460:102 Notes Historical Geology Notes
... Geology - another story - religious climate still limited advances in geology - the science of the Earth itself. Genesis portrayed an Earth that was 6000 yrs. old. Creationists considered the Earth as stable since the Noachian flood catastrophe. 1. Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519) recognized that mater ...
... Geology - another story - religious climate still limited advances in geology - the science of the Earth itself. Genesis portrayed an Earth that was 6000 yrs. old. Creationists considered the Earth as stable since the Noachian flood catastrophe. 1. Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519) recognized that mater ...
here
... asteroid and the earth: 4.6-4.2bybp • Formation of crust: continents and ocean: oldest continental crust: 4.2-4.1bybp • High rates of meteorite bombardment on the Earth’s ...
... asteroid and the earth: 4.6-4.2bybp • Formation of crust: continents and ocean: oldest continental crust: 4.2-4.1bybp • High rates of meteorite bombardment on the Earth’s ...
SSAC2004.QE539.LV1.5-stdnt
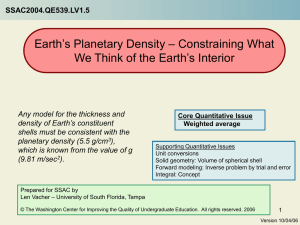
... The goal of this module is to make a first cut at describing how the density of the Earth varies as a function of depth. We know the depths of the discontinuities. The abrupt increases in seismic velocities at the discontinuities demonstrate that the densities increase from shell to shell as we go d ...
... The goal of this module is to make a first cut at describing how the density of the Earth varies as a function of depth. We know the depths of the discontinuities. The abrupt increases in seismic velocities at the discontinuities demonstrate that the densities increase from shell to shell as we go d ...
2015 Earth`s Structure
... on the compounds that make up each layer. A compound is a substance composed of two or more elements. The least dense compounds make up the crust and mantle, the densest compounds make up the core. The layers form because heavier elements are pulled toward the center of the Earth by gravity, and the ...
... on the compounds that make up each layer. A compound is a substance composed of two or more elements. The least dense compounds make up the crust and mantle, the densest compounds make up the core. The layers form because heavier elements are pulled toward the center of the Earth by gravity, and the ...
Inside the Earth
... About half of our planet’s mass. The mantle is composed of very hot dense rocks, That move and flow, always on the go, they never lock, Never stop, and they’re responsible for tectonic shift Please believe the Earth’s plates are adrift It’s pretty thick and the heat is awesome 1,600 at the top, 4,00 ...
... About half of our planet’s mass. The mantle is composed of very hot dense rocks, That move and flow, always on the go, they never lock, Never stop, and they’re responsible for tectonic shift Please believe the Earth’s plates are adrift It’s pretty thick and the heat is awesome 1,600 at the top, 4,00 ...
Michelle Mindick
... The final, significant contributor to Earth’s ever-‐changing topography is the result of various processes of gradation. As earthquakes, volcanoes, and impact craters break up and reform Earth’s ...
... The final, significant contributor to Earth’s ever-‐changing topography is the result of various processes of gradation. As earthquakes, volcanoes, and impact craters break up and reform Earth’s ...
Earth's Heat
... heat and it comes from particle-physics experiments. Seated one kilometer underground, in an unused zinc mine west of Tokyo, the KamLAND detector is measuring Earth's radiogenic heat flux one geoneutrino at a time. A geoneutrino is the antineutrino produced by the natural decay of radioactive 238 U, ...
... heat and it comes from particle-physics experiments. Seated one kilometer underground, in an unused zinc mine west of Tokyo, the KamLAND detector is measuring Earth's radiogenic heat flux one geoneutrino at a time. A geoneutrino is the antineutrino produced by the natural decay of radioactive 238 U, ...
Plate Boundaries
... What are the primary rocks which make up the continental and oceanic crusts? continental crust ...
... What are the primary rocks which make up the continental and oceanic crusts? continental crust ...
