Thermodynamics - Bowles Physics
... Carnot a believed that there was an absolute zero of temperature, from which he figured out that on being cooled to absolute zero, the fluid would give up all its heat energy. Therefore, if it falls only half way to absolute zero from its beginning temperature, it will give up half its heat, and an ...
... Carnot a believed that there was an absolute zero of temperature, from which he figured out that on being cooled to absolute zero, the fluid would give up all its heat energy. Therefore, if it falls only half way to absolute zero from its beginning temperature, it will give up half its heat, and an ...
AP Physics B Thermodynamics
... Carnot a believed that there was an absolute zero of temperature, from which he figured out that on being cooled to absolute zero, the fluid would give up all its heat energy. Therefore, if it falls only half way to absolute zero from its beginning temperature, it will give up half its heat, and an ...
... Carnot a believed that there was an absolute zero of temperature, from which he figured out that on being cooled to absolute zero, the fluid would give up all its heat energy. Therefore, if it falls only half way to absolute zero from its beginning temperature, it will give up half its heat, and an ...
Section 1 – Thermal Energy
... º As a substance absorbs heat its temperature changes depending on the nature of the substance. º Also depends on how much heat is added. º Specific Heat – the amount of heat that is needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1 degree or 1K. º Measured in joules per kilogram Kelvin [J/ ...
... º As a substance absorbs heat its temperature changes depending on the nature of the substance. º Also depends on how much heat is added. º Specific Heat – the amount of heat that is needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1 degree or 1K. º Measured in joules per kilogram Kelvin [J/ ...
Air and Conduction Cooling for 3U COTS Cards
... conductivity actually exhibited only 1/10th of that value. Had that material been designed into products without testing, thermal failures may have resulted. Because these materials have been designed for use in commercial applications they also need to be tested for rugged properties such as long-t ...
... conductivity actually exhibited only 1/10th of that value. Had that material been designed into products without testing, thermal failures may have resulted. Because these materials have been designed for use in commercial applications they also need to be tested for rugged properties such as long-t ...
Lect1.LawsofThr
... Thermodynamic state - equilibrium Thermodynamic intensive coordinates are uniform across the whole system (T, P, ) or across each macroscopic phase (e.g., water and ice density density at the melting point. All thermodynamic coordinates are time independent Mechanical equilibrium, thermal eq ...
... Thermodynamic state - equilibrium Thermodynamic intensive coordinates are uniform across the whole system (T, P, ) or across each macroscopic phase (e.g., water and ice density density at the melting point. All thermodynamic coordinates are time independent Mechanical equilibrium, thermal eq ...
Helium-Liquefaction By Cryocooler For High
... a cylindrical copper fin was thermally anchored to the first and second stage coldheads in order to extend the available heat transfer surface. A heat exchanger tube was attached on the outer surface of each cylindrical fin, and heat exchange occurs between the tube and the helium gas that is passin ...
... a cylindrical copper fin was thermally anchored to the first and second stage coldheads in order to extend the available heat transfer surface. A heat exchanger tube was attached on the outer surface of each cylindrical fin, and heat exchange occurs between the tube and the helium gas that is passin ...
Physics 202 Homework
... equation for thermal expansion, ∆L = αL0 ∆T , we have: ∆L = (12 × 10−6 )(370)(19) = 0.084360 3. A 0.35-kilogram coffee mug is made from a material that has a specific heat capacity of 920 J/kg-◦ C and contains 0.25 kilograms of water. The cup and water are at 15 ◦ C. To make a cup of coffeee, a smal ...
... equation for thermal expansion, ∆L = αL0 ∆T , we have: ∆L = (12 × 10−6 )(370)(19) = 0.084360 3. A 0.35-kilogram coffee mug is made from a material that has a specific heat capacity of 920 J/kg-◦ C and contains 0.25 kilograms of water. The cup and water are at 15 ◦ C. To make a cup of coffeee, a smal ...
Chapter 5, Problem 1
... A double-pane window consists of two 3-mm thick layers of glass separated by a 12-mm wide stagnant air space. For specified indoors and outdoors temperatures, the rate of heat loss through the window and the inner surface temperature of the window are to be determined. Assumptions 1 Heat transfer th ...
