Promega Notes: Separate Isolation of Genomic DNA and Total RNA
... Promega's SV Total RNA Isolation System provides a rapid and safe method for the purification of high quality total RNA. The SV RNA System is based on a silica membrane that can be used in either a centrifugation ("spin") or vacuum format. Nucleic acid isolation is achieved without the use of organi ...
... Promega's SV Total RNA Isolation System provides a rapid and safe method for the purification of high quality total RNA. The SV RNA System is based on a silica membrane that can be used in either a centrifugation ("spin") or vacuum format. Nucleic acid isolation is achieved without the use of organi ...
Karyotype
... So, how many chromosomes do we have? 23 pairs or 46 total This is considered to be a diploid cell because it has all 23 pairs of chromosomes—a complete set for a human. ...
... So, how many chromosomes do we have? 23 pairs or 46 total This is considered to be a diploid cell because it has all 23 pairs of chromosomes—a complete set for a human. ...
Structure and functions of lampbrush chromosomes
... The progress in biotechnology that was witnessed at the turn of 20th and 21st century was a breakthrough in scientific research – predominantly of experimental nature. The methods and quality of laboratory experiments were improved. A chance also appeared to explain the unverified cytogenetic and mo ...
... The progress in biotechnology that was witnessed at the turn of 20th and 21st century was a breakthrough in scientific research – predominantly of experimental nature. The methods and quality of laboratory experiments were improved. A chance also appeared to explain the unverified cytogenetic and mo ...
Document
... genes which results in chromosomes that consist of segments from one homolog intermixed with segments from the other • In the first nuclear division, the homologous chromosomes are separated from each other, one member of each pair going to opposite poles of the ...
... genes which results in chromosomes that consist of segments from one homolog intermixed with segments from the other • In the first nuclear division, the homologous chromosomes are separated from each other, one member of each pair going to opposite poles of the ...
Cytology of Genetics
... divisions to produce 2 sperm nuclei and one generative nucleus. The generative nucleus directs the growth of the pollen tube. The two sperm nuclei are for the double fertilization of the egg and endosperm nuclei in the female. ...
... divisions to produce 2 sperm nuclei and one generative nucleus. The generative nucleus directs the growth of the pollen tube. The two sperm nuclei are for the double fertilization of the egg and endosperm nuclei in the female. ...
pdf, 1.3 MB - DNA and Natural Algorithms Group
... The process of replication is complete by this point; we started with two parental superstrands, and we now have two additional daughter superstrands. Just as DNA, replication was semi-conservative; each of the superduplexes contain one parental strand and one daughter strand. All that remains to be ...
... The process of replication is complete by this point; we started with two parental superstrands, and we now have two additional daughter superstrands. Just as DNA, replication was semi-conservative; each of the superduplexes contain one parental strand and one daughter strand. All that remains to be ...
A-2015A: Amplified Fragment Length
... when multiple samples (3 per species) were utilized. The number and nature of the selective nucleotides were optimized when applied to these species (as indicated in the Figure 7 caption), but no other changes were necessary. It is important to note that when working with a new species, a large numb ...
... when multiple samples (3 per species) were utilized. The number and nature of the selective nucleotides were optimized when applied to these species (as indicated in the Figure 7 caption), but no other changes were necessary. It is important to note that when working with a new species, a large numb ...
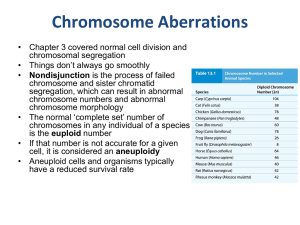
Chromosome Aberrations
... • Gene dosage is the main impact of aneuploidy • Increased or decreased numbers of genes means increased or decreased amounts of gene products – disrupting the chemical balance of the cell • Plants tend to handle gene dosage imbalances better than animals • Datura stramonium is a weed with 2n=24 • 1 ...
