Posted 1/25/07 Mary Case
... Subsequently the suspension is calibrated so that the suspension contains 5 X 10-6 conidial/ml. Ten ml. of this suspension is dispensed into a 150X15 mm Petri dish and placed on a magnetic stirrer at 25°C to keep the conidia in suspension. A 15-Watt General Electric germicidal lamp with approximatel ...
... Subsequently the suspension is calibrated so that the suspension contains 5 X 10-6 conidial/ml. Ten ml. of this suspension is dispensed into a 150X15 mm Petri dish and placed on a magnetic stirrer at 25°C to keep the conidia in suspension. A 15-Watt General Electric germicidal lamp with approximatel ...
Go to - Net Start Class
... This explore is best when the students can use computers but can be done globally if necessary. ...
... This explore is best when the students can use computers but can be done globally if necessary. ...
Students Visit DNA Learning Center
... of the kind that accumulates around spoiled fruit. It is also one of the most valuable of organisms in biological research, particularly in genetics and developmental biology. Drosophila has been used as a model organism for research for almost a century, and today, several thousand scientists are w ...
... of the kind that accumulates around spoiled fruit. It is also one of the most valuable of organisms in biological research, particularly in genetics and developmental biology. Drosophila has been used as a model organism for research for almost a century, and today, several thousand scientists are w ...
About Genetic Diseases
... Genetic diseases are defined as diseases caused by aberrations of genetic material. Therefore, these diseases can potentially be passed from generation to generation. However, not every patient has a family history of a similar problem. This is because new mutations can occur when an individual inhe ...
... Genetic diseases are defined as diseases caused by aberrations of genetic material. Therefore, these diseases can potentially be passed from generation to generation. However, not every patient has a family history of a similar problem. This is because new mutations can occur when an individual inhe ...
During the last years we have observed a rapid development of
... diagnostic services. An increasing number of laboratories replace their “in-house” developed techniques by the commercial diagnostic assays, but they often modify manufacturer's instructions. Therefore, it is necessary to validate and verify all methods and techniques before their implementation int ...
... diagnostic services. An increasing number of laboratories replace their “in-house” developed techniques by the commercial diagnostic assays, but they often modify manufacturer's instructions. Therefore, it is necessary to validate and verify all methods and techniques before their implementation int ...
Learning Target #1: Know vocabulary that builds the
... Learning Target #1: Know vocabulary that builds the framework for understanding genetics. Match each vocabulary word with the definition that best describes it. ______ 1. A segment of DNA; the set of information that controls a trait. ______ 2. An organism’s physical appearance, or visible trait. __ ...
... Learning Target #1: Know vocabulary that builds the framework for understanding genetics. Match each vocabulary word with the definition that best describes it. ______ 1. A segment of DNA; the set of information that controls a trait. ______ 2. An organism’s physical appearance, or visible trait. __ ...
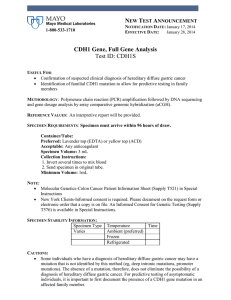
CDH1 Gene, Full Gene Analysis Test ID: CDH1S
... Some individuals who have a diagnosis of hereditary diffuse gastric cancer may have a mutation that is not identified by this method (eg, deep intronic mutations, promoter mutations). The absence of a mutation, therefore, does not eliminate the possibility of a diagnosis of hereditary diffuse gast ...
... Some individuals who have a diagnosis of hereditary diffuse gastric cancer may have a mutation that is not identified by this method (eg, deep intronic mutations, promoter mutations). The absence of a mutation, therefore, does not eliminate the possibility of a diagnosis of hereditary diffuse gast ...
Heredity Study Guide
... 32. _____________________: happens when a part of the parent organism, such as a hydra, pinches off and forms a new organism. 33. _____________________: parts of the organism, such as a flat worm, break off and a new organism grows identical to the parent. 34. _____________________: organism, such a ...
... 32. _____________________: happens when a part of the parent organism, such as a hydra, pinches off and forms a new organism. 33. _____________________: parts of the organism, such as a flat worm, break off and a new organism grows identical to the parent. 34. _____________________: organism, such a ...