... A double-pane window consists of two 3-mm thick layers of glass separated by a 12-mm wide stagnant air space. For specified indoors and outdoors temperatures, the rate of heat loss through the window and the inner surface temperature of the window are to be determined. Assumptions 1 Heat transfer th ...
v = Y
... ◦ Also, the temperature of the working substance must be the same as the cold reservoir when heat is discarded into it (TC). ◦ Any finite temperature drop would result in an irreversible processes. ◦ Every process that involves heat transfer must be isothermal. ◦ Any process in which the the working ...
... ◦ Also, the temperature of the working substance must be the same as the cold reservoir when heat is discarded into it (TC). ◦ Any finite temperature drop would result in an irreversible processes. ◦ Every process that involves heat transfer must be isothermal. ◦ Any process in which the the working ...
Thermodynamics
... get heat inside a house and to put the cold reservoir outside the house. Some heat pumps work with the reservoir as the air around us, while others use ground source heat, which has about the same temperature the whole year. The COP can be found around 3.5-4.0 in such apparatus. The COP definition f ...
... get heat inside a house and to put the cold reservoir outside the house. Some heat pumps work with the reservoir as the air around us, while others use ground source heat, which has about the same temperature the whole year. The COP can be found around 3.5-4.0 in such apparatus. The COP definition f ...
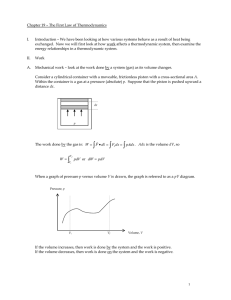
Chapter 19 – The First Law of Thermodynamics
... Interesting Note: If a system changes from an initial state i to a final state f along different paths (e.g., Path A and Path B), the change in internal energy will be the same along those paths. And, in fact, all paths that go from i to f. That is, U = Uf - Ui . From the first law, that means that ...
... Interesting Note: If a system changes from an initial state i to a final state f along different paths (e.g., Path A and Path B), the change in internal energy will be the same along those paths. And, in fact, all paths that go from i to f. That is, U = Uf - Ui . From the first law, that means that ...
Optimal heating and cooling strategies for heat exchanger design
... illustrating the optimal heating/cooling strategy that minimizes entropy production. The process is constrained to proceed in a fixed, given time (as is common in industry where fixed production rates are a constraint). The problem selected is illustrative in that it has a simple closedform analytic ...
... illustrating the optimal heating/cooling strategy that minimizes entropy production. The process is constrained to proceed in a fixed, given time (as is common in industry where fixed production rates are a constraint). The problem selected is illustrative in that it has a simple closedform analytic ...
Lecture 5: Heat transmission
... rest of the room and eventually heat the entire room. How do convection currents work? The hot radiator warms the air that is closest to the radiator. The warm air expands, becomes less dense and rises to the top of the room. When the air reaches the top of the room it is pushed sideways towards the ...
... rest of the room and eventually heat the entire room. How do convection currents work? The hot radiator warms the air that is closest to the radiator. The warm air expands, becomes less dense and rises to the top of the room. When the air reaches the top of the room it is pushed sideways towards the ...
The average Nusselt number with the use of nanofluid is higher than
... CuOeEGeWater variable thermal conductivity and viscosity models employed. In general, the effects the viscosity models are predicted to be more predominant on the behavior of the average Nusselt number than the influence of the thermal conductivity models. The enclosure aspect ratio is predicted to h ...
... CuOeEGeWater variable thermal conductivity and viscosity models employed. In general, the effects the viscosity models are predicted to be more predominant on the behavior of the average Nusselt number than the influence of the thermal conductivity models. The enclosure aspect ratio is predicted to h ...
Thermal Chem Review and Key
... 15. What equation is used to calculate the energy involved in a phase change? Does this equation pertain to the diagonal or plateau sections on your heating and cooling curve? 16. What equation is used to calculate the energy involved in increasing or decreasing the temperature of a substance? Does ...
... 15. What equation is used to calculate the energy involved in a phase change? Does this equation pertain to the diagonal or plateau sections on your heating and cooling curve? 16. What equation is used to calculate the energy involved in increasing or decreasing the temperature of a substance? Does ...