... • Gene dosage is the main impact of aneuploidy • Increased or decreased numbers of genes means increased or decreased amounts of gene products – disrupting the chemical balance of the cell • Plants tend to handle gene dosage imbalances better than animals • Datura stramonium is a weed with 2n=24 • 1 ...
From the Department of Zoology, University of
... of the behavior of genie substance seems at present our most direct approach to this problem" (Stadler (14)). This genie substance is localized in the chromosomes. The morphological, chemical, and physiological investigation of chromosomes is therefore one of the main approaches to the nature of the ...
... of the behavior of genie substance seems at present our most direct approach to this problem" (Stadler (14)). This genie substance is localized in the chromosomes. The morphological, chemical, and physiological investigation of chromosomes is therefore one of the main approaches to the nature of the ...
Ch. 7: Presentation Slides
... • There is no loss of genetic information but the functions of specific genes may be altered • Reciprocal translocation may affect one or both pairs of chromosomes ...
... • There is no loss of genetic information but the functions of specific genes may be altered • Reciprocal translocation may affect one or both pairs of chromosomes ...
What is Cytogenetics?
... chromosomes: XX female or XY male • Each chromosome has a characteristic length and3 banding pattern ...
... chromosomes: XX female or XY male • Each chromosome has a characteristic length and3 banding pattern ...
DNA-dependent protein kinase in nonhomologous end joining: a
... and a DNA terminus. This latter requirement makes the DNAPKCS protein kinase truly DNA dependent. Many targets for the DNA-PKCS kinase have been identified in vitro, including XRCC4, Ku 70/80, Artemis, p53, and even DNA-PKCS itself (autophosphorylation). This plethora of possible targets suggests th ...
... and a DNA terminus. This latter requirement makes the DNAPKCS protein kinase truly DNA dependent. Many targets for the DNA-PKCS kinase have been identified in vitro, including XRCC4, Ku 70/80, Artemis, p53, and even DNA-PKCS itself (autophosphorylation). This plethora of possible targets suggests th ...
Alpha -antitrypsin alleles in patients with ... emphysema, detected by DNA amplification ...
... by complex formation with the protease inhibitors [4]. The most potent inhibitor in humans is the serine protease inhibitor alpha1-antitrypsin (AAT or Pi), which is almost exclusively secreted by liver cells (for review see [5]). The inactivation of the elastase is normally so efficient that no acti ...
... by complex formation with the protease inhibitors [4]. The most potent inhibitor in humans is the serine protease inhibitor alpha1-antitrypsin (AAT or Pi), which is almost exclusively secreted by liver cells (for review see [5]). The inactivation of the elastase is normally so efficient that no acti ...
April Fools Paper slide
... • Cleavage efficiency was tested with an array of crRNAs with a single base mismatch from the target • Mismatches up to 11 bp 5’ of the PAM site abolished cleavage • Mismatches farther upstream retained efficient cleavage activity Target EMX1 locus crRNA (wt) chimeric RNA with mismatched guide seque ...
... • Cleavage efficiency was tested with an array of crRNAs with a single base mismatch from the target • Mismatches up to 11 bp 5’ of the PAM site abolished cleavage • Mismatches farther upstream retained efficient cleavage activity Target EMX1 locus crRNA (wt) chimeric RNA with mismatched guide seque ...
Document
... is turned off, all the molecules are stopped within the gel. If a dye is added to the samples placed in the wells, individual groups of molecules can be identified by a distinct, colored band within the gel. When the distance each band (group of molecules) traveled is measured and compared to the ot ...
... is turned off, all the molecules are stopped within the gel. If a dye is added to the samples placed in the wells, individual groups of molecules can be identified by a distinct, colored band within the gel. When the distance each band (group of molecules) traveled is measured and compared to the ot ...
R - Genetics
... The technical procedure for measuring the relative frequency of SIII-N and SIII-2 transformants in a reaction from which both types may appear (reactions 10 or 11) is somewhat complicated. The complication is due to the necessity of providing in the reaction mixture antibodies against the untransfor ...
