U / ∂V
... suggested that heat is an invisible fluid (gas), called caloric, which resided between the particles of the substance. In the caloric theory, it had been assumed that the temperature of a substance is determined by the quantity of the caloric gas which it contains; it was also assumed that the amoun ...
... suggested that heat is an invisible fluid (gas), called caloric, which resided between the particles of the substance. In the caloric theory, it had been assumed that the temperature of a substance is determined by the quantity of the caloric gas which it contains; it was also assumed that the amoun ...
Shrinking a power supply and the challenge to maintain high
... heat transfer of kinetic energy from one molecule to another. Heat is transferred through a solid medium where a temperature difference exists between the two bodies. This mode of transfer can be easily modelled if compared to the flow of current within a conducting material. Different materials wil ...
... heat transfer of kinetic energy from one molecule to another. Heat is transferred through a solid medium where a temperature difference exists between the two bodies. This mode of transfer can be easily modelled if compared to the flow of current within a conducting material. Different materials wil ...
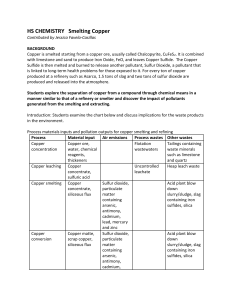
Smelting Copper
... Copper is smelted starting from a copper ore, usually called Chalcopyrite, CuFeS 2. It is combined with limestone and sand to produce Iron Oxide, FeO, and leaves Copper Sulfide. The Copper Sulfide is then melted and burned to release another pollutant, Sulfur Dioxide, a pollutant that is linked to l ...
... Copper is smelted starting from a copper ore, usually called Chalcopyrite, CuFeS 2. It is combined with limestone and sand to produce Iron Oxide, FeO, and leaves Copper Sulfide. The Copper Sulfide is then melted and burned to release another pollutant, Sulfur Dioxide, a pollutant that is linked to l ...
Latent Heat
... We know that when we heat the water from 0°C to 100°C, we can calculate how much heat is necessary to add in order to accomplish this by using Q = mcΔT. However, if we plot the heat added to the system against the temperature increase over the entire -40°C to 110°C range, we would not find as linear ...
... We know that when we heat the water from 0°C to 100°C, we can calculate how much heat is necessary to add in order to accomplish this by using Q = mcΔT. However, if we plot the heat added to the system against the temperature increase over the entire -40°C to 110°C range, we would not find as linear ...
Practice sheet #8: thermodynamics.
... d. The molar enthalpy of formation for FeBr2 is -249.8 KJ/mol and that for FeBr3 is -268.2 KJ/mol. What is the H of the following reaction? 2FeBr2 (s) + Br2 (l) 2 FeBr3 (s) ...
... d. The molar enthalpy of formation for FeBr2 is -249.8 KJ/mol and that for FeBr3 is -268.2 KJ/mol. What is the H of the following reaction? 2FeBr2 (s) + Br2 (l) 2 FeBr3 (s) ...
Physics Perspectives of Environments
... The system is based upon sun shine and water. Plants produce carbohydrates (sugars) to feed animals. Animals’ excretory substances are degraded by bacteria. The substances degraded by bacteria are used ...
... The system is based upon sun shine and water. Plants produce carbohydrates (sugars) to feed animals. Animals’ excretory substances are degraded by bacteria. The substances degraded by bacteria are used ...
Specific heat measurement of crystals to be used in
... detecting possible increase of the low temperature specific heat in the case of Nb doping (possible paramagnetic effects at very low temperatures from Nb3+ uneven ions) check the value of specific heat for TeO2 crystals made by different manufacturers. ...
... detecting possible increase of the low temperature specific heat in the case of Nb doping (possible paramagnetic effects at very low temperatures from Nb3+ uneven ions) check the value of specific heat for TeO2 crystals made by different manufacturers. ...
Lecture_1_ Heat and - Arizona State University
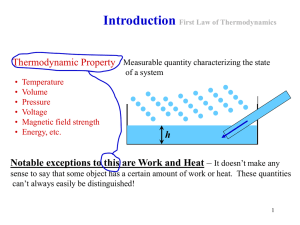
... of the system is decreased work is done on the system, increasing its energy; hence the positive sign in the equation W pdV . The unusual convention was established to fit the behavior of heat engines whose normal operation involves the input of heat and the output of work. So according to this u ...
... of the system is decreased work is done on the system, increasing its energy; hence the positive sign in the equation W pdV . The unusual convention was established to fit the behavior of heat engines whose normal operation involves the input of heat and the output of work. So according to this u ...
Chapter2 The First Law of Thermodynamics
... Neither heat nor work can be destroyed;they can only change from one to another, that is: ...
... Neither heat nor work can be destroyed;they can only change from one to another, that is: ...
Measurement Of Thermal Conductivity Using Thermal Comparator
... value for materials like Iron, Aluminium, Copper, etc., can be taken from the data book. * But for composite materials there is no such data. * This project helps us to find the value of thermal conductivity for composite materials also. ...