Introduction to Genetic - Home
... Errors in recombination are responsible for mutations called translocations, such as occur in leukemias and other cancers. Normal recombination produces genetic variation by the exchange of genetic material between paired chromosomes. ...
... Errors in recombination are responsible for mutations called translocations, such as occur in leukemias and other cancers. Normal recombination produces genetic variation by the exchange of genetic material between paired chromosomes. ...
2-centrioles & fibers disappear
... • When the tRNA matches its anticodons to the mRNA’s codons at the ribosomes, it brings with it a particular amino acid. After the tRNA’s drops off amino acids from the start to the stop codon, the protein is complete. ...
... • When the tRNA matches its anticodons to the mRNA’s codons at the ribosomes, it brings with it a particular amino acid. After the tRNA’s drops off amino acids from the start to the stop codon, the protein is complete. ...
Mutation in Mitosis and Meiosis
... but have a higher risk of Alzheimer’s disease - genetic testing can tell a pregnant woman if the child will have Down Syndrome or not ...
... but have a higher risk of Alzheimer’s disease - genetic testing can tell a pregnant woman if the child will have Down Syndrome or not ...
Genetics – Human Genetic Disorders and Genetic Engineering
... recognize the same base sequences. 2. Insert the foreign DNA into the plasmid. 3. Replace the plasmid into the bacterium 4. Allow the bacterium to reproduce – all future generations have the new DNA 5. Collect the product – it might be insulin or growth hormone, or some other molecule. ...
... recognize the same base sequences. 2. Insert the foreign DNA into the plasmid. 3. Replace the plasmid into the bacterium 4. Allow the bacterium to reproduce – all future generations have the new DNA 5. Collect the product – it might be insulin or growth hormone, or some other molecule. ...
Document
... • Mismatch repair fixes incorrectly matched base pairs • The AP endonuclease system repairs nucleotide sites at which the base has been lost • Special enzymes repair damage caused to DNA by ultraviolet light • Excision repair works on a wide variety of damaged DNA • Postreplication repair skips over ...
... • Mismatch repair fixes incorrectly matched base pairs • The AP endonuclease system repairs nucleotide sites at which the base has been lost • Special enzymes repair damage caused to DNA by ultraviolet light • Excision repair works on a wide variety of damaged DNA • Postreplication repair skips over ...
DNA Vocabulary Study Option
... Carbohydrate, Lipid and Protein unit for Biology. The unit is one of the larger units and contains a lot of vocabulary to keep straight. In order the help the students I have created this study option for home. ...
... Carbohydrate, Lipid and Protein unit for Biology. The unit is one of the larger units and contains a lot of vocabulary to keep straight. In order the help the students I have created this study option for home. ...
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid ) **Long molecule made up of units
... information from one generation of an organism to the next. ...
... information from one generation of an organism to the next. ...
Document
... Question: How do “new” genes arise? Duplications might allow for major mutation in the extra copy of the gene. Over time, mutations could result in a new function for the duplicated gene - essentially a new gene. Example: myoglobin and hemoglobin ...
... Question: How do “new” genes arise? Duplications might allow for major mutation in the extra copy of the gene. Over time, mutations could result in a new function for the duplicated gene - essentially a new gene. Example: myoglobin and hemoglobin ...
Ch. 6 Section 1 Active Reading/Quiz
... A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a protein or RNA molecule. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes lined up like the cars of a train. When genes are being used, the strand of DNA is stretched out so that the information it contains can be decoded and used to direct the synthesis of ...
... A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a protein or RNA molecule. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes lined up like the cars of a train. When genes are being used, the strand of DNA is stretched out so that the information it contains can be decoded and used to direct the synthesis of ...
L8 cells PPt - Moodle
... X chromosome larger than Y Alleles on X chromosome may not have equivalent on Y ...
... X chromosome larger than Y Alleles on X chromosome may not have equivalent on Y ...
F. Mutation and Repair 1. Background on DNA Mutations
... essential component of evolutionary change • Mutations that become part of the multicellular genome must occur in the cells of the germ line • Somatic mutations may or may not affect the individual but cannot affect the population • Low rates of mutation can result in high rates of ...
... essential component of evolutionary change • Mutations that become part of the multicellular genome must occur in the cells of the germ line • Somatic mutations may or may not affect the individual but cannot affect the population • Low rates of mutation can result in high rates of ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.