... The technical procedure for measuring the relative frequency of SIII-N and SIII-2 transformants in a reaction from which both types may appear (reactions 10 or 11) is somewhat complicated. The complication is due to the necessity of providing in the reaction mixture antibodies against the untransfor ...
10p proximal deletions from 10p11 and 10p12
... Each new version of the genome is often referred to as an ‘assembly’ or a ‘build’. Every few years a new assembly is released. The genetic information in this guide is based on the Genome Reference Consortium (GRC) human (h) genome assembly number 37 (GRCh37), which was released in 2009. Confusingly ...
... Each new version of the genome is often referred to as an ‘assembly’ or a ‘build’. Every few years a new assembly is released. The genetic information in this guide is based on the Genome Reference Consortium (GRC) human (h) genome assembly number 37 (GRCh37), which was released in 2009. Confusingly ...
A small organic compound enhances the religation reaction of
... The different steps of the human Top1 (topoisomerase I) catalytic cycle have been analysed in the presence of a pentacyclic-diquinoid synthetic compound. The experiments indicate that it efficiently inhibits the cleavage step of the enzyme reaction, fitting well into the catalytic site. Surprisingly ...
... The different steps of the human Top1 (topoisomerase I) catalytic cycle have been analysed in the presence of a pentacyclic-diquinoid synthetic compound. The experiments indicate that it efficiently inhibits the cleavage step of the enzyme reaction, fitting well into the catalytic site. Surprisingly ...
Comparative genomic hybridization

Comparative genomic hybridization is a molecular cytogenetic method for analysing copy number variations (CNVs) relative to ploidy level in the DNA of a test sample compared to a reference sample, without the need for culturing cells. The aim of this technique is to quickly and efficiently compare two genomic DNA samples arising from two sources, which are most often closely related, because it is suspected that they contain differences in terms of either gains or losses of either whole chromosomes or subchromosomal regions (a portion of a whole chromosome). This technique was originally developed for the evaluation of the differences between the chromosomal complements of solid tumor and normal tissue, and has an improved resoIution of 5-10 megabases compared to the more traditional cytogenetic analysis techniques of giemsa banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) which are limited by the resolution of the microscope utilized.This is achieved through the use of competitive fluorescence in situ hybridization. In short, this involves the isolation of DNA from the two sources to be compared, most commonly a test and reference source, independent labelling of each DNA sample with a different fluorophores (fluorescent molecules) of different colours (usually red and green), denaturation of the DNA so that it is single stranded, and the hybridization of the two resultant samples in a 1:1 ratio to a normal metaphase spread of chromosomes, to which the labelled DNA samples will bind at their locus of origin. Using a fluorescence microscope and computer software, the differentially coloured fluorescent signals are then compared along the length of each chromosome for identification of chromosomal differences between the two sources. A higher intensity of the test sample colour in a specific region of a chromosome indicates the gain of material of that region in the corresponding source sample, while a higher intensity of the reference sample colour indicates the loss of material in the test sample in that specific region. A neutral colour (yellow when the fluorophore labels are red and green) indicates no difference between the two samples in that location.CGH is only able to detect unbalanced chromosomal abnormalities. This is because balanced chromosomal abnormalities such as reciprocal translocations, inversions or ring chromosomes do not affect copy number, which is what is detected by CGH technologies. CGH does, however, allow for the exploration of all 46 human chromosomes in single test and the discovery of deletions and duplications, even on the microscopic scale which may lead to the identification of candidate genes to be further explored by other cytological techniques.Through the use of DNA microarrays in conjunction with CGH techniques, the more specific form of array CGH (aCGH) has been developed, allowing for a locus-by-locus measure of CNV with increased resolution as low as 100 kilobases. This improved technique allows for the aetiology of known and unknown conditions to be discovered.