... value for materials like Iron, Aluminium, Copper, etc., can be taken from the data book. * But for composite materials there is no such data. * This project helps us to find the value of thermal conductivity for composite materials also. ...
Power Point File
... In the image below, where is average kinetic energy greater? Higher temperature ...
... In the image below, where is average kinetic energy greater? Higher temperature ...
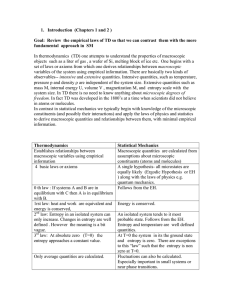
1. Introduction (Chapters 1 and 2 ) Goal: Review the empirical laws
... isolated and time independent. The universe and everything in it is constantly changing on some time scale. Two systems A and B have the same empirical temperature if when brought in thermal contact there is no net heat transfer from one to the another. In principle any closed system can be used to ...
... isolated and time independent. The universe and everything in it is constantly changing on some time scale. Two systems A and B have the same empirical temperature if when brought in thermal contact there is no net heat transfer from one to the another. In principle any closed system can be used to ...
LECTURE 5 Temperature Scales The equation of state of any
... and is path independent. So we can pick a convenient path for doing the integral. In particular, we envision a quasi-static process in going from the initial to the final state. That way the system is always arbitrarily close to equilibrium and the temperature and heat capacity are well defined at a ...
... and is path independent. So we can pick a convenient path for doing the integral. In particular, we envision a quasi-static process in going from the initial to the final state. That way the system is always arbitrarily close to equilibrium and the temperature and heat capacity are well defined at a ...
ph202_overhead_ch15
... • A measure of the disorder (or randomness) of a system • For a reversible the change in entropy is measured as the ratio of heat gained to temperature DS = (Q/T)R = Sfinal - Sinitial – When heat energy is gained by a system, entropy is gained by the system (and lost by the surrounding environment) ...
... • A measure of the disorder (or randomness) of a system • For a reversible the change in entropy is measured as the ratio of heat gained to temperature DS = (Q/T)R = Sfinal - Sinitial – When heat energy is gained by a system, entropy is gained by the system (and lost by the surrounding environment) ...
Heat Transfer
... molecules transmit their kinetic energy to other molecules by colliding with them. ...
... molecules transmit their kinetic energy to other molecules by colliding with them. ...
Geology :: 3. Energy and the Dynamic Earth
... conduction. Conduction does not cause the movement of hot material from one place to another. The atoms remain in the crystalline structure and transport the heat by oscillation. In gases and liquids, heat transport take place by convection. Convection, unlike conduction, does cause movement. It is ...
... conduction. Conduction does not cause the movement of hot material from one place to another. The atoms remain in the crystalline structure and transport the heat by oscillation. In gases and liquids, heat transport take place by convection. Convection, unlike conduction, does cause movement. It is ...
FSK Shield
... A insulation facing. The product also can be used as an effective vapor barrier. FSK Shield™ is available in 1000 square foot rolls 54” wide. Other widths available by special order. Radiant Barrier System (RBS) is a building construction consisting of a low emittance (normally 0.1 or less) surface ...
... A insulation facing. The product also can be used as an effective vapor barrier. FSK Shield™ is available in 1000 square foot rolls 54” wide. Other widths available by special order. Radiant Barrier System (RBS) is a building construction consisting of a low emittance (normally 0.1 or less) surface ...
Study of the Dependence Effectiveness of Low
... (shopsand others) are equipped with conditioning systems operated in the winter time in the heat pump regime and heating apartments. But the operation of air conditioners in this regime is physically possible and economically effective only up to temperatures of free air higher then minus 15 °C. At ...
... (shopsand others) are equipped with conditioning systems operated in the winter time in the heat pump regime and heating apartments. But the operation of air conditioners in this regime is physically possible and economically effective only up to temperatures of free air higher then minus 15 °C. At ...
Step 4: Cut along the 2 fold lines to make 3 flaps
... and write these 3 words on the tabs. (Do not write the words Cold are just the instructions.) ...
... and write these 3 words on the tabs. (Do not write the words Cold are just the instructions.) ...
solutions
... Note from the diagram above that Qin is the heat absorbed from the high temperature source. Also note that you can substitute the Wnet,out = Qin – Qout equation into the ηth definition. ...
... Note from the diagram above that Qin is the heat absorbed from the high temperature source. Also note that you can substitute the Wnet,out = Qin – Qout equation into the ηth definition. ...
Thermochemistry Energy - the capacity to do work Potential energy
... Energy leaving a system (exothermic) has a negative sign. Heat absorbed by the system has a positive sign. Heat lost by the system has a negative sign. Work done on a system has a positive sign. Work done by the system has a negative sign. Note: these conventions are not the same for all fields; an ...
... Energy leaving a system (exothermic) has a negative sign. Heat absorbed by the system has a positive sign. Heat lost by the system has a negative sign. Work done on a system has a positive sign. Work done by the system has a negative sign. Note: these conventions are not the same for all fields; an ...