No Slide Title
... Out of Africa • Neanderthal mT DNA: – Very different from modern humans – Hard to reconcile difference with possible presence of some Neanderthal ancestry in modern ...
... Out of Africa • Neanderthal mT DNA: – Very different from modern humans – Hard to reconcile difference with possible presence of some Neanderthal ancestry in modern ...
Sample Submission Form
... uniparental disomy (UPD) on the genome level 1 CMA is indicated for clinical disorders in which a chromosomal abnormality is suspected. 2 This analysis can detect deletions or duplications ranging in length from 15 kb to an entire chromosome. In certain regions, it can detect deletions or duplicatio ...
... uniparental disomy (UPD) on the genome level 1 CMA is indicated for clinical disorders in which a chromosomal abnormality is suspected. 2 This analysis can detect deletions or duplications ranging in length from 15 kb to an entire chromosome. In certain regions, it can detect deletions or duplicatio ...
Developmental Validation of the DNAscan™ Rapid DNA Analysis
... reliability, reproducibility and robustness of the DNAscan Rapid DNA Analysis System across a number of laboratories and buccal sample variations. The goal of this extensive study was to obtain, document, analyze, and assess if the data generated by the DNAscan and its internal Expert System can rel ...
... reliability, reproducibility and robustness of the DNAscan Rapid DNA Analysis System across a number of laboratories and buccal sample variations. The goal of this extensive study was to obtain, document, analyze, and assess if the data generated by the DNAscan and its internal Expert System can rel ...
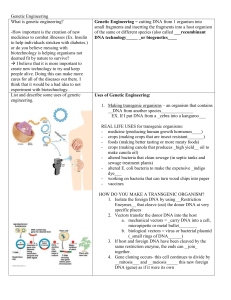
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... medicines to combat illnesses (Ex. Insulin to help individuals stricken with diabetes.) or do you believe messing with biotechnology is helping organisms not deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can m ...
... medicines to combat illnesses (Ex. Insulin to help individuals stricken with diabetes.) or do you believe messing with biotechnology is helping organisms not deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can m ...
A Genomic Timeline
... James Gusella and co-workers locate a genetic marker for Huntington’s disease on chromosome 4. This leads to scientists having the ability to screen people for a disease without being able ot cure it. Kary Mullis conceives of the polymerase chain reaction, a chemical DNA replication process that gr ...
... James Gusella and co-workers locate a genetic marker for Huntington’s disease on chromosome 4. This leads to scientists having the ability to screen people for a disease without being able ot cure it. Kary Mullis conceives of the polymerase chain reaction, a chemical DNA replication process that gr ...
Name Designation Constitution Number of chromosomes
... • Subset of R bands in proximity of the telomers, T-bands are the most intense R-bands extreme heat treatment followed by Giemsa stain ...
... • Subset of R bands in proximity of the telomers, T-bands are the most intense R-bands extreme heat treatment followed by Giemsa stain ...
Biochemical Testing 3/25/2016 Chapter 4B: Methods of Microbial Identification
... Cooling allows complementary strands to base pair. • this technique is used in a variety of ways to see if DNA from two different sources are similar • usually the DNA from one source is immobilized, the other is labeled to allow detection ...
... Cooling allows complementary strands to base pair. • this technique is used in a variety of ways to see if DNA from two different sources are similar • usually the DNA from one source is immobilized, the other is labeled to allow detection ...
Name
... 1. The complete set of genetic information an organism carries in its DNA is its A. karyotype. B. genome. C. chromosomes. D. autosomes. 2. From what is a karyotype made? A. A photograph of cells in mitosis B. A series of X-diffraction images C. A preparation of gametes on a microscope slide D. A Pun ...
... 1. The complete set of genetic information an organism carries in its DNA is its A. karyotype. B. genome. C. chromosomes. D. autosomes. 2. From what is a karyotype made? A. A photograph of cells in mitosis B. A series of X-diffraction images C. A preparation of gametes on a microscope slide D. A Pun ...
國立嘉義大學九十一學年度
... 2.The entire complement of genetic material of an organism, virus, or organelle. 3.A DNA sequence that is used to detect the presence of a complementary sequence by hybridization with a nucleic acid sample. 4.The transfer of DNA to a eukaryotic cell. 5.An RNA-dependent DNA polymerase that uses an RN ...
... 2.The entire complement of genetic material of an organism, virus, or organelle. 3.A DNA sequence that is used to detect the presence of a complementary sequence by hybridization with a nucleic acid sample. 4.The transfer of DNA to a eukaryotic cell. 5.An RNA-dependent DNA polymerase that uses an RN ...
Visualizing DNA
... Thus, larger fragments will move slower than smaller fragments. This allows separation of all different sizes of DNA fragments. ...
... Thus, larger fragments will move slower than smaller fragments. This allows separation of all different sizes of DNA fragments. ...
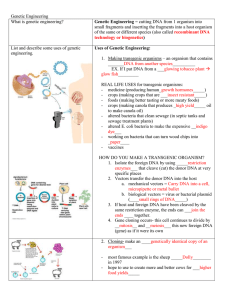
Genetic Engineering
... 4. Gene cloning occurs- this cell continues to divide by __mitosis__ and __meiosis___ this new foreign DNA (gene) as if it were its own 2. Cloning- make an ____genetically identical copy of an organism___ ...
... 4. Gene cloning occurs- this cell continues to divide by __mitosis__ and __meiosis___ this new foreign DNA (gene) as if it were its own 2. Cloning- make an ____genetically identical copy of an organism___ ...
