Rock Cycle Teacher Notes
... Mineral: Any naturally occurring inorganic crystalline solid with a definite chemical composition Rocks: Make up the crust of the earth (the part of the earth we live on) Form mountains and the ocean bottom (exist everywhere, but often buried under soil) Made up of single mineral or combinatio ...
... Mineral: Any naturally occurring inorganic crystalline solid with a definite chemical composition Rocks: Make up the crust of the earth (the part of the earth we live on) Form mountains and the ocean bottom (exist everywhere, but often buried under soil) Made up of single mineral or combinatio ...
Rocks - Mesquite ISD
... Making up the majority of the Earth's crust, rock is usually defined as a mixture of common minerals. Rocks can be hard or soft, as small as a grain or as large as a building. They have been an integral part of the history of mankind, first being used as tools for hunting and defense, and as a build ...
... Making up the majority of the Earth's crust, rock is usually defined as a mixture of common minerals. Rocks can be hard or soft, as small as a grain or as large as a building. They have been an integral part of the history of mankind, first being used as tools for hunting and defense, and as a build ...
Twenty Questions
... When we use a pencil to write When we eat For airplanes, buildings, and washing machines Jewelry and money ...
... When we use a pencil to write When we eat For airplanes, buildings, and washing machines Jewelry and money ...
Types_of_Rocks_and_Rock_Formation_ppt
... Extrusive Rocks: forms when magma erupts onto the Earth’s surface (lava), cools quickly with very small or no crystals formed ...
... Extrusive Rocks: forms when magma erupts onto the Earth’s surface (lava), cools quickly with very small or no crystals formed ...
PwrPt - University of Minnesota Duluth
... Stoping – rising magma detaches blocks of country rock, which sinks into it Timing of Emplacement (relative to deformation): Pre-kinematic– Intrusion is deformed in the same way as the rocks it intrudes Syn-kinematic – Intrusion shape conforms to regional structures Post-kinematic – Intrusion shape ...
... Stoping – rising magma detaches blocks of country rock, which sinks into it Timing of Emplacement (relative to deformation): Pre-kinematic– Intrusion is deformed in the same way as the rocks it intrudes Syn-kinematic – Intrusion shape conforms to regional structures Post-kinematic – Intrusion shape ...
Rocks and Minerals Web Quest
... of the Earth. As the magma loses heat, it cools and crystallizes into an igneous rock. Magma can cool on the Earth's surface, where it has erupted from a _______________________ (extrusive rock) or under the Earth's surface, where it has intruded older rocks (intrusive rock). o The composition of ma ...
... of the Earth. As the magma loses heat, it cools and crystallizes into an igneous rock. Magma can cool on the Earth's surface, where it has erupted from a _______________________ (extrusive rock) or under the Earth's surface, where it has intruded older rocks (intrusive rock). o The composition of ma ...
Rocks PowerPoint
... Existing Rocks are changed by pressure, heat, or chemical reactions They were once igneous or sedimentary ...
... Existing Rocks are changed by pressure, heat, or chemical reactions They were once igneous or sedimentary ...
Igneous Rocks
... Intrusive Rock: Formed from magma that cools and hardens inside the Earth Course grained Larger crystals all roughly the same size pegmatite ...
... Intrusive Rock: Formed from magma that cools and hardens inside the Earth Course grained Larger crystals all roughly the same size pegmatite ...
Types of Rocks
... Igneous rocks are formed when magma (molten rock deep within the earth) cools and hardens. Sometimes the magma cools inside the earth, and other times it erupts onto the surface from volcanoes (in this case, it is called lava). When lava cools very quickly, no crystals form and the rock looks shiny ...
... Igneous rocks are formed when magma (molten rock deep within the earth) cools and hardens. Sometimes the magma cools inside the earth, and other times it erupts onto the surface from volcanoes (in this case, it is called lava). When lava cools very quickly, no crystals form and the rock looks shiny ...
End of Unit One
... These special kinds of sedimentary rocks do not contain ________________. __________ is an example of this type of rock. Metamorphic Rocks form when __________________ or _________________________ rocks are _______________________ by _________________ and ____________ but _______________ ___________ ...
... These special kinds of sedimentary rocks do not contain ________________. __________ is an example of this type of rock. Metamorphic Rocks form when __________________ or _________________________ rocks are _______________________ by _________________ and ____________ but _______________ ___________ ...
Rocks
... mixture of minerals, mineraloids, glass, or organic matter. Three main types of Rock – Igneous – Metamorphic – Sedimentary ...
... mixture of minerals, mineraloids, glass, or organic matter. Three main types of Rock – Igneous – Metamorphic – Sedimentary ...
Classifying Igneous Rock
... Classifying Igneous Rock For a rock to be classified as igneous, it must have been melted at some time and then hardened to become solid again. When melted rock material (magma or lava) cools and hardens, it may form crystals, depending on how fast it. How fast the rock material cools depends on whe ...
... Classifying Igneous Rock For a rock to be classified as igneous, it must have been melted at some time and then hardened to become solid again. When melted rock material (magma or lava) cools and hardens, it may form crystals, depending on how fast it. How fast the rock material cools depends on whe ...
a rock is - MR. TRAN @ JWG
... up of arkose, a coursegrained sandstone rich in feldspar at least 2.5 km thick. Uplifting and folding between 400-300 mya turned the sedimentary layers nearly 90 degrees to their present position. The surface has then ...
... up of arkose, a coursegrained sandstone rich in feldspar at least 2.5 km thick. Uplifting and folding between 400-300 mya turned the sedimentary layers nearly 90 degrees to their present position. The surface has then ...
rocks-sec 2 igneous
... from magma below the Earth’s surface (see pg. 63, figure 6) - Takes a long time for these to cool, so they rock crystals are larger and can be easily seen. - Found at the Earth’s surface only after layers of rock and soil have eroded away. - Erosion takes place as these rocks are pushed up towards t ...
