNA at the sites. The result is the production of fragments of DNA of various lengths corresponding to the distance between identical DNA sequences within the chromosome. Some restriction enzymes cut ...
Comparative studies on molecular techniques for detecting
... other hand, the purity of DNA for PCR is not very important. Therefore, the quick extraction method has been recommended by some researchers (Daryl et al. 1994). Because of the presence of inhibitors of Taq polymerase in chiggers after engorgement, it was necessary to remove them when employed for P ...
... other hand, the purity of DNA for PCR is not very important. Therefore, the quick extraction method has been recommended by some researchers (Daryl et al. 1994). Because of the presence of inhibitors of Taq polymerase in chiggers after engorgement, it was necessary to remove them when employed for P ...
Your Spitting Image Guide DOC - University of Maryland School of
... genetic information is the same in each cell. Unless you are an identical twin, no one else in the world has the same genetic information as you. The structure of DNA is a double helix with alternating sugar and phosphate along the sides. DNA is made up of four building blocks which are arranged in ...
... genetic information is the same in each cell. Unless you are an identical twin, no one else in the world has the same genetic information as you. The structure of DNA is a double helix with alternating sugar and phosphate along the sides. DNA is made up of four building blocks which are arranged in ...
DNA Scissors: Introduction to Restriction
... enzyme DNA ligase, which forms phosphodiester bonds between the 5' and 3' ends of nucleotides. As you might expect, any blunt ended DNA can be ligated to any other blunt ended DNA without regard to the sequence of the two molecules. Restriction fragments with singlestranded protrusions, as the EcoRI ...
... enzyme DNA ligase, which forms phosphodiester bonds between the 5' and 3' ends of nucleotides. As you might expect, any blunt ended DNA can be ligated to any other blunt ended DNA without regard to the sequence of the two molecules. Restriction fragments with singlestranded protrusions, as the EcoRI ...
FastGene Taq DNA Polymerase
... If low yields and/or non-specific amplification is obtained, an annealing temperature gradient PCR is recommended to determine the optimal annealing temperature for the primer set empirically within the FastGene® Taq PCR system. ...
... If low yields and/or non-specific amplification is obtained, an annealing temperature gradient PCR is recommended to determine the optimal annealing temperature for the primer set empirically within the FastGene® Taq PCR system. ...
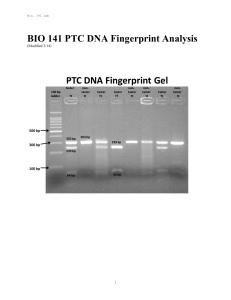
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... DNA Fingerprinting and its Role in Forensics Genetic uniqueness is a fact of life. From generation to generation, characteristics are inherited, combined, and assorted among individuals through a common denominator: the chemical deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. No two individuals have identical DNA seq ...
... DNA Fingerprinting and its Role in Forensics Genetic uniqueness is a fact of life. From generation to generation, characteristics are inherited, combined, and assorted among individuals through a common denominator: the chemical deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. No two individuals have identical DNA seq ...
Genetics - Max Appeal!
... chromosomes is examined under a microscope. This is used for detecting large chromosomal rearrangements or deletions, or extra chromosomes like in Down’s syndrome. The 22q11.2 deletion is too small to be seen by this method so other tests have been developed. The descriptions of these tests are huge ...
... chromosomes is examined under a microscope. This is used for detecting large chromosomal rearrangements or deletions, or extra chromosomes like in Down’s syndrome. The 22q11.2 deletion is too small to be seen by this method so other tests have been developed. The descriptions of these tests are huge ...
5 min Insect DNA/RNA Preservation and Extraction Kit
... 5 min Insect DNA/RNA Preservation and Extraction Kit Biofactories’ 5 min Insect DNA/RNA Preservation and Extraction Kit provides the fastest method for the storage/preservation and isolation/purification of total DNA/RNA from insect samples. The kit is specially designed for preservation and extract ...
... 5 min Insect DNA/RNA Preservation and Extraction Kit Biofactories’ 5 min Insect DNA/RNA Preservation and Extraction Kit provides the fastest method for the storage/preservation and isolation/purification of total DNA/RNA from insect samples. The kit is specially designed for preservation and extract ...
Kodaq 2X PCR MasterMix
... PCR MasterMix advanced buffer system not only tolerates A/T- and G/C-rich content, but also many PCR inhibitors commonly found in a typical DNA sample. Kodaq 2X PCR MasterMix is the most robust PCR MasterMix commercially available and will deliver an exceptional product yield with high fidelity. Kod ...
... PCR MasterMix advanced buffer system not only tolerates A/T- and G/C-rich content, but also many PCR inhibitors commonly found in a typical DNA sample. Kodaq 2X PCR MasterMix is the most robust PCR MasterMix commercially available and will deliver an exceptional product yield with high fidelity. Kod ...
Comparative genomic hybridization

Comparative genomic hybridization is a molecular cytogenetic method for analysing copy number variations (CNVs) relative to ploidy level in the DNA of a test sample compared to a reference sample, without the need for culturing cells. The aim of this technique is to quickly and efficiently compare two genomic DNA samples arising from two sources, which are most often closely related, because it is suspected that they contain differences in terms of either gains or losses of either whole chromosomes or subchromosomal regions (a portion of a whole chromosome). This technique was originally developed for the evaluation of the differences between the chromosomal complements of solid tumor and normal tissue, and has an improved resoIution of 5-10 megabases compared to the more traditional cytogenetic analysis techniques of giemsa banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) which are limited by the resolution of the microscope utilized.This is achieved through the use of competitive fluorescence in situ hybridization. In short, this involves the isolation of DNA from the two sources to be compared, most commonly a test and reference source, independent labelling of each DNA sample with a different fluorophores (fluorescent molecules) of different colours (usually red and green), denaturation of the DNA so that it is single stranded, and the hybridization of the two resultant samples in a 1:1 ratio to a normal metaphase spread of chromosomes, to which the labelled DNA samples will bind at their locus of origin. Using a fluorescence microscope and computer software, the differentially coloured fluorescent signals are then compared along the length of each chromosome for identification of chromosomal differences between the two sources. A higher intensity of the test sample colour in a specific region of a chromosome indicates the gain of material of that region in the corresponding source sample, while a higher intensity of the reference sample colour indicates the loss of material in the test sample in that specific region. A neutral colour (yellow when the fluorophore labels are red and green) indicates no difference between the two samples in that location.CGH is only able to detect unbalanced chromosomal abnormalities. This is because balanced chromosomal abnormalities such as reciprocal translocations, inversions or ring chromosomes do not affect copy number, which is what is detected by CGH technologies. CGH does, however, allow for the exploration of all 46 human chromosomes in single test and the discovery of deletions and duplications, even on the microscopic scale which may lead to the identification of candidate genes to be further explored by other cytological techniques.Through the use of DNA microarrays in conjunction with CGH techniques, the more specific form of array CGH (aCGH) has been developed, allowing for a locus-by-locus measure of CNV with increased resolution as low as 100 kilobases. This improved technique allows for the aetiology of known and unknown conditions to be discovered.