Part II. Convection Currents and the Mantle
... C. The Layers of the Earth website: http://www.sciencemonster.com/earth-science/layers-of-the-earth.html 1. What are tectonic plates? _______________________________________________________________ 2. What is something else that you learned from pages 1-3? ______________________________________ ___ ...
... C. The Layers of the Earth website: http://www.sciencemonster.com/earth-science/layers-of-the-earth.html 1. What are tectonic plates? _______________________________________________________________ 2. What is something else that you learned from pages 1-3? ______________________________________ ___ ...
Summary of Heat Transfer
... Purely thermal conduction: in solid opaque bodies (opaque: not permeable for radiation) the thermal conduction is the significant heat transfer mechanism because the material doesn’t flow and there is no radiation. In flowing fluids, thermal conduction dominates in the region very close to the bound ...
... Purely thermal conduction: in solid opaque bodies (opaque: not permeable for radiation) the thermal conduction is the significant heat transfer mechanism because the material doesn’t flow and there is no radiation. In flowing fluids, thermal conduction dominates in the region very close to the bound ...
First Law of Thermodynamics
... Introduced the idea of internal energy. All of the energy of the system. Discussed that the internal energy is a state function. That is that it only depends on the state of the system (its particular properties T,V,P, ...) not how the system arrived in this state. Changes in internal energy are the ...
... Introduced the idea of internal energy. All of the energy of the system. Discussed that the internal energy is a state function. That is that it only depends on the state of the system (its particular properties T,V,P, ...) not how the system arrived in this state. Changes in internal energy are the ...
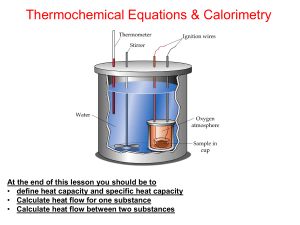
Thermochemistry Lesson 2
... Use data of standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf) Use data of standard enthalpy of combustion (ΔHc) Use data of standard enthalpy of atomization (ΔHa) or Energy bonding (D). At the end of this lesson you should be to • define calorimeter and calorimetry • Know five (5) ways to determine enthalpy chan ...
... Use data of standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf) Use data of standard enthalpy of combustion (ΔHc) Use data of standard enthalpy of atomization (ΔHa) or Energy bonding (D). At the end of this lesson you should be to • define calorimeter and calorimetry • Know five (5) ways to determine enthalpy chan ...
Detecting temperature change External temperature change
... Fun fact: Have you ever noticed that metals tend to feel cold? Believe it or not, they are not colder! They only feel colder because they conduct heat away from your hand. You perceive the heat that is leaving your hand as cold. ...
... Fun fact: Have you ever noticed that metals tend to feel cold? Believe it or not, they are not colder! They only feel colder because they conduct heat away from your hand. You perceive the heat that is leaving your hand as cold. ...
Chemistry/Physical Science - Thermodynamics
... (a) Sproducts > Sreactants and ΔS is + (b) Sproducts < Sreactants and ΔS is – c. Change of Entropy Situations: (1) Can predict changes in entropy associated w/ changes in phases (2) Entropy increases w/ increase in KE (3) Dissolving gas in a solvent results in decrease in S (4) Increase in T causes ...
... (a) Sproducts > Sreactants and ΔS is + (b) Sproducts < Sreactants and ΔS is – c. Change of Entropy Situations: (1) Can predict changes in entropy associated w/ changes in phases (2) Entropy increases w/ increase in KE (3) Dissolving gas in a solvent results in decrease in S (4) Increase in T causes ...
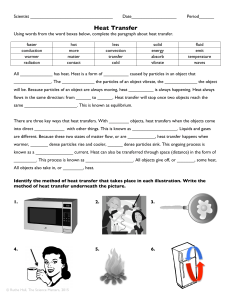
Heat Transfer - Granville County Public Schools
... All _____________ has heat. Heat is a form of __________ caused by particles in an object that _______________. The _____________ the particles of an object vibrate, the _____________ the object will be. Because particles of an object are always moving, heat __________ is always happening. Heat alwa ...
... All _____________ has heat. Heat is a form of __________ caused by particles in an object that _______________. The _____________ the particles of an object vibrate, the _____________ the object will be. Because particles of an object are always moving, heat __________ is always happening. Heat alwa ...