... from magma below the Earth’s surface (see pg. 63, figure 6) - Takes a long time for these to cool, so they rock crystals are larger and can be easily seen. - Found at the Earth’s surface only after layers of rock and soil have eroded away. - Erosion takes place as these rocks are pushed up towards t ...
Geology Article http://www.minimegeology.com/home/mgeo
... throughout the specimen. Minerals can be found as single crystals or clusters of many crystals. Rocks are a group of minerals that are found together. The type of rock is determined by the type of minerals that are formed together along with the place where the formation occurs, such as deep in the ...
... throughout the specimen. Minerals can be found as single crystals or clusters of many crystals. Rocks are a group of minerals that are found together. The type of rock is determined by the type of minerals that are formed together along with the place where the formation occurs, such as deep in the ...
Rocks and the Rock Cycle
... rocks from one kind to another over long periods of time. But what are these igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks anyway? ...
... rocks from one kind to another over long periods of time. But what are these igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks anyway? ...
Name - 7. Science and Basecamp
... Geologists usually group these six kinds of igneous rocks in pairs, because each pair generally contains the same minerals. Study the table below to see which igneous rocks are the same but different. Common Igneous Rocks Intrusive rocks ...
... Geologists usually group these six kinds of igneous rocks in pairs, because each pair generally contains the same minerals. Study the table below to see which igneous rocks are the same but different. Common Igneous Rocks Intrusive rocks ...
Section 20.3 - CPO Science
... Decreased pressure and the addition of water lower the melting temperature of mantle rock so that it melts. ...
... Decreased pressure and the addition of water lower the melting temperature of mantle rock so that it melts. ...
SEDIMENTARY ROCK DESCRIPTIONS A description of rocks
... descriptions of sedimentary rocks should include the following characteristics (where applicable) and roughly in this order. The Miscellaneous category is intended to accomodate special features not included elsewhere on the sheet. You may adapt this approach for descriptions of igneous and metamorp ...
... descriptions of sedimentary rocks should include the following characteristics (where applicable) and roughly in this order. The Miscellaneous category is intended to accomodate special features not included elsewhere on the sheet. You may adapt this approach for descriptions of igneous and metamorp ...
Key for Chapter 4, Section 2 Igneous Rocks Directed Reading A
... rock units 17. Magma intrudes or pushes, into surrounding rock below the Earth’s surface to create such formations as batholiths and sills. 18. Intrusive igneous rock usually has a(n) coarse grained texture. 19. Igneous rock that forms from lava, or magma that erupts onto the Earth’s surface, is cal ...
... rock units 17. Magma intrudes or pushes, into surrounding rock below the Earth’s surface to create such formations as batholiths and sills. 18. Intrusive igneous rock usually has a(n) coarse grained texture. 19. Igneous rock that forms from lava, or magma that erupts onto the Earth’s surface, is cal ...
The Rock Cycle - Geevor Tin Mine
... from the surface as volcanoes or intrusive rocks that form when the magma cools and solidifies beneath the surface. Granite is an igneous rock that forms by the slow cooling of magma deep within the Earth’s crust; it is composed of silica-rich minerals such as quartz, feldspar and mica. The rocks kn ...
... from the surface as volcanoes or intrusive rocks that form when the magma cools and solidifies beneath the surface. Granite is an igneous rock that forms by the slow cooling of magma deep within the Earth’s crust; it is composed of silica-rich minerals such as quartz, feldspar and mica. The rocks kn ...
BUGS Rocks Station 2 Types of Igneous, Metamorphic
... • hand lenses • box of minerals samples labeled station 2 (on the Third Grade Shelf) Activity and Discussion: First read the materials on rocks and minerals in preparation for the session. Each rock has a capital letter before the name. There will be an I for Igneous, an M for Metamorphic and an S f ...
... • hand lenses • box of minerals samples labeled station 2 (on the Third Grade Shelf) Activity and Discussion: First read the materials on rocks and minerals in preparation for the session. Each rock has a capital letter before the name. There will be an I for Igneous, an M for Metamorphic and an S f ...
Document
... All rocks can be transformed into other rock types Rocks are divided into 3 categories Igneous- crystalline- forms as liquid cools Metamorphic- crystalline-forms as rocks are heated and squeezed ...
... All rocks can be transformed into other rock types Rocks are divided into 3 categories Igneous- crystalline- forms as liquid cools Metamorphic- crystalline-forms as rocks are heated and squeezed ...
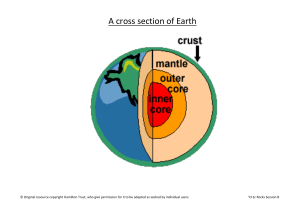
Cross section of the Earth
... layer of red-hot solid rocks; some of these rocks are so soft that they ooze about and can blast out of cracks in the crust, as lava. The layer under the mantle is called the Outer Core. It is made of liquid iron and nickel. Special movement in this section is responsible for the Earth’s magnetic ...
... layer of red-hot solid rocks; some of these rocks are so soft that they ooze about and can blast out of cracks in the crust, as lava. The layer under the mantle is called the Outer Core. It is made of liquid iron and nickel. Special movement in this section is responsible for the Earth’s magnetic ...
Igneous rock

Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire) is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rock may form with or without crystallization, either below the surface as intrusive (plutonic) rocks or on the surface as extrusive (volcanic) rocks. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Over 700 types of igneous rocks have been described, most of them having formed beneath the surface of Earth's crust.