Possible Multiple-choice Questions about Gravity
... c. The speed at which we launch rockets from the Earth d. The number of sunspots on the Sun. e. The number of meteors that hit an object. 27. A person on Pluto’s surface would experience a(n) _____ gravitational force compared to on Earth. a. Weaker, because Pluto is further from the Sun. b. Weaker, ...
... c. The speed at which we launch rockets from the Earth d. The number of sunspots on the Sun. e. The number of meteors that hit an object. 27. A person on Pluto’s surface would experience a(n) _____ gravitational force compared to on Earth. a. Weaker, because Pluto is further from the Sun. b. Weaker, ...
Week 3 (Norton), part c (pdf, 4.5 MB)
... In her compendium on why Plate Tectonics took so long to be accepted in the U.S., one of Oreskes’ contributors, David Sandwell, advances an arresting proposition. In a chapter entitled “Earth’s plate tectonics from a Martian perspective,” he suggests that the problem faced by earthbound geologists ...
... In her compendium on why Plate Tectonics took so long to be accepted in the U.S., one of Oreskes’ contributors, David Sandwell, advances an arresting proposition. In a chapter entitled “Earth’s plate tectonics from a Martian perspective,” he suggests that the problem faced by earthbound geologists ...
Inside the Earth
... layers of the earth. Be sure to include: • A Title • Subtitles For Each Topic • Drawings Where Applicable ...
... layers of the earth. Be sure to include: • A Title • Subtitles For Each Topic • Drawings Where Applicable ...
UNIT 1, Chapter 1, Lesson 2
... _______________ ________________ and __________________ _________________. Today, the atmosphere is a mixture of mostly _________________ and ________________. Therefore, the atmosphere has undergone many changes since earth formed. 12. Much of the ____________________ in our atmosphere came from vo ...
... _______________ ________________ and __________________ _________________. Today, the atmosphere is a mixture of mostly _________________ and ________________. Therefore, the atmosphere has undergone many changes since earth formed. 12. Much of the ____________________ in our atmosphere came from vo ...
Notes!
... than the asthenosphere! Finally, the inner and outer core are extremely hot with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you were able to go to the center of the Earth! ...
... than the asthenosphere! Finally, the inner and outer core are extremely hot with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball smaller than a marble if you were able to go to the center of the Earth! ...
Grade 7
... Students understand the structure of the solar system including movement of the sun, moon, Earth, and other planets. Relate the orientation, direction and duration of the movement of the Earth around its axis and around the sun to day/night cycles and the seasons. Explain how the changes in the ...
... Students understand the structure of the solar system including movement of the sun, moon, Earth, and other planets. Relate the orientation, direction and duration of the movement of the Earth around its axis and around the sun to day/night cycles and the seasons. Explain how the changes in the ...
EARTH
... • Earth formed out of solar nebula • Formed at same time as other planets (4.6 billion years ago) • Started out as rocky ball of uniform composition and density ...
... • Earth formed out of solar nebula • Formed at same time as other planets (4.6 billion years ago) • Started out as rocky ball of uniform composition and density ...
Schiehallion experiment

The Schiehallion experiment was an 18th-century experiment to determine the mean density of the Earth. Funded by a grant from the Royal Society, it was conducted in the summer of 1774 around the Scottish mountain of Schiehallion, Perthshire. The experiment involved measuring the tiny deflection of a pendulum due to the gravitational attraction of a nearby mountain. Schiehallion was considered the ideal location after a search for candidate mountains, thanks to its isolation and almost symmetrical shape. One of the triggers for the experiment were anomalies noted during the survey of the Mason–Dixon Line.The experiment had previously been considered, but rejected, by Isaac Newton as a practical demonstration of his theory of gravitation. However, a team of scientists, notably Nevil Maskelyne, the Astronomer Royal, were convinced that the effect would be detectable and undertook to conduct the experiment. The deflection angle depended on the relative densities and volumes of the Earth and the mountain: if the density and volume of Schiehallion could be ascertained, then so could the density of the Earth. Once this was known, then this would in turn yield approximate values for those of the other planets, their moons, and the Sun, previously known only in terms of their relative ratios. As an additional benefit, the concept of contour lines, devised to simplify the process of surveying the mountain, later became a standard technique in cartography.