Nucleic acid review sheet
... If the sequence of bases of one of the two strands of DNA were A G T C C G T A G T T, what would be the sequence of the other strand? ...
... If the sequence of bases of one of the two strands of DNA were A G T C C G T A G T T, what would be the sequence of the other strand? ...
9 Genomics and Beyond
... Determine the arrangement of genes or markers with unknown functions on a chromosome based on how often two genes on the same chromosome are to be involved in crossing over, which is the exchange of genetic information between pairs of chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis. ...
... Determine the arrangement of genes or markers with unknown functions on a chromosome based on how often two genes on the same chromosome are to be involved in crossing over, which is the exchange of genetic information between pairs of chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis. ...
2.2 Sequencing learning grid File
... 2.2.9 DNA manipulation – separating and probing Electrophoresis separates DNA fragments by...? What size fragments travel slower in the agarose? What cuts DNA into fragments? ...
... 2.2.9 DNA manipulation – separating and probing Electrophoresis separates DNA fragments by...? What size fragments travel slower in the agarose? What cuts DNA into fragments? ...
sample report - Integrated Genetics
... INTERPRETATION: APPARENT COMMON DESCENT arr (1-22,X)x2 The whole genome chromosome SNP microarray (REVEAL)analysis did not demonstrate significant DNA copy number changes within the clinically significant criteria for this analysis indicated below. There are, however, extended contiguous regions of ...
... INTERPRETATION: APPARENT COMMON DESCENT arr (1-22,X)x2 The whole genome chromosome SNP microarray (REVEAL)analysis did not demonstrate significant DNA copy number changes within the clinically significant criteria for this analysis indicated below. There are, however, extended contiguous regions of ...
array CGH - Unique The Rare Chromosome Disorder Support Group
... (where a section of a chromosome is inverted or reversed), will not be identified using array CGH. This is because balanced chromosome rearrangements do not result in any loss or gain of chromosome material. It will also not detect some types of polyploidy (more than the usual 2 sets of chromosomes) ...
... (where a section of a chromosome is inverted or reversed), will not be identified using array CGH. This is because balanced chromosome rearrangements do not result in any loss or gain of chromosome material. It will also not detect some types of polyploidy (more than the usual 2 sets of chromosomes) ...
Name Ch 12 Study Guide
... 7) In DNA A always bonds with ______ & G always bonds with __________. 8) What are purines? Name and DRAW. ...
... 7) In DNA A always bonds with ______ & G always bonds with __________. 8) What are purines? Name and DRAW. ...
DNA - heredity2
... • Approximately 5% of your DNA codes for proteins • The other ~95% is non-coding or ‘junk’ DNA which varies greatly between individuals • In this ‘junk’ there are sections which have repeated patterns • These repeated patterns are what is used to identify an individual when doing DNA profiling • a m ...
... • Approximately 5% of your DNA codes for proteins • The other ~95% is non-coding or ‘junk’ DNA which varies greatly between individuals • In this ‘junk’ there are sections which have repeated patterns • These repeated patterns are what is used to identify an individual when doing DNA profiling • a m ...
Comparative genomic hybridization

Comparative genomic hybridization is a molecular cytogenetic method for analysing copy number variations (CNVs) relative to ploidy level in the DNA of a test sample compared to a reference sample, without the need for culturing cells. The aim of this technique is to quickly and efficiently compare two genomic DNA samples arising from two sources, which are most often closely related, because it is suspected that they contain differences in terms of either gains or losses of either whole chromosomes or subchromosomal regions (a portion of a whole chromosome). This technique was originally developed for the evaluation of the differences between the chromosomal complements of solid tumor and normal tissue, and has an improved resoIution of 5-10 megabases compared to the more traditional cytogenetic analysis techniques of giemsa banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) which are limited by the resolution of the microscope utilized.This is achieved through the use of competitive fluorescence in situ hybridization. In short, this involves the isolation of DNA from the two sources to be compared, most commonly a test and reference source, independent labelling of each DNA sample with a different fluorophores (fluorescent molecules) of different colours (usually red and green), denaturation of the DNA so that it is single stranded, and the hybridization of the two resultant samples in a 1:1 ratio to a normal metaphase spread of chromosomes, to which the labelled DNA samples will bind at their locus of origin. Using a fluorescence microscope and computer software, the differentially coloured fluorescent signals are then compared along the length of each chromosome for identification of chromosomal differences between the two sources. A higher intensity of the test sample colour in a specific region of a chromosome indicates the gain of material of that region in the corresponding source sample, while a higher intensity of the reference sample colour indicates the loss of material in the test sample in that specific region. A neutral colour (yellow when the fluorophore labels are red and green) indicates no difference between the two samples in that location.CGH is only able to detect unbalanced chromosomal abnormalities. This is because balanced chromosomal abnormalities such as reciprocal translocations, inversions or ring chromosomes do not affect copy number, which is what is detected by CGH technologies. CGH does, however, allow for the exploration of all 46 human chromosomes in single test and the discovery of deletions and duplications, even on the microscopic scale which may lead to the identification of candidate genes to be further explored by other cytological techniques.Through the use of DNA microarrays in conjunction with CGH techniques, the more specific form of array CGH (aCGH) has been developed, allowing for a locus-by-locus measure of CNV with increased resolution as low as 100 kilobases. This improved technique allows for the aetiology of known and unknown conditions